University of Tokyo
-
All of the quadrupeds we cover have rigid one-piece bodies, which seems to be a good shout for most of the antics they get up to. But a flexible spine might be better in certain climbing situations, and that's where the KLEIYN robodog could shine.
-
In Japanese mythology, dragons aren't the fire-breathing, treasure-hoarding monsters you'll find in Tolkien, Martin, et al. Instead, they're wise, serpentine creatures who control rain, fly through the clouds, and protect sacred areas.
-
Scientists in Japan have created hybrid plant-animal cells, essentially making animal cells that can gain energy from sunlight like plants. The breakthrough could have major benefits for growing organs and tissues for transplant, or lab-grown meat.
-
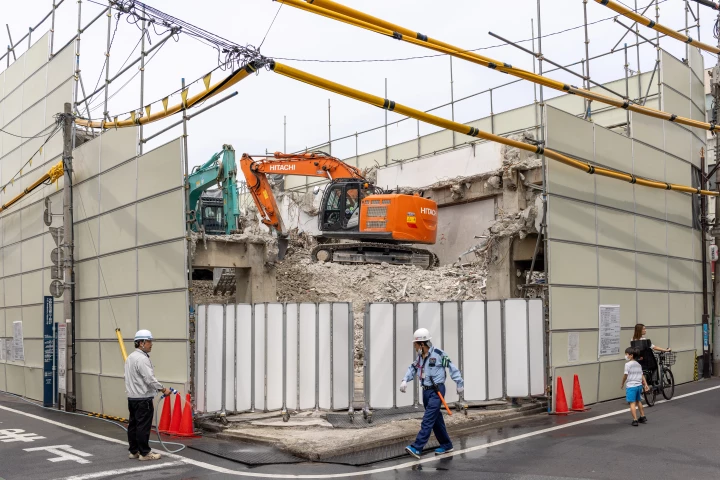
Back in 2021, researchers came up with a recipe for greener concrete that had building waste and CO2 among its ingredients. Now the same team has used rubble from a demolished school and the greenhouse gas to produce bricks to build new structures.
-
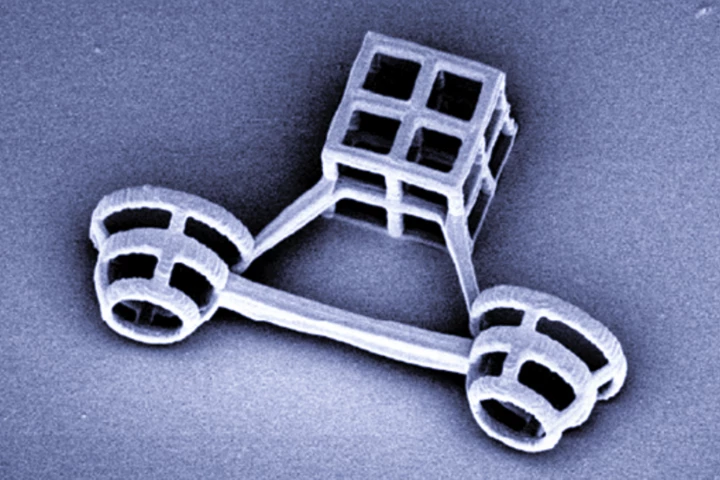
From dog sleds to horse-drawn carts, animals have been pulling vehicles for thousands of years. Now, scientists in Tokyo have made what might be the smallest version ever, designing microscopic vehicles that can be pulled by single-celled algae.
-
In a breakthrough that isn't at all creepy, scientists have devised a method of anchoring living human skin to robots' faces. The technology could actually have some valuable applications, beyond making Westworld-like scenarios a reality.
-
Japanese researchers have released footage of a humanoid robot called Musashi sitting in the driving seat of an electric micro-car to examine a possible future direction for autonomous vehicle technologies.
-
A new experimental drone can fly in the air as needed, then morph into a motorized wheel and roll on the ground to save energy. It could one day find use in applications such as searching disaster sites for victims trapped in the rubble.
-
When it comes to protecting crops via insect-blocking netting, you may think that the size of the holes in that netting is the most important factor. According to new research, however, the color of red netting makes an even bigger difference.
-
CBT is a multifaceted approach recommended as a treatment for chronic insomnia. A new study looked at CBT components to determine which are most effective for improving sleep, finding that relaxation techniques may potentially be counterproductive.
-
While it's important for your dog or cat to have a form of ID in case they get lost, tags can fall off, and microchips can migrate out of place. Japanese scientists are developing an alternative, in the form of quick and painless tattoos.
-
Causality is key to our experience of reality: dropping a glass, for example, causes it to smash, so it can’t smash before it’s dropped. But scientists have now demonstrated how that understanding of time can be violated to charge a quantum battery.
Load More