University of Maryland
-
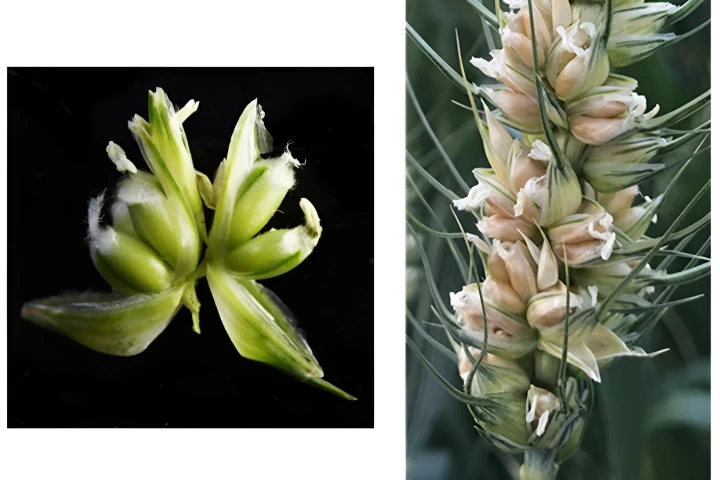
Imagine if three times as much grain could be obtained from the same amount of wheat plants as is currently possible, using the same amount of land, water and fertilizer. Well, that could soon be possible, thanks to a new genetic discovery.
-
As if hard vacuum, intense cosmic radiation, corrosive dust, meteors, and temperatures whiplashing hundreds of degrees between night and day weren't enough, personnel at future Moon bases will be at significant peril from moonquakes.
-
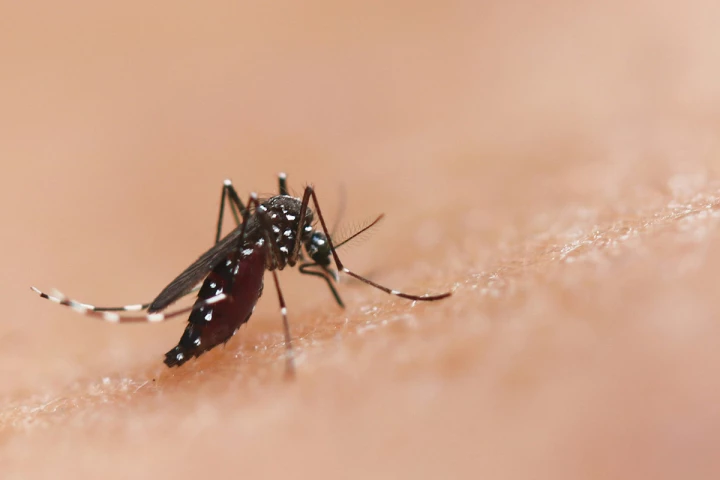
Mosquitoes have long been among humanity’s most formidable adversaries, causing more deaths than any other animal. With traditional control methods facing mounting resistance, researchers are seeking innovative ways to combat mosquito-borne disease.
-
A Maryland-based startup is set to begin mass producing Superwood, which is made from regular timber using a densification process, and exhibits strength greater than that of steel.
-
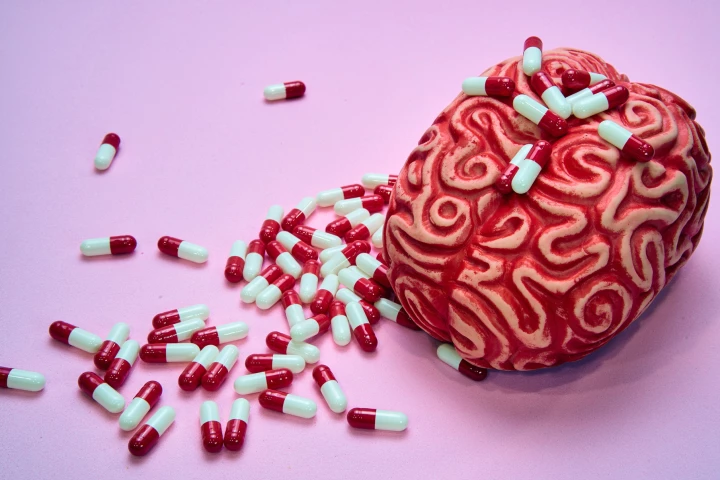
Not everyone with ADHD responds to stimulants like Ritalin, which increase dopamine levels. New research suggests the drug’s effectiveness is less about the dopamine it produces and more about the number and type of brain receptors that respond to it.
-
A 3,775-year-old log discovery has lent credence to the idea of burying wood to sequester the carbon it contains. Known as a wood vault, the concept helps keep CO2 out of the atmosphere while allowing the soil to be used for crops and other purposes.
