Washington State University
-
A new study has found that a majority of medical cannabis users suffering from insomnia and poor-quality sleep are ditching conventional over-the-counter and prescription sleep aids in favor of using the drug to treat sleep-related problems.
-
Normally, staying up for extended time periods leads to the need for extra sleep. But researchers have just found that activating astrocyte cells in mice caused the rodents to stay awake for six hours longer than usual, with no noticeable sleep debt.
-
Different types of metal have different qualities, so combining them can result in items that outperform those made of any one metal. A new technique now allows such mixing to be performed by 3D printers, faster and easier than ever before.
-
Robotic versions of flying insects hold a lot of promise for numerous applications, but controlling their yaw axis while in flight has proven challenging. A new bee robot, however, addresses that problem with a clever design.
-
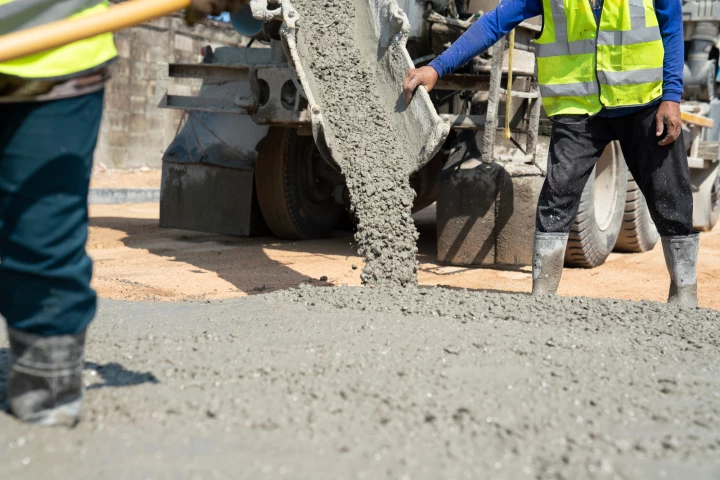
Concrete is one of the largest single sources of human-induced carbon dioxide emissions. Engineers at Washington State University have now developed a new method for making concrete that absorbs more carbon than it emits.
-
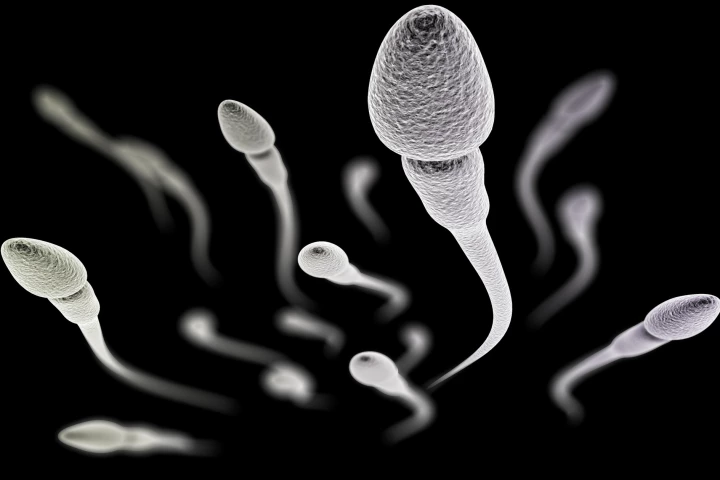
Researchers have discovered a gene in the testicular tissue in multiple mammals, including humans. Disabling it changed the shape and function of sperm and could lead to an oral contraceptive for men that would only work while it is administered.
-
A new study has shown that for people with chronic pain taking opioids over the long term, incorporating an internet-based self-management program into treatment may help reduce both pain and opioid intake.
-
If you've ever been to the Moon (and who hasn't?), then you'll know that the dust which covers its surface can damage spacesuits. According to a new study, a spray of liquid nitrogen may offer the best method of getting the stuff off.
-
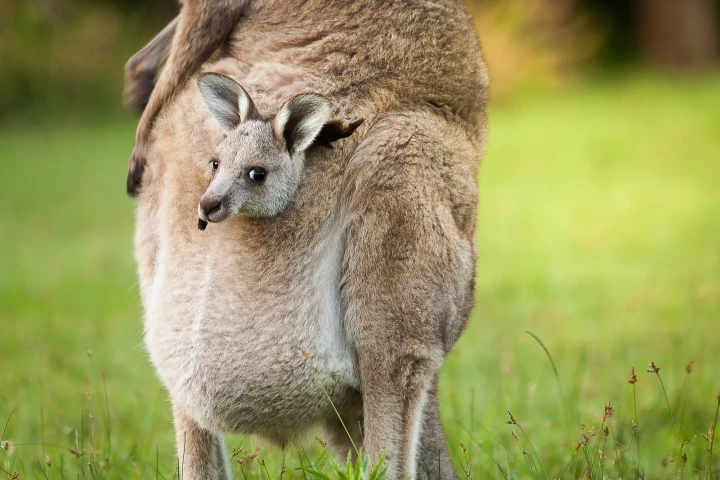
Make all the jokes you want, but the methane emitted in the form of cow burps and farts is actually a major source of greenhouse gas emissions. That could soon change, however, thanks to bacteria found in baby kangaroo feces.
-
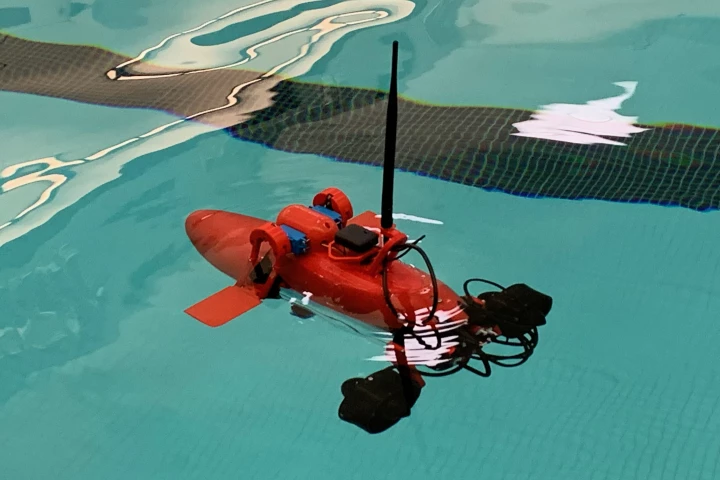
Many readers will already be familiar with so-called narco subs, used to smuggle narcotics from South America into Florida. Well, according to a new study, the design of such watercraft could actually have some practical applications.
-
New research has homed in on the way our genes can be turned up or down depending on levels of physical activity. The unique study focused on exercise-induced epigenetic differences in genetically identical twins.
-
A research team has discovered a novel mechanism in which a key protein drives the inflammatory damage associated with rheumatoid arthritis. The foundational finding could lead to entirely new pathways to treat this autoimmune disease affecting millions.
Load More