Water Conservation
-
While greenhouses produce wastewater, microalgae-growing operations require a source of water – which is scarce in many regions. A new project aims to address both problems, by growing water-purifying algae in readily available greenhouse runoff.
-
While solar farms are a source of green energy, many people don't like the fact that they occupy land which could be otherwise utilized. A new project is exploring an alternative, by placing solar panels over canals that will benefit from the shade.
-
The James Dyson Award is an international competition to encourage students to get creative to solve the world's pressing problems. The national finalists have been announced for 2021, showcasing ideas that help people and the environment.
-
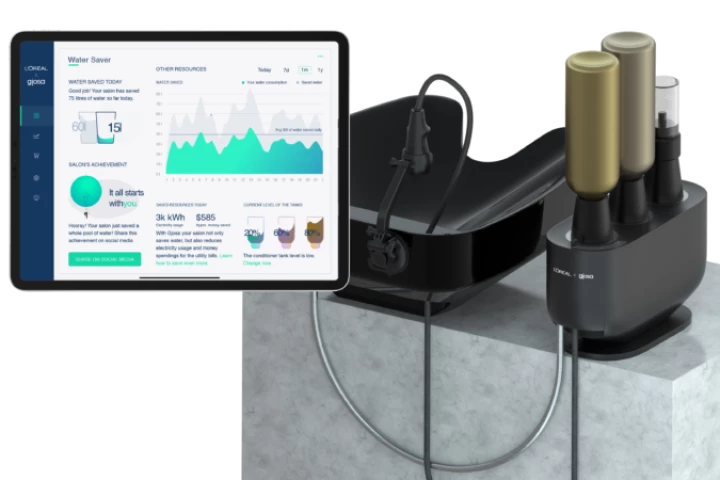
Besides laundry-washing and lawn-sprinkling, the daily washing of hair uses up a lot of water. L’Oréal's new Water Saver system is designed to help, by reportedly reducing the amount of water used in hair-washing by up to 80 percent.
-
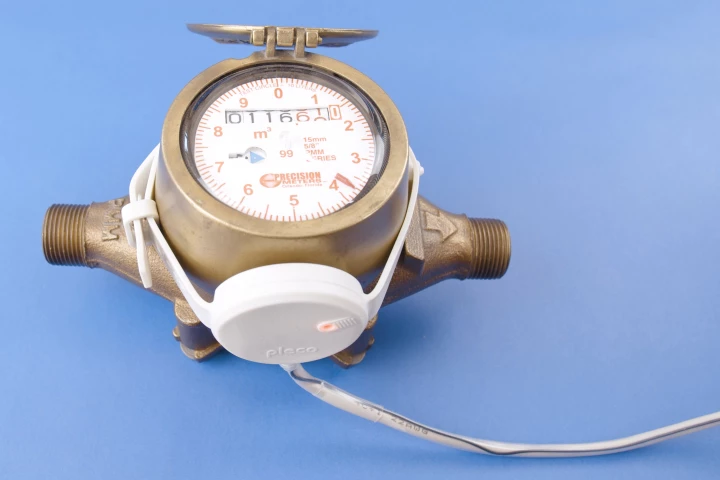
One of the keys to reducing your household water usage lies in knowing how much water you use for what purposes. Debuting at CES 2021, the Pleco Smart Water Watch is designed to provide you with that information.
-
The UK Department of Environment, Food & Rural Affairs has issued a warning: large areas of England will face significant risk of drought due to climate change, and water companies need to find billions of extra liters per day by 2050 to keep up.
-
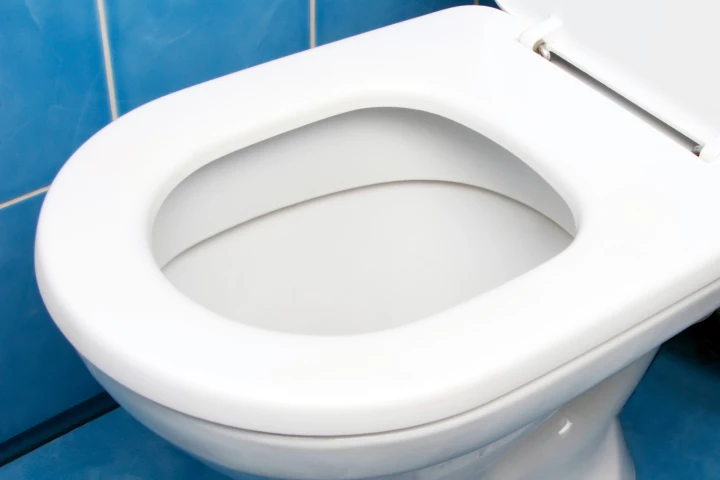
Given the scarcity of fresh water in many regions, it does seem a bit crazy to be flushing the stuff down the toilet. And while a few coastal areas use seawater instead, doing so is problematic in its own way – new research, however, may change that.
-
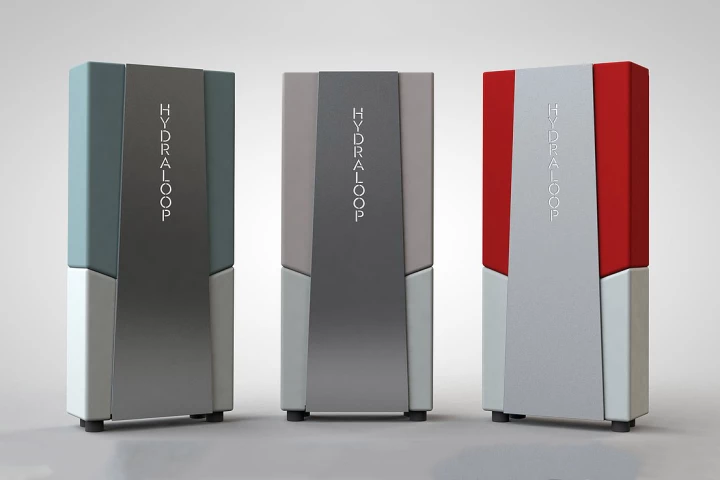
Recycling almost all your shower water and half of what you use in your washing machine, Hydraloop lets you re-use about 85% of your domestic water, significantly dropping your water usage for a unit cost of around US$4,000.
-
Given the current worldwide push for water conservation, it's certainly ironic that people are still flushing great quantities of the stuff down their toilets. They may soon be using much less, however, thanks to a slippery new toilet bowl coating.
-
A new sensor system is designed to catch polluters, by sampling and analyzing water within the sewer line.
-
Ordinarily, city officials only know about leaks in municipal water pipes once those leaks have become quite large and troublesome. A new artificial intelligence-based system, however, could catch such leaks much earlier – by listening for them.
-
When it rains heavily, even in arid places where water is scarce, the stormwater typically just runs off the streets and down the sewer drains. Thanks to a new "engineered sand," though, that road-polluted liquid could soon be cleaned up and used for drinking water.
Load More