University of Hong Kong
-
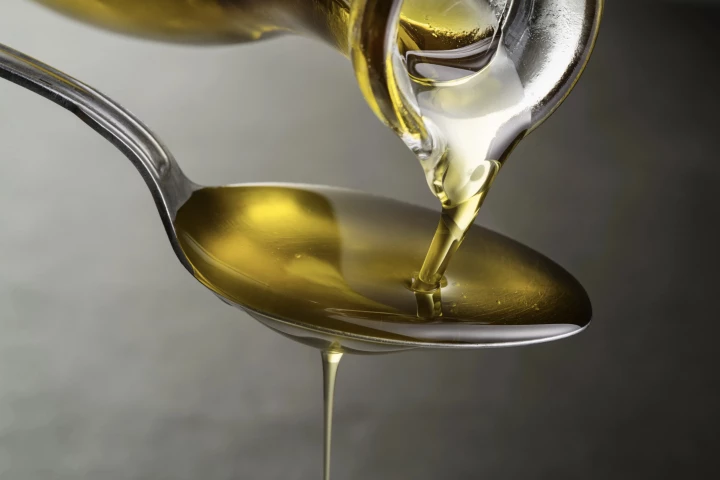
In a groundbreaking study, a healthy fatty acid in olive oil has been found to "supercharge" immune cells that fight cancer. Meanwhile, another kind of natural fat undermines the health of the same cells, killing them off and triggering inflammation.
-
The North Atlantic has a new title as the global hotspot for hurricane clusters, with the likelihood of multi-storm events forming here increasing tenfold in 46 years. It's the first clear picture of how Earth's warming has shifted cluster patterns.
-
For the first time, scientists have uncovered a distinct biological process triggered in those who suffer from high levels of Monday anxiety, resulting in chronic stress. And it can lead to serious health problems if it's left unmanaged.
-
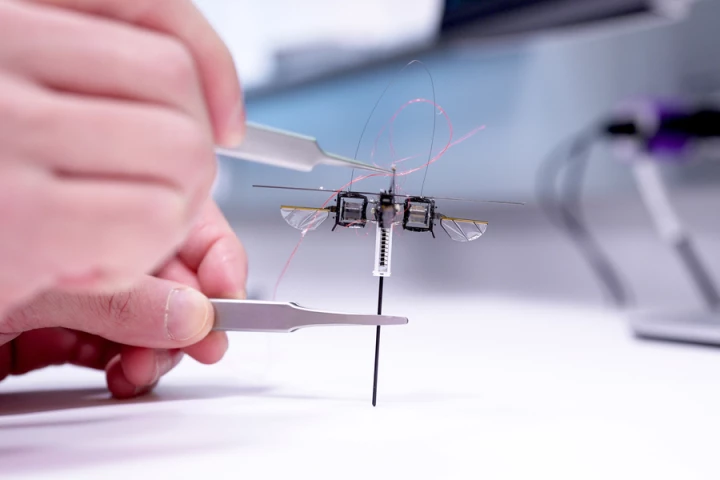
Flying robots do have advantages over their ground-going counterparts, but they're not very energy-efficient. A new bot addresses that tradeoff by using a wing-assisted mechanism to hop instead of walking or flying in the traditional sense.
-
Scientists have engineered a hybrid mouse with a gene that predates all animal life. The team replaced a single gene in the mouse stem cells with a version from an ancient, single-celled ancestor, and successfully grew healthy live mice from it.
-
Sometimes it seems that as soon as an anti-counterfeiting process is created, someone finds a way of circumventing it. A new system could be particularly hard to foil, however, as it utilizes tiny diamonds.
-
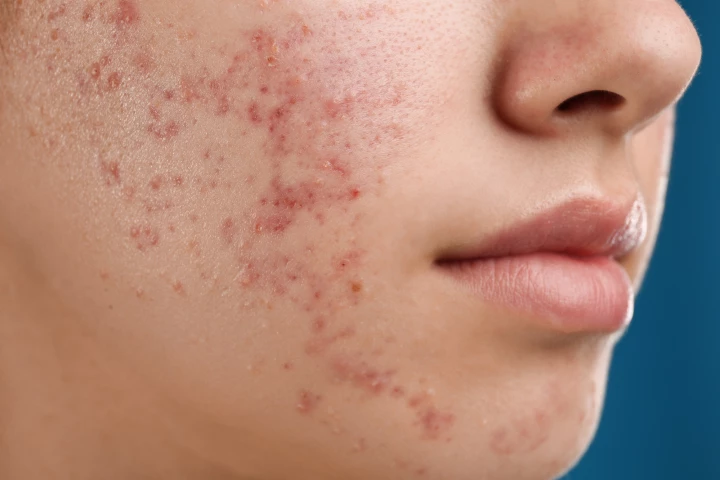
A novel microneedle patch may bring new hope to people who struggle to keep their acne under control. Instead of utilizing antibiotics, the device releases nanoparticles that kill acne-causing bacteria when triggered by exposure to ultrasound.
-
A new light-activated ink can change color on demand. It’s made up of colored microbeads that rise in response to different wavelengths of light to change a surface color, which could be useful for new displays or active camouflage systems.
-
Despite protective measures, endangered fish species are regularly caught then sold in open markets. And while visually searching them out can be difficult, a new technology could more easily allow authorities to know which species are being sold.
-
MRI is a powerful diagnostic tool, but the size and cost limits where it can be used. A compact, affordable new MRI system uses a much smaller magnetic field and doesn’t require shielding, and is still able to diagnose brain disorders in patients.
-
A new study has shed light on a molecular process underpinning impaired metabolism and endurance in skeletal muscle associated with obesity, and reveals how a growth factor found in a South American plant can alleviate these deleterious effects.
-
NASA’s Curiosity rover has been exploring Gale crater for nine years, studying sediments that look an awful lot like those left behind from an ancient lake. But new research from the University of Hong Kong proposes a much drier explanation.
Load More