For a rough idea of a dog’s physiological age, a popular approach is to simply multiply its actual age by seven, but new research upends this piece of conventional wisdom. Scientists have developed a new molecular tool described as an “epigenetic clock,” which they say offers a more precise picture of a dog’s age in human years by drilling into the rate of molecular changes in their DNA.
The work was carried out by scientists at the University of California San Diego (UCSD) School of Medicine, who worked with genome experts to examine blood samples taken from 105 Labrador retrievers, ranging in age from a few weeks to 16 years old.
The purpose of this was to try and and uncover patterns of change in chemical markers on the DNA that are driven by age. These modifications are created by methyl groups that interact with the DNA molecule and influence which genes are turned on or off, without altering the DNA sequence. These changes can be driven by all kinds of environmental factors, and are referred to as epigenetic changes.
Epigenetics has emerged as a valuable tool for tracking the physiological age of humans, and the UCSD team set out to explore its potential in doing the same for canines. The analysis of the 105 Labradors enabled them to tease out patterns of methylation change that revealed a truer picture of their physilogical age.
"I tend to think of it very much like when you look at someone's face and guess their age based on their wrinkles, gray hair, and other features," says senior author Trey Ideker of UCSD. “These are just similar kinds of features on the molecular level."
These patterns were then compared to those in people, enabling the team to come up with a formula to calculate the equivalent age of dogs in human years. This revealed that they follow a far from linear path, with dogs aging rapidly while young and then slowing down as they move through life.
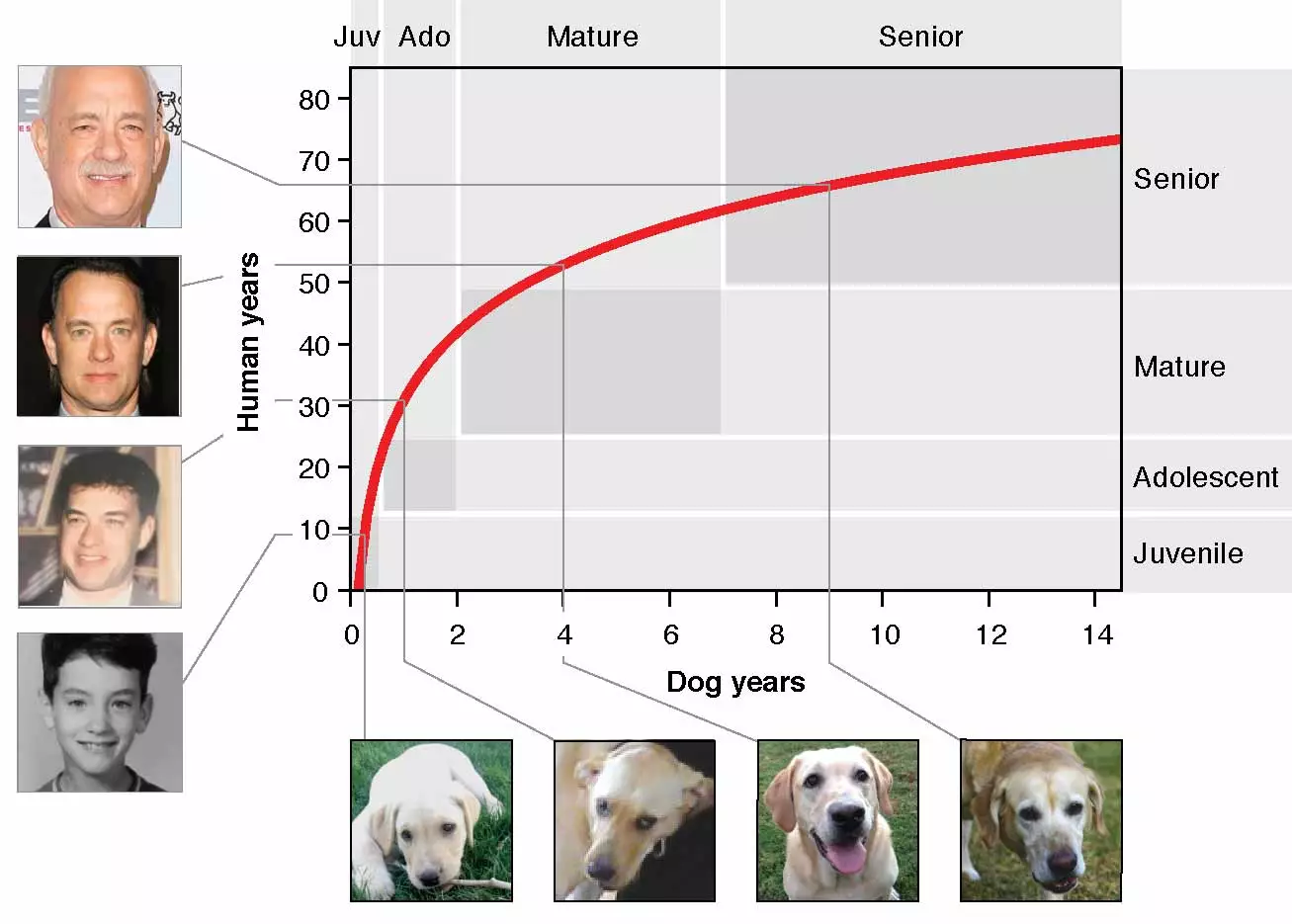
The team says that a one-year-old dog is actually similar to a 30-year-old-human, rather than a seven-year-old human. A four-year-old dog is similar in age to a 52-year-old-human, and when they reach seven years old the aging process starts to slow down significantly.
“This makes sense when you think about it – after all, a nine-month-old dog can have puppies, so we already knew that the 1:7 ratio wasn’t an accurate measure of age,” Ideker says.
One limitation of the research, as the scientists note, is that it was focused on one breed of dog, something they plan to expand on through further work. They hope that the formula could become a valuable tool for veterinarians as a way of offering improved diagnostics for dogs and treatment plans.
The research was published in the journal Cell Systems.