University of Michigan
-
These microscopic robots are smaller than a grain of sand. At 200 micrometers wide, they're autonomous, programmable, and cheap enough that high school students are already learning to operate them in labs.
-
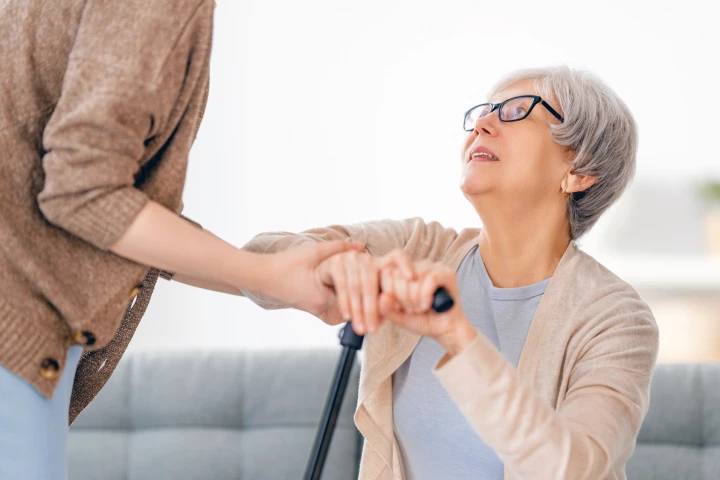
Even brief, friendly interactions can lift the emotional weight of dementia caregiving, with new research showing that connections, especially casual ones, offer powerful protection against loneliness and isolation.
-
An engineered protein that acts like a molecular sponge can hunt down CO molecules in the bloodstream and safely flush them out of the body in just minutes, without the risk of short- or long-term organ damage that comes with current oxygen treatment.
-
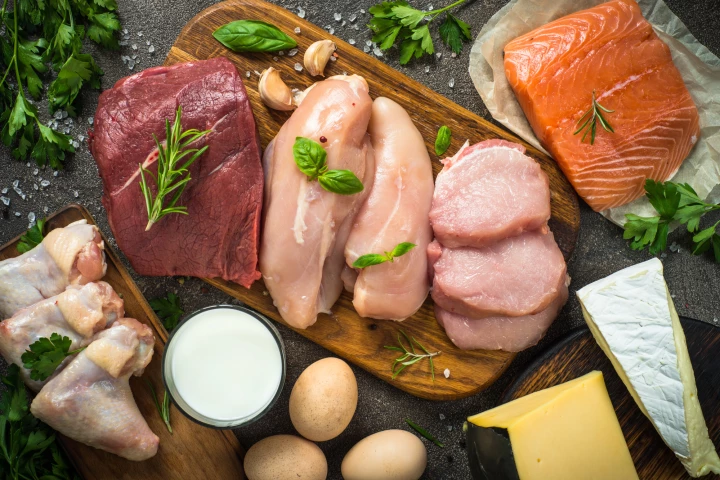
Forget carrots. Researchers have determined that one of the most common amino acids has the power to keep retinas thick and healthy. The finding has the potential to fight vision loss and blindness through this newly discovered metabolic pathway.
-
We've long known how the nerve endings in our skin detect cold and swiftly relay the information to our brains, but we haven't understood exactly how it works. Scientists have now solved the puzzle, unlocking the mystery of this temperature pathway.
-
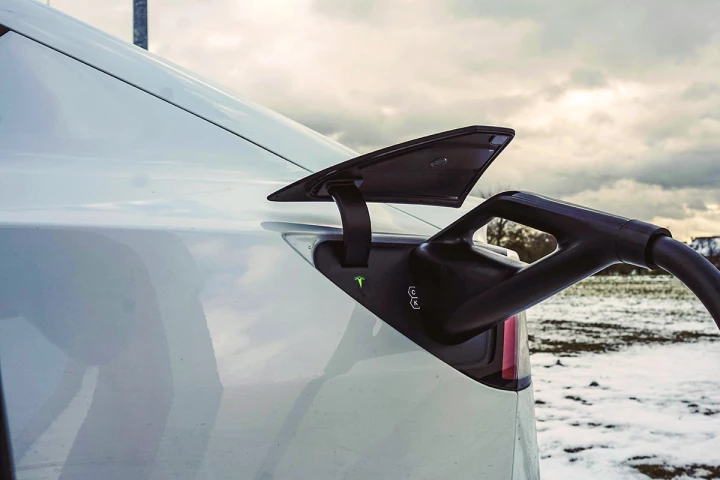
Researchers at the University of Michigan have developed a way to enable rapid EV battery charging at awfully low temperatures – up to five times as fast – without reducing the batteries' energy density.
