University of North Carolina
-
In a comprehensive new study looking at 39,763 different foods and drinks from the biggest 25 companies in the country, scientists discovered that almost 20% rely on synthetic food dyes to attract consumers. Now, the fight is on to ban them for good.
-
In a fascinating discovery, scientists have pinpointed just what happens in our brains when we're expecting pain relief but are unknowingly given a placebo. It reveals just how powerful the mind is in moderating physiological responses such as pain.
-
Scientists are again on high alert, as whole genome sequencing of the H5N1 virus has revealed that it is capable of multidirectional infections across species. While human risk is low, it's a step forward for the pathogen in this biological arm's race.
-
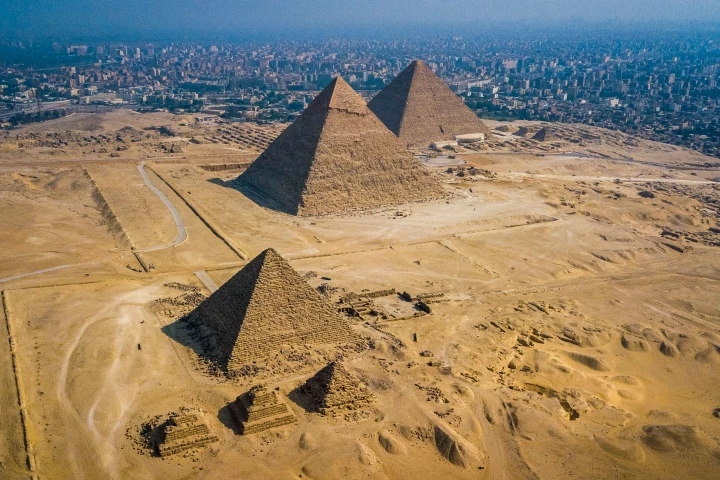
The ancient Egyptians may have had help building the pyramids after all – not from aliens but a long-lost river. Evidence of a previously uncharted branch of the Nile has been found snaking along the pyramids, suggesting blocks were floated to sites.
-
Using DNA and proteins, scientists have created new synthetic cells that act like living cells. These cells can be reprogrammed to perform multiple functions, opening the door to new synthetic biology tech that goes beyond nature’s abilities.
-
It may not be to everyone's taste, but kombucha tea may be able to deliver the benefits of fasting, without the hardest part – the fasting. Its yeast and bacteria altered fat metabolism, without any other dietary changes, resulting in lower fat stores.
-
For the first time, scientists have uncovered the precise molecular mechanism that gives the tardigrade, one of the toughest organisms on the planet, its ability to switch on a near-invincibility cloak when faced with life-threatening conditions.
-
Nobody likes having to get needles on a frequent basis, or even having to take multiple medications orally throughout the day. A wearable patch could help, by painlessly administering different drugs through the skin when triggered by a smartphone.
-
The most comprehensive genetic map of oral stem cells to date has provided new insight into their specialized development pathways and opens the door to targeted regenerative medicine and interventions, such as therapies to grow or repair bone.
-
Researchers have found that administering under-the-tongue immunotherapy given to young peanut-allergic children is a safe and effective way of desensitizing them to the food. It may provide another method of curbing this potentially deadly allergy.
-
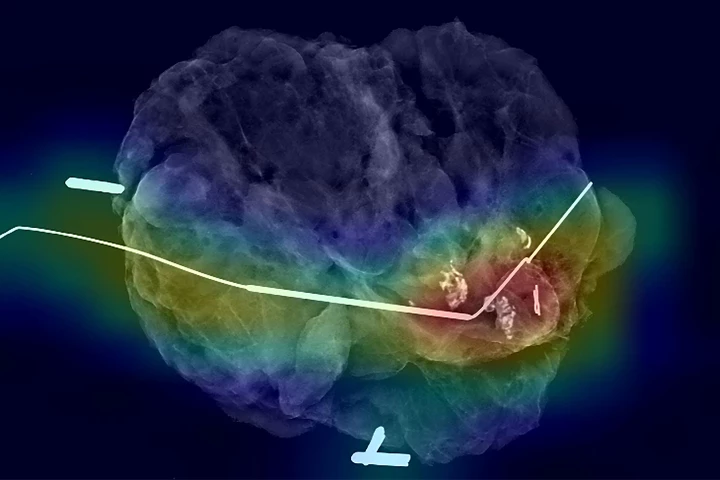
Researchers have developed an AI model that can predict in real-time whether a surgeon has removed all cancerous tissue during breast cancer surgery. The model performed as well as, or better than, human doctors.
-
By removing certain amino acids from the diets fed to rodents suffering from glioblastoma, researchers found that brain cancer cells began dying. What's more, mice put on the restrictive diets were also more receptive to chemotherapy treatment.
Load More