University of Texas
-
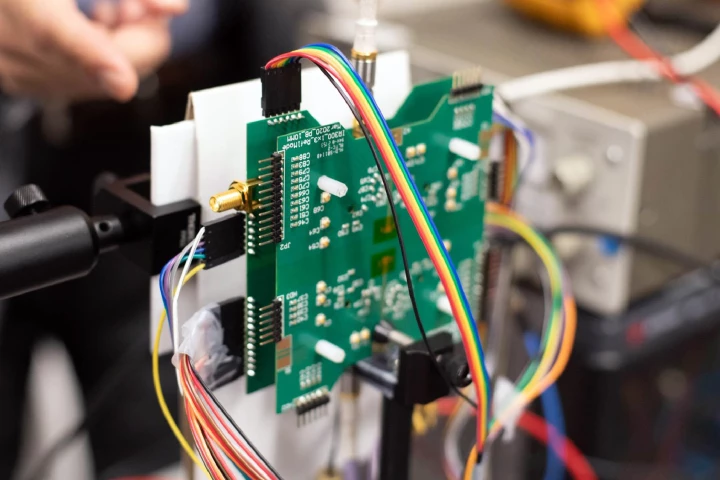
A personalized facial e-tattoo wirelessly monitors the brain and can tell when it’s being overworked and can use the data it collects to predict mental overload, according to a new study. The tech could help us maintain a productivity sweet spot.
-
A group of Texas-based researchers has developed an effective way to treat post-traumatic stress disorder that involves zapping the vagus nerve around the neck, using a device the size of a shirt button.
-
A subtle yet significant phenomenon is occurring beneath the North American continent; its ancient bedrock is slowly dripping into the Earth’s mantle, creating a funnel-like structure concentrated over the Midwest of the United States.
-
While electroencephalography (EEG) can provide a lot of information on the electrical activity of an individual's brain, that person is required to wear a clumsy skull cap. Such caps could soon be replaced, however, with inkjet-printed scalp tattoos.
-
While there are already AI systems that generate sound effects to match silent images of city streets, an experimental new technology does just the opposite. It generates images that match audio recordings of streets, with uncanny accuracy.
-
Glass-fragment waste typically just ends up in landfills, but perhaps that doesn't always have to be the case. A study shows that ground glass particles can be mixed with soil to produce a plant growth medium that's actually better than soil alone.
-
One dose of a new treatment, delivered by nasal spray, clears away build-ups of the toxic tau protein associated with Alzheimer’s disease from inside brain cells, improving memory, according to new research. It paves the way for new treatments for the debilitating disease.
-
Scientists at the University of Texas at Austin have developed a “smart soil” that can keep plants better hydrated and provide a controlled release of nutrients. In tests it drastically improved crop growth while using far less water.
-
For the first time, scientists have successfully created a mouse with a 100% functional human immune system and microbiome. This 'humanized' mouse takes the guesswork out of research and may revolutionize how we test new drugs and understand diseases.
-
In pre-clinical trials, a small molecule effectively regrew neurons, reduced inflammation, and improved memory, speed, coordination, grip strength, and more. The finding could have a profound impact on aging and the diseases that accompany it.
-
Researchers have created a tiny chip that can take images of objects through cardboard. The technology, designed to fit inside a smartphone, brings us a step closer to wielding Superman’s X-ray vision abilities (without the X-rays).
-
Researchers have finally investigated a widely held belief that men who are more dissatisfied with the size of their penis are more likely to own a gun. And the results are not what they expected.
Load More