University of Utah
-
Scientists remain puzzled as to why some people taking popular weight loss and diabetes medications like Ozempic and Wegovy are losing their vision suddenly, highlighting that there's still so much we don't know about this life-changing class of drugs.
-
While tobacco and alcohol are known to increase the risk of head and neck cancer, new research has found the amount of coffee and tea we drink can have a protective effect, reducing the risk of developing these sorts of cancers. Yes, even decaf.
-
A head-mounted ultrasound device has now completed two human trials. One showed how the targeted sound waves could improve pain symptoms, while another revealed a marked improvement in depression symptoms after just one session.
-
UFOs are having a renaissance lately, moving beyond the tinfoil-hatted crowd and into the realm of serious government investigation. Now a study has analyzed the geography of almost 100,000 sightings and found a few clues about how they cluster.
-
Being diagnosed with potentially fatal metastatic breast cancer inspired one man to gather a team of diverse professionals to create an AI-based tool to help oncologists provide an individualized treatment care plan to patients with metastatic cancer.
-
Earth has been blasted by the second strongest ultrahigh-energy cosmic ray ever observed. While its origins remain unknown, astrophysicists are pointing the finger at the Local Void, a fundamentally empty area of the cosmos next to the Milky Way.
-
The Earth’s inner core is incredibly tricky to study, since it’s buried beneath thousands of miles of rock. New seismic studies suggest that it’s not just a solid ball of iron, as has been assumed, but might have pockets of liquid iron throughout.
-
Long before dinosaurs roamed the earth, the oceans were full of creatures known as ammonites. Scientists have now created a number of robotic ammonites, to see how the different shell shapes they evolved affected their movement through the water.
-
A 25-year search for another source of a promising anti-cancer chemical produced by a rare coral species has now started to bear fruit, with the discovery other readily available corals produce the chemical in abundance.
-
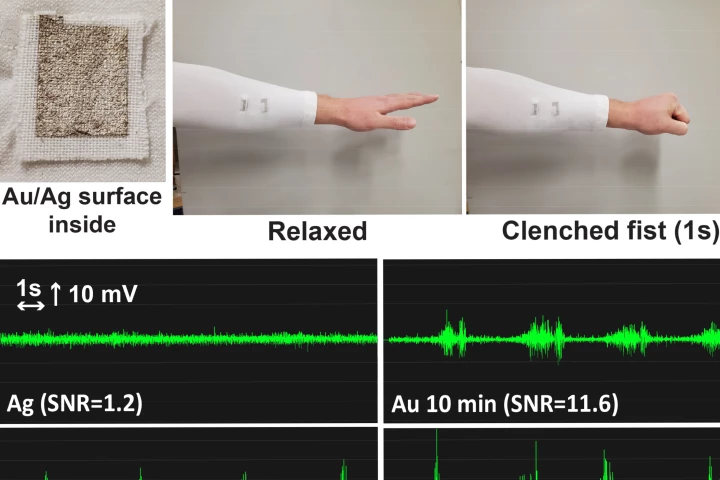
Currently, if you wish to track the electrical activity of someone's muscles, you have stick electrodes onto their skin. An experimental new technology, however, simply utilizes conductive fabric that's incorporated into washable pieces of clothing.
-
Scientists at the University of Utah have been keeping a close eye on these famous geysers of Yellowstone National Park, and have now managed to image the plumbing system of the tallest one in the world to a depth of 450 feet.
-
For many people, the beauty of spring is countered by the sneezing, runny nose and itchy eyes of allergies that come with warmer weather. For those people, science has some bad news – climate change may be making pollen season longer and more severe.
Load More