University of Pittsburgh
-
Researchers have devised a biomarker test that can spot small amounts of clumping tau protein in the brain and cerebrospinal fluid, which lead to Alzheimer's Disease. This test can help detect the tangled proteins years early, enabling intervention.
-
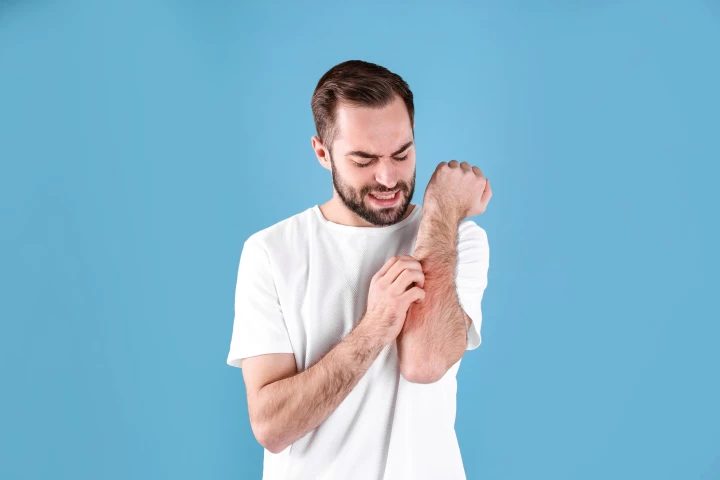
The itch from bug bites, rashes, and other skin conditions can sometimes be so overpowering that it feels impossible to avoid scratching them. But new research explains why you might want to hold off as long as you can.
-
Whether we've watched athletes do it or experienced it ourselves, 'choking' in a high-stakes moment comes down to more than composure. For the first time, scientists have uncovered a set of neurons that fail to do their job when the payoff is greatest.
-
Thanks to the increase of electric vehicles and other battery-using technologies, the demand for lithium is expected to skyrocket in the coming years. One odd but potent source of the metal is a Pennsylvania wastewater stream, says a new study.
-
Organ transplants save lives, but rejection is a key hurdle. Now scientists have demonstrated a potential new way to prime a recipient’s immune system to accept a transplanted organ, by first giving them an infusion of immune cells from the donor.
-
Researchers have uncovered the mechanism that causes wounds to heal more slowly in diabetics, putting them at increased risk of infection and other serious complications. They say their findings could offer a new approach to the disease.
-
Traditional concrete is so last century. A team of engineers has created a concrete that is strong but flexible, can generate electricity and have its qualities fine-tuned for tailor-made builds. And one day it might even help guide driverless cars.
-
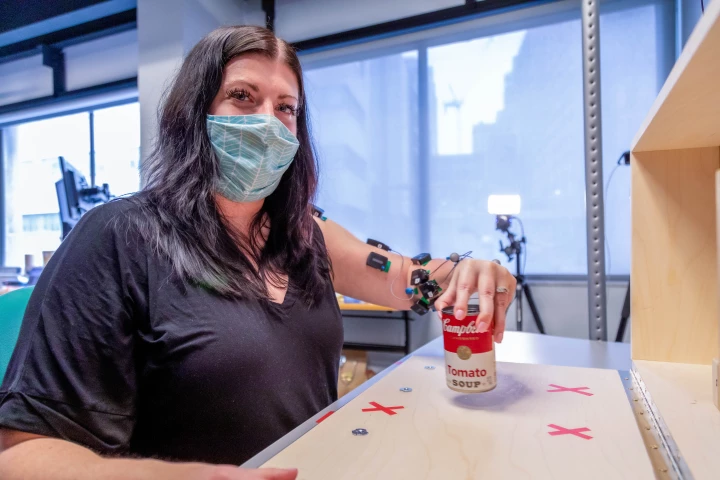
Loss of arm and hand mobility is a common and devastating disability among stroke survivors, but a promising new study shows how cervical spinal cord stimulation could improve limb function and restore quality of life.
-
A genetic predisposition to ADHD has been linked to an increased risk of cognitive decline and Alzheimer's disease in old age, according to new research. The findings are the first to associate ADHD genetic risk with age-related cognitive impairment.
-
Following successful trials in adults and subsequent FDA approval last year, an emerging obesity drug has now shown promise in overweight adolescents, inducing similar weight loss effects in this younger cohort.
-
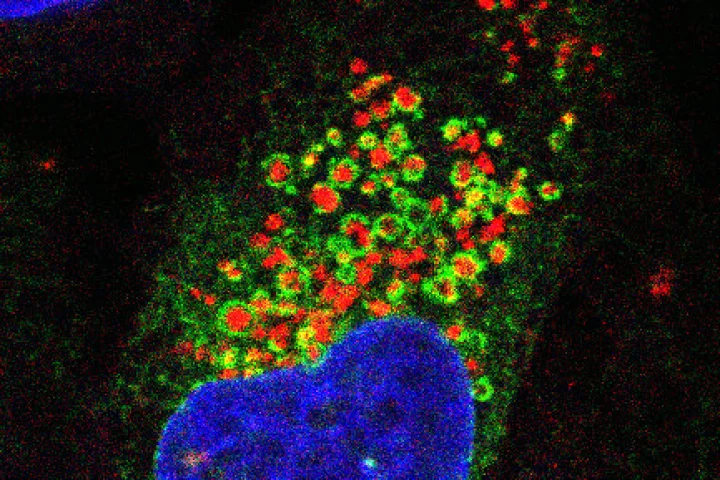
A new understanding of the way lysosomes called organelles repair themselves could help keep cells young and fresh, and offer new ways to stop age-related diseases like Alzheimer's and Parkinson's in their tracks.
-
Scientists continue to illuminate the many ways exercise can positively influence brain health by examining its effects on the many forms of cognitive function, and the latest places a spotlight on our ability to recall past experiences.
Load More