University of Glasgow
-
In order to stay warm on frigid winter days, small birds may do more than just fluff up their feathers. According to new research, they're actually able to make their blood run hotter, creating a sort of central heating system.
-
An international team of scientists has identified a protein in the lungs that offers a new target for asthma treatments, along with another common condition affected by inflammation in the lungs, in chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD).
-
In an experiment, scientists at the University of Glasgow have confirmed a half-century-old theory previously thought impossible to test, which claims a super-advanced alien civilization could use a black hole as an energy source.
-
A newly discovered microbe identified in wild mosquito populations in Kenya has been found to protect the insects from malaria infection and could be recruited for malaria control strategies to limit transmission of the disease into human populations.
-
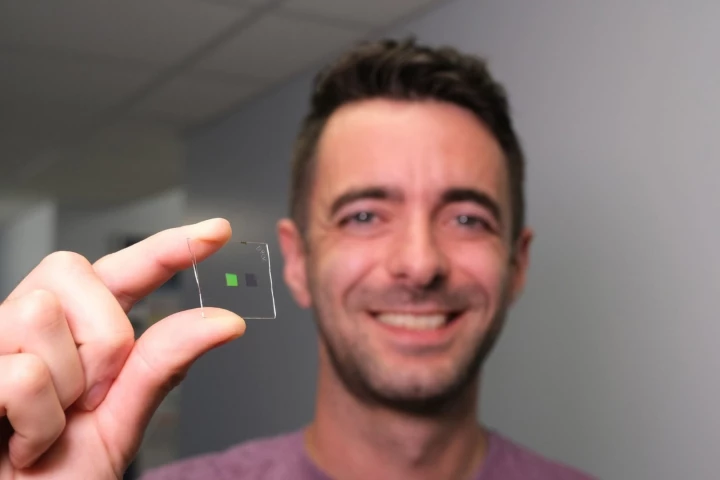
A tiny artificial tongue which can identify individual whiskies by taste has been invented by a team of Scottish engineers . The device could mean big things for drink makers wanting to ensure a consistent product, and protect their precious brands from counterfeiters at the same time.
-
Quantum entanglement, where two objects become intertwined and remain so no matter the distance that grows between them, is a tricky phenomenon to study let alone photograph. But scientists doing the former have now managed the latter, for the first time ever.
-
A high-tech drill originally slated for use on Mars is heading for Antarctica. The drill is on its way to a British Antarctic Survey research station, where it will be used to drill deep under the ice cap to help gain a better understanding of Earth's climate history.
-
Scientists have developed a small handheld device that can scan for biomarkers to quickly and easily diagnose people with certain diseases and illnesses. Inspired (as always) by Star Trek’s tricorder, the new “multicorder” is designed to help doctors track illness from just about anywhere.
-
Thanks to a breakthrough by chemists at the University of Glasgow, the filling station of tomorrow could service electric and hydrogen-fueled cars from the same pump. They've developed a new battery system using nanomolecules that can produce either electricity or hydrogen on demand.
-
A team of engineers has built and test-fired a new style of "autophage" rocket engine that eats its own structure from the bottom up during flight. They believe it could lead to cheaper, more efficient and less wasteful small satellite launches.
-
Scientists are reporting a breakthrough in which they have integrated solar cells into a graphene-based electronic skin, raising the possibility of prosthetic limbs that are both sensitive to touch and entirely self-powered.
-
If you're having trouble shaking your cravings for doughnuts, hamburgers and pizza, the key to curbing them could come from a new appetite-suppressing supplement based on a compound released by gut bacteria.
Load More