Yonsei University
-
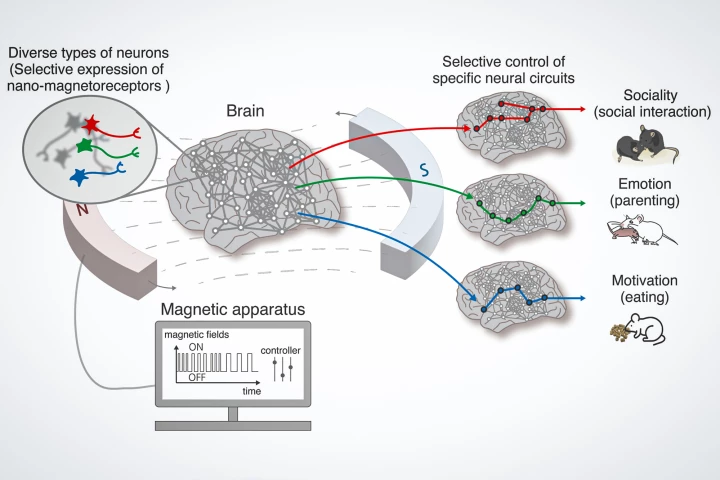
Researchers have developed a remote, non-invasive method of selectively controlling neurons in the brain using magnetic fields. The technique opens the door to a greater understanding of brain function and, potentially, new treatments for disorders.
-
When it comes to the treatment of Parkinson's disease, electrical deep brain stimulation (DBS) is a commonly used technique. It does have some drawbacks, however, which is why scientists are now looking to tiny wirelessly activated magnets instead.
-
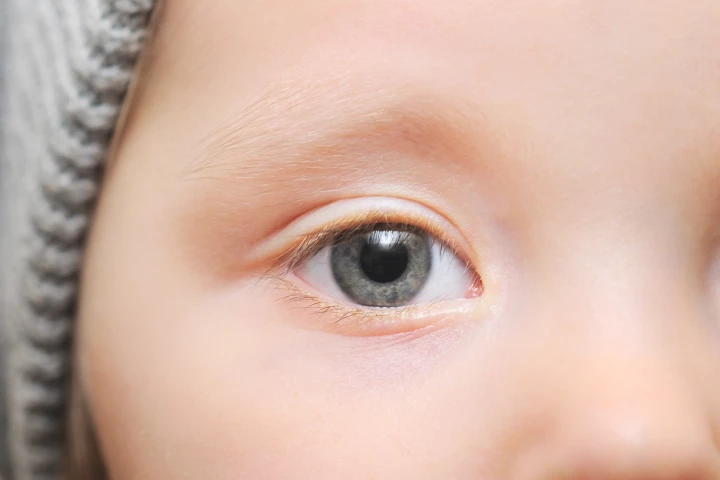
Researchers have used AI to screen photographs of children’s retinas to diagnose autism with 100% accuracy. The findings suggest AI is a viable screening tool for early diagnosis, especially when access to a specialist child psychiatrist is limited.
-
Most people already know that house plants such as pothos help neutralize indoor air pollutants. In the near future, however, a special coating applied to lampshades could serve much the same purpose.
-
While brain-implanted electrodes do show promise for applications such as restoring capabilities to the disabled, they tend to lose their functionality over time. A new coating, however, could allow them to work much longer once implanted.
-
A materials science and engineering team from Korea's Yonsei University has developed a 3D printing technique enabling OLED screens to be printed into transparent structures of any shape, meaning nearly anything can become a see-through color display.
-
Sunlight can be used to generate electricity either through a photovoltaic effect, or by harnessing the heat produced by the light. There are already hybrid systems that combine both, but scientists have now developed a type of hybrid setup that they claim works better.
-
A team of international researchers has developed a molecule capable of triggering cancer cell death by carrying chloride into cancer cell membranes. The molecule flushes the cells with salt and causes them to self-destruct, potentially paving the way for new types of anti-cancer drugs.