University of Delaware
-
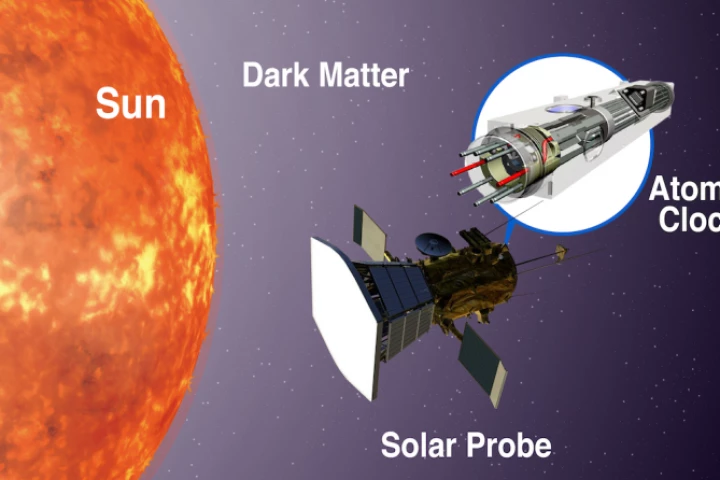
Dark matter remains elusive despite decades of searching. Now physicists have proposed a new experiment that would try to find signals by sending atomic clocks to where dark matter should be at its most dense – right near the Sun.
-
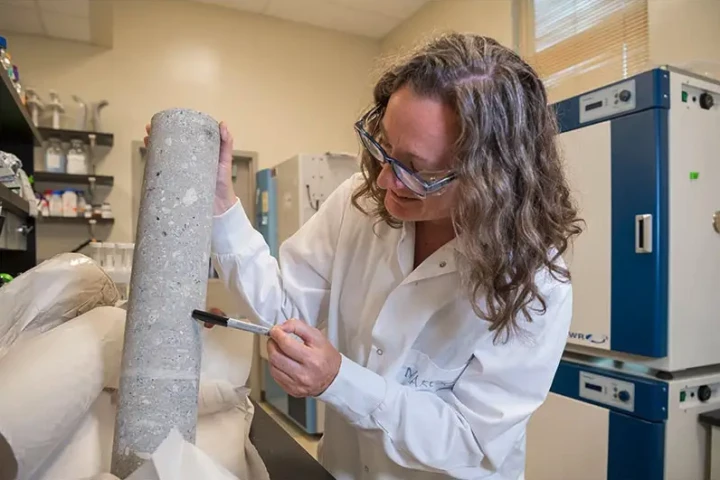
Concrete may not seem welcoming, but bacteria do live inside it. A new study has examined this concrete microbiome to find out how they get there, how they change over time, and how we might use them in future to monitor or even repair defects.
-
According to a new study, seniors wishing to boost their cognitive performance would likely do well to drink plenty of Montmorency tart cherry juice. Improvements observed in test subjects who drank the juice may be due to "bioactive compounds" that occur naturally in the cherries.
-
Imagine if there were comfortable and inexpensive wearable fabrics that were capable of detecting a wide range of pressure and motion. Well, scientists at the University of Delaware have created just such a technology, and it could have some interesting applications.
-
Although the scent of freshly-cut grass may SEEM nice, what you're actually smelling is a distress signal. Thanks to a recent-conducted study, scientists from the University of Delaware now believe that such signals could be used to summon insect-eating birds to valuable crops.
-
Imagine if your car's windshield glass could turn from being clear to reflective, when the car was parked in the hot sun. Well, such things may soon be possible, thanks to a new liquid-activated "smart glass" being developed at the University of Delaware.
-
In the fight to cut greenhouse gas emissions, we tend to think of trees as our allies, but new research suggests they might not be as "green" as we think. Researchers have found that some types of trees emit methane through their trunks, partly countering their role as a greenhouse gas sink.
-
Rather than always replacing parts, fixing things or just throwing them away, self-healing materials can patch themselves up as required. Now, researchers at are working on extending the life of membranes in hydrogen fuel cells by equipping them with similar self-healing powers.
-
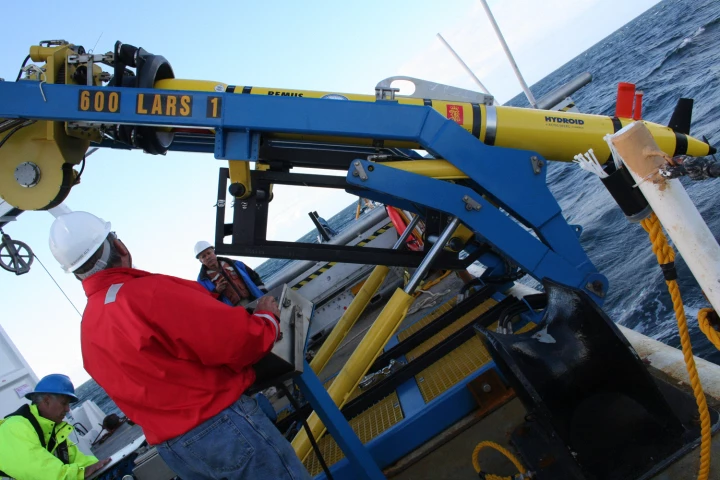
Two marine scientists have shown that autonomous underwater vehicles (AUVs) can be programmed to make independent decisions and trigger new missions in real time based on data coming from multiple sensors. They believe this could reveal much about the life of squid and other marine creatures.
-
People suffering from joint problems tend to take a lot of anti-inflammatory drugs, even though such medications affect their whole body. Now, scientists are developing an alternative. It's a hydrogel that can be injected into the joint, and it releases medication whenever the joint is used.
-
Using data from the IceCube Neutrino Observatory at the South Pole, scientists have reported progress in understanding the longstanding mystery of how and where cosmic rays originate, in a development that might help us find ways to shield astronauts and electronics from cosmic radiation.
-
A new study claims that renewable energy could reliably power a large electrical grid 99.9 per cent of the time by 2030, at a cost that matches today’s electricity prices.