University of Cambridge
-
A stroke can make it difficult to speak fluently, clearly, or in full sentences. Scientists have been working to change this, by developing a wearable device called Revoice. It helps people who lack the power of speech to communicate more naturally.
-
Deep in the growth rings of Pyrenean trees lies the strongest evidence yet for what set the Black Death in motion – a direct link between a sudden climate shift and the plague’s arrival in Europe, where it killed millions between 1347 and 1353.
-
Avian influenza viruses have a gene that makes them incredibly resistant to heat, rendering our body's natural defense system – fever – powerless in fighting infection. In fact, higher temperatures actually help those bird-derived bugs replicate.
-
High-efficiency, inexpensive LEDs and solar cells may arise from crystalline structures cheaper than silicon. A new vapor-based method works like superconductor manufacturing, creating perovskite layers at the Angstrom level for greater durability.
-
In a new study, researchers discovered that the human brain has four pivotal periods when it goes through marked changes, sparking five "epochs" that last for years. The adolescent phase, for example, was found to extend into our early 30s.
-
Scientists have made history with a device that successfully eavesdrops on the neuronal chatter between the brain and the gut, furthering our understanding of its intrinsic interconnectedness – and how it drives health and disease throughout the body.
-
A new breakthrough removes the dangers involved in a process called STING, in which the body's own immune system can be enlisted to fight cancer. The finding clears the way for a powerful, and safe, weapon against tumors.
-
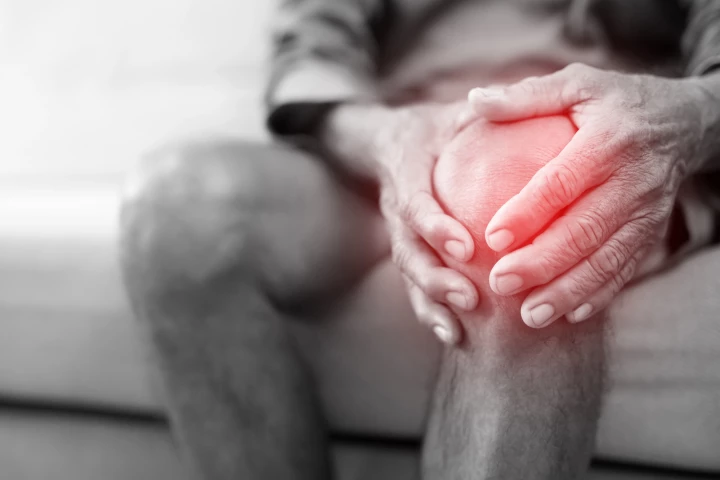
A squishy cartilage-like material has been developed by researchers at the University of Cambridge. It can be loaded up with either long-term or short-term pain killers that are released when the material senses chemical stress from arthritis.
-
After reviewing a series of studies involving hundreds of thousands of participants, a team of researchers found three eating plans that significantly reduced the development of type 2 diabetes. All are relatively easy to follow.
-
Longing for the past? You’re not alone, and chances are, the place you’re missing is by the water. A new study found that “blue” landscapes like beaches, rivers and lakes are powerful nostalgia triggers that also boost psychological well-being.
-
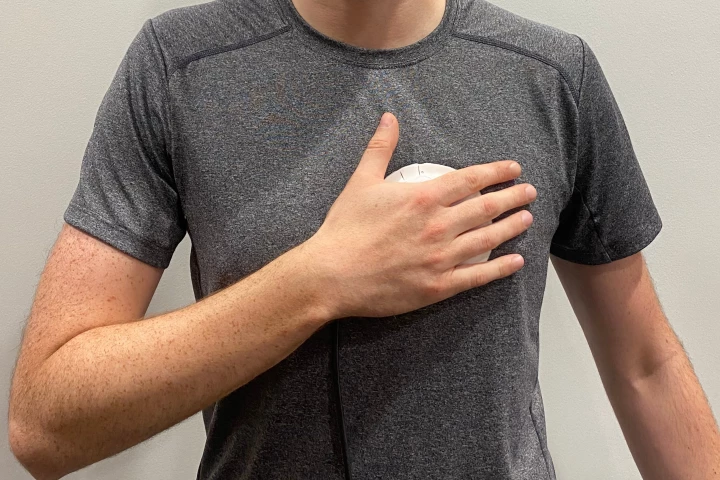
Valvular heart disease (VHD) is a potentially fatal condition, yet it's hard to diagnose with a regular stethoscope. A possibly life-saving new stethoscope is claimed to be much better at the job, plus it can be used by just about anyone.
-
Scientists have created a new type of display with the smallest pixels and highest pixel density ever. Individual pixels were shrunk to 90 nanometers – about the size of a virus – and a record 127,000 of them were crammed into every inch of a display
Load More