-
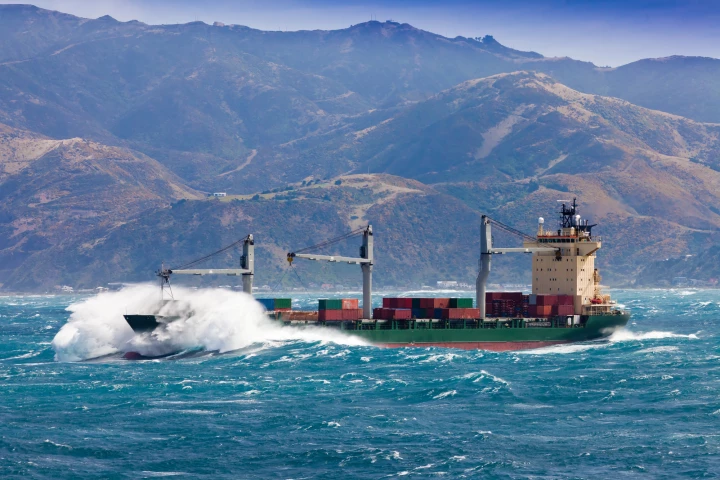
Unpredictable monster waves at sea can severely damage ships and offshore platforms, putting the lives of those who work on them at risk. A new system out of the University of Maryland uses a neural network to provide valuable early-warning alerts.
-
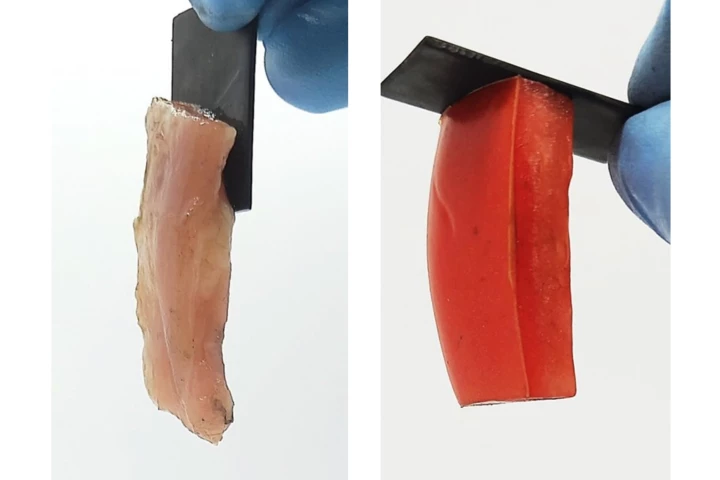
Imagine if a hard metal implant could be bonded to soft biological tissue without using any adhesive, then easily removed when no longer needed. That and other nifty things could soon be possible, thanks to a new understanding of electroadhesion.
-
Scientists have discovered that viruses can latch onto other viruses to insert their genes into host cells. Lab results with apparent contamination led the team to directly see the strange interaction for the first time.
-
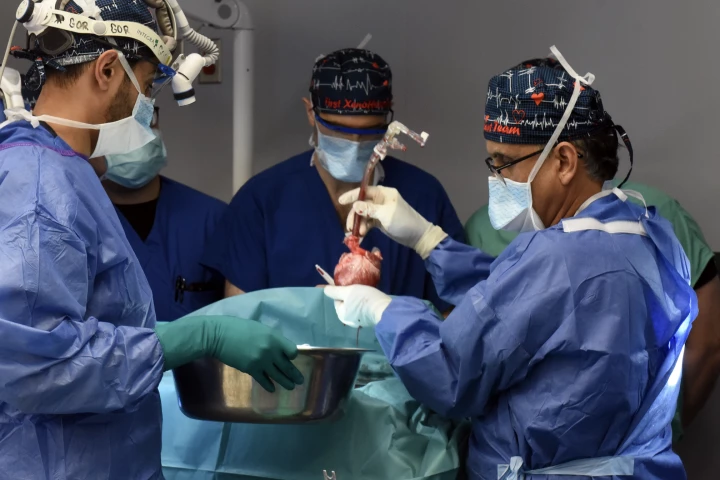
A 58-year-old man with terminal heart disease has become the second patient to receive a pig's heart, in a complicated, high-risk xenotransplant. The first recipient died last year from complications, two months after the landmark world-first surgery.
-
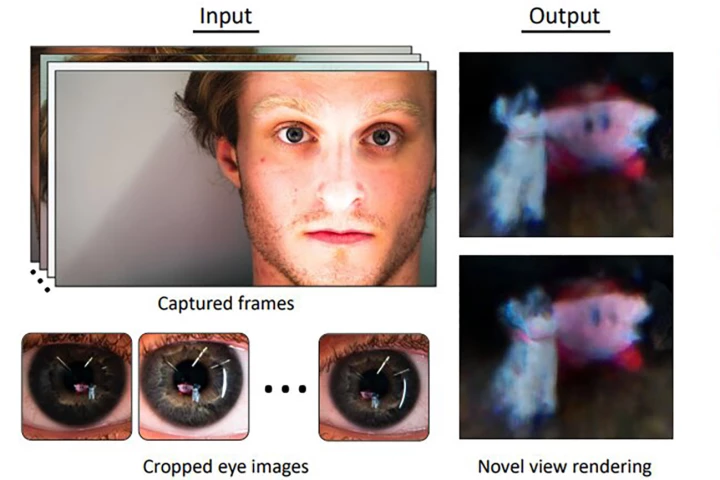
Neural radiance field (NeRF) technology is starting to show some incredible capabilities in turning 2D images and videos into 3D models, but University of Maryland researchers are taking things to another level, using nothing but eye reflections.
-
When someone overdoses on opioid drugs, a medication called naloxone can save their life by quickly mitigating the effects of the narcotics. A new chemical shows promise for serving a similar role, but it also works on non-opioid drugs.
Load More