Wyss Institute
-
Treating life-threatening bloodstream infections in combat situations is challenging, especially when the pathogen responsible is unknown. So, DARPA has called on Harvard’s Wyss Institute to use its groundbreaking biotech to fight this deadly threat.
-
In a medical emergency, quick treatment is critical. But a widely used drug could be repurposed to induce a hibernation-like state, to slow down organ damage and save lives by giving patients more time to reach a hospital.
-
Researchers have worked with biology rather than against it, fitting microparticle 'backpacks' to important inflammatory cells called macrophages to significantly reduce lesion size and inflammation caused by traumatic brain injury.
-
Researchers have used human cells to create tiny biobots that can encourage healing in damaged neurons without requiring genetic modifications. The tiny bots have the potential to transform regenerative medicine and the treatment of disease.
-
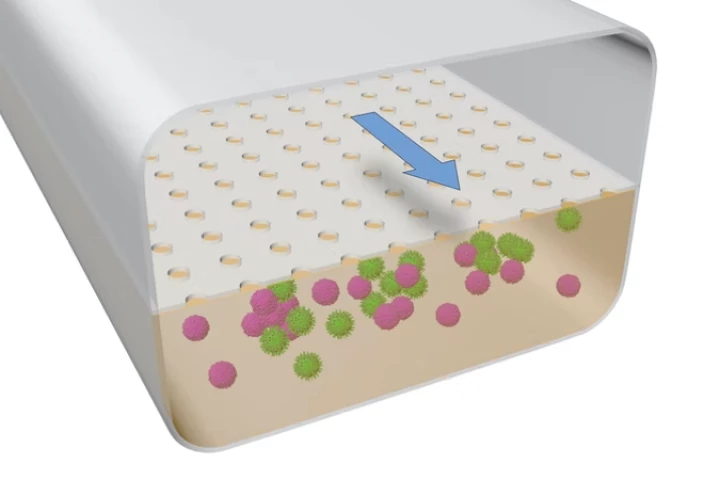
A new breakthrough could help unravel the immune system's secrets. Researchers have created an accurate model of the human immune system in a microfluidic chip, providing a better platform to study how immune cells respond to vaccines and pathogens.
-
Animals like axolotls can regrow fully functional replacements for lost limbs. In a breakthrough new study, scientists have demonstrated how one dose of a drug cocktail can regrow lost limbs in frogs that don’t normally have regenerative abilities.
-
A new slug-inspired biomaterial improves tendon healing, with one sticky side and a low-friction outer surface that keeps it gliding against other tissues. Better yet, they can be loaded with slow-release drugs to reduce scarring and inflammation.
-
Scientists have developed first-of-a-kind "Xenobots" from frog cells with the ability to self-replicate, a technology that could find use in regenerative medicine and and reveals a type of biological reproduction never before observed in science.
-
Eardrum perforations are painful, impair hearing and are tricky to repair. The PhonoGraft, developed at Harvard, is a 3D-printed implant that can patch up damage by encouraging natural cells to regrow, and now it’s ready for commercial production.
-
Scientists at Harvard have demonstrated an alternative to CRISPR – a genetic engineering system called Retron Library Recombineering (RLR) that works without cutting DNA and can be quickly applied to huge populations of cells.
-
Using AI to spot melanoma in its early stages is an exciting possibility, and a new deep-learning system developed by Harvard and MIT scientists promises a new level of sophistication, by using a method known as the “ugly duckling” criteria.
-
Cancer spreads easily, and a common location for secondary tumors to appear is the lungs. Now, scientists at Harvard’s Wyss Institute have developed a way to treat metastatic tumors in the lungs, by attaching immune-baiting drugs to red blood cells.
Load More