University of Otago
-
You can forget the “no screens, no exercise, no snacks” bedtime rules that are designed to provide teens with good sleep. New research shows that almost all teens break them – and they still sleep just fine.
-
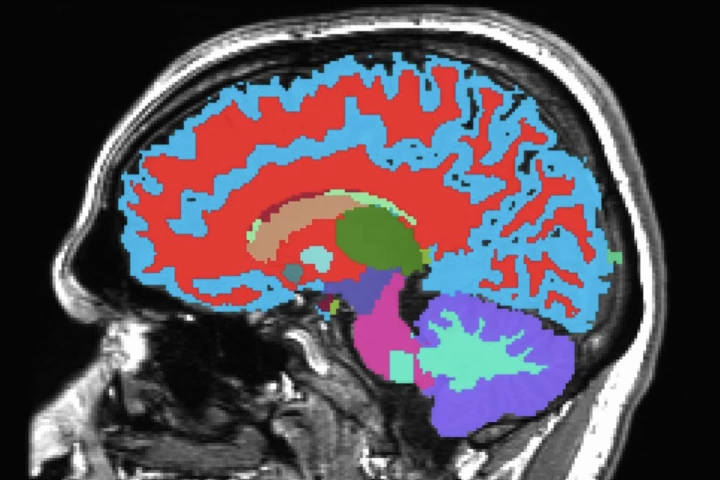
If you could get a quick, easy scan in your 40s, which could add decades to your life and aging healthily, would you? Scientists have made such a tool, letting you glimpse into a crystal ball that identifies age-related disease risk long before onset.
-
Step aside, golden beaches – New Zealand has stretches of sand sparkling with real gold. And with this, scientists have been able to assemble the world's first atlas of highly detailed beach gold found along the country's South Island coastline.
-
A slow-release, twice-a-week ketamine tablet significantly reduced depression symptoms, according to the results of a clinical trial. The tablet can be taken at home without medical supervision, making it more convenient than current ketamine treatments.
-
The female Green Honeycreeper bird is appropriately enough colored green, whereas the male is blue. So, what happens when a Honeycreeper is half of each sex? Well, as recently taken photos show us, the bird is blue on the right and green on the left.
-
Some more bad news for gluten. While we’ve been aware of how gluten can impact the digestive tract, New Zealand scientists have now identified for the first time that it can also cause brain inflammation, likely triggered by an immune response.
-
Researchers have discovered a plant extract that targets the glucose-regulating regions of the brain that are inflamed in type 2 diabetics, improving blood glucose levels. The findings open the door to a novel, natural treatment for the disease.
-
UK and University of Otago researchers have presented a "world-first weight loss device," which attaches to the teeth and prevents patients from opening their mouths wider than 2 mm using "magnetic devices and custom-manufactured locking bolts."
-
A novel wearable that stimulates the olfactory system using electrical pulses has been proposed as a way to prevent or slow dementia-related neurodegeneration. A dysfunctional sense of smell is suspected to be one of the earliest signs of Alzheimer’s.
-
After analyzing DNA found in Loch Ness, a scientist believes the monster might be a type of giant eel.
-
When women are experiencing primary dysmenorrhea (better known as period pain), usually the last thing that they feel like doing is getting up and exercising. According to a new first-of-its-kind study, however, doing so may be exactly what's needed to reduce the discomfort.
-
Livestock like sheep and cows are responsible for huge amounts of methane emissions. Now, an international team of researchers has analyzed the gut microbes of different sheep and found clues that may help us curb the problem.
Load More