-
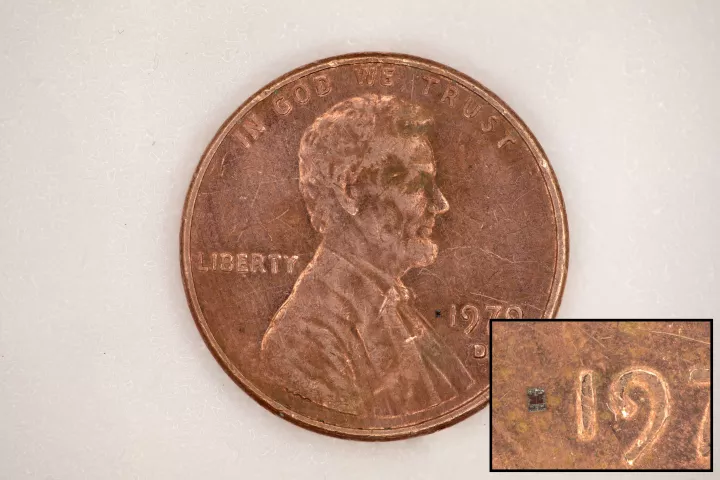
A test for pee-based markers of prostate cancer has previously relied on an uncomfortable first step. A new study has revealed that the now-available test remains just as accurate without it, paving the way from an easy in-home testing option.
-
Forget LEDs, researchers from the University of Michigan have developed a new type of incandescent light bulb. The device is capable of emitting elliptically polarized light, described as "twisted" light.
-
Computers generally go a bit wonky when you stick them in the oven for a bit, but engineers at the University of Michigan are looking to change that by developing a new computer memory that can run at the temperature of molten lead.
-
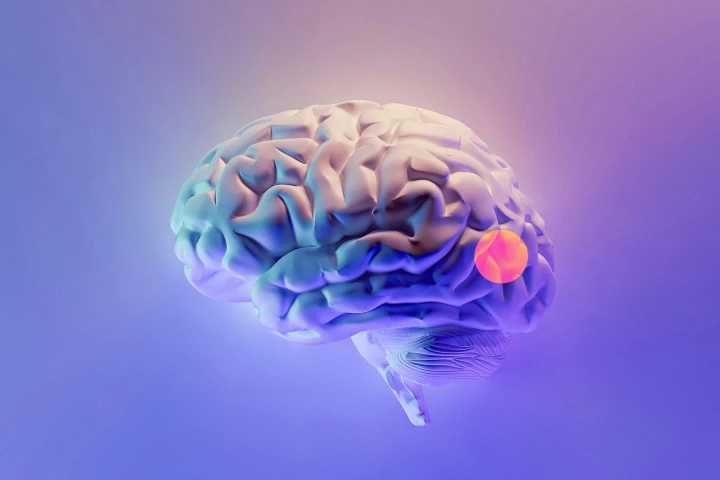
Researchers have developed an AI model that can spot bits of brain tumors that surgeons may miss while removing them from patients. It can detect these remaining tissues in as little as 10 seconds, and help prevent post-procedure complications.
-
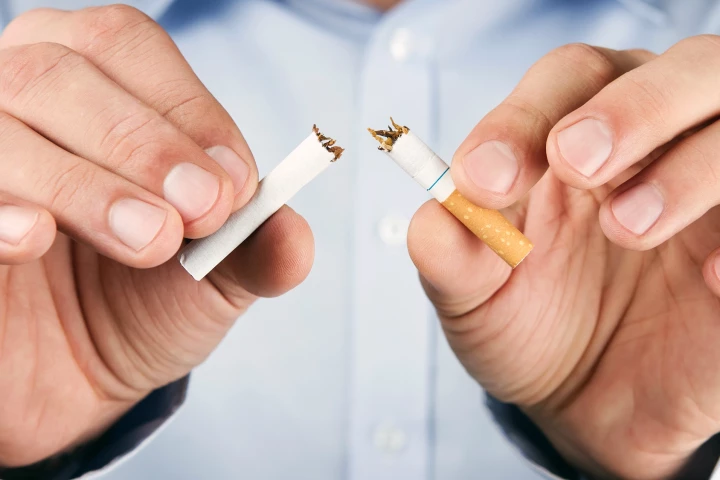
A new study has found that, whether you do it at 35 or 75, quitting cigarette smoking will add years to your life. The findings go to prove that you’re never too old to reap the benefits of stopping smoking.
-
Inspired by the color-changing skin of squids and other cephalopods, researchers have developed a flexible screen capable of storing and displaying encrypted images without using electronics – just tiny magnetic particles.
Load More