Editor's Note: Julian Hunt, the lead researcher on this study, has contacted us to say the figures quoted in the original press release, as well as the research paper and subsequently this piece, are incorrect. Figures quoted in MWh should be in kWh – a simple error as Hunt rushed to submit the research paper. This error was not noticed by the paper's co-authors, or by the peer reviewers for the Journal of Energy Storage. We have left this article as originally written, and appended our further questions with Hunt's replies at the end for clarity.
The Sun doesn't always shine exactly when you want to boil a kettle; the more we rely on renewable energy, the more energy storage we'll need. You can store your excess electricity by using it to pump water up a hill. You can use it to compress air, or to spin up a giant flywheel, or lift a huge concrete block off the ground. Most commonly, you can simply use it to charge up some big ol' grid-scale batteries.
These are rapidly gaining popularity, and prices for large-scale battery storage are coming down quickly. At the moment, the cost of storing and releasing a megawatt-hour of electricity in a newly-installed grid-scale lithium battery is about US$150. That will continue to drop, but researchers at the International Institute for Applied Systems Analysis (IIASA) have put forth an option that could reduce the cost to $50-100 per MWh in certain locations.
Buoyancy Energy Storage Technology, or BEST, harnesses a force that'll be familiar to anyone who's ever held a beach ball under the surface of the water and let it go. Effectively, the proposed design starts with a platform secured deep into the sea floor with weighted anchors. This is connected via cables to an enormous square array – 100 meters (328 ft) a side – of high-density polyethylene pipes, each full of a compressed gas, like air or hydrogen.
Electricity transmitted from the surface via power cables is used to drive powerful electric motors, which pull the buoyant tubes down toward the sea floor to store the energy. When it's time to release energy, the tubes are released, and their powerful buoyancy pulls the electric motor in reverse, turning it into a generator and feeding power back into the grid.
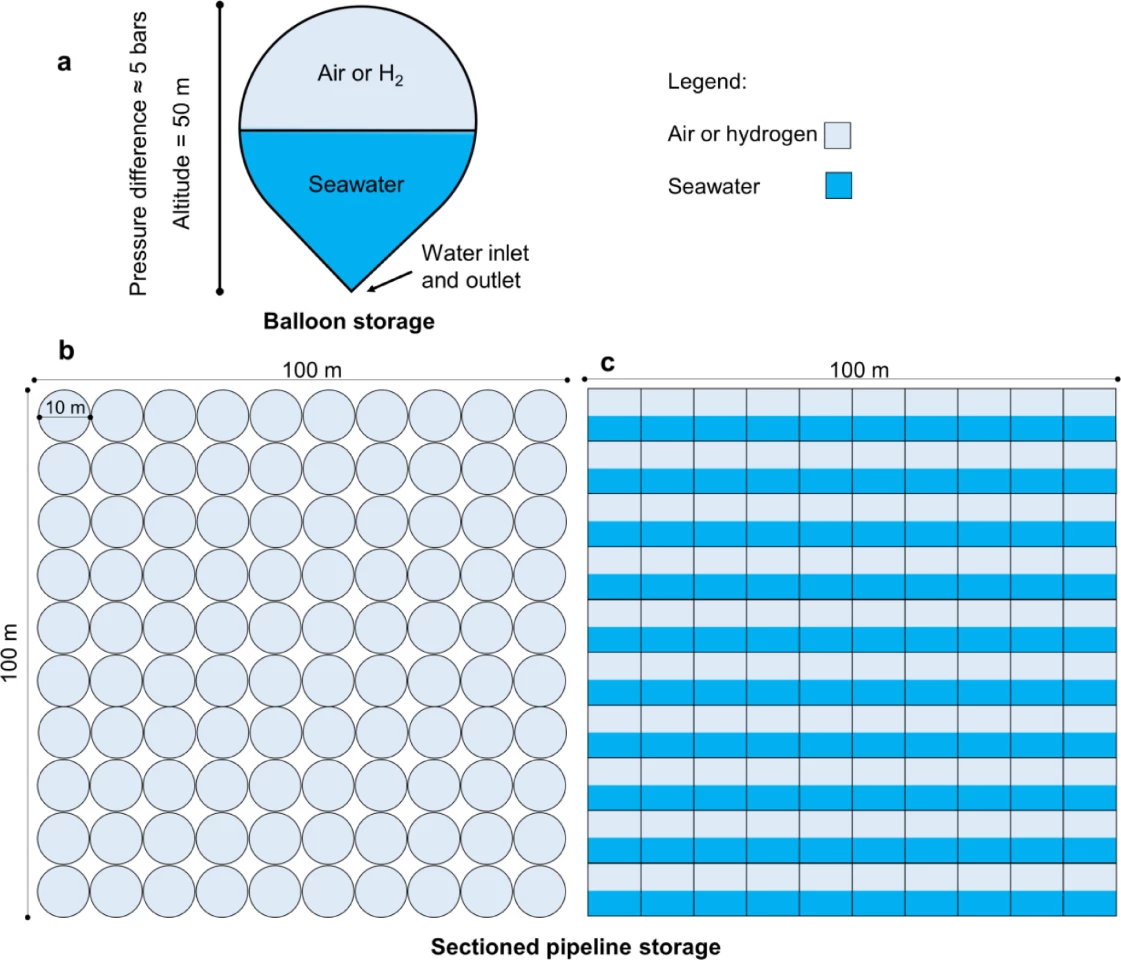
The team's simulations project that this could end up being a cheap and effective energy storage system in certain situations – particularly offshore wind farms operating close to coastlines and islands with no mountains. But it won't replace batteries altogether.
It's an energy density versus power density tradeoff: the BEST system can store lots of energy at a competitive cost, but batteries are better at storing and releasing that energy quickly.
“While the cost of batteries today is around $150/MWh, the cost of BEST is just $50 to $100 per MWh," says IIASA researcher Julian Hunt. "Given that the cost of installed capacity for batteries is smaller than in BEST systems ($4 to $8 million per megawatt), battery and BEST systems could be operated in conjunction to provide energy storage for a coastal city or for an offshore wind power plant. It is important to also bear in mind that the cost of BEST systems can be significantly reduced if substantial investment is made to the technology."
An assessment of global potential for this system showed considerably lower costs for air than for hydrogen, with the highest potential around "oceanic islands and on the coasts of Japan, Philippines, Indonesia, Australia, USA, Mexico, Chile, Peru, Ecuador, Colombia, Cuba, Jamaica, Guatemala, Honduras, Brazil, Portugal, Oman, South Africa, Madagascar and Somalia, Ivory Coast and Ghana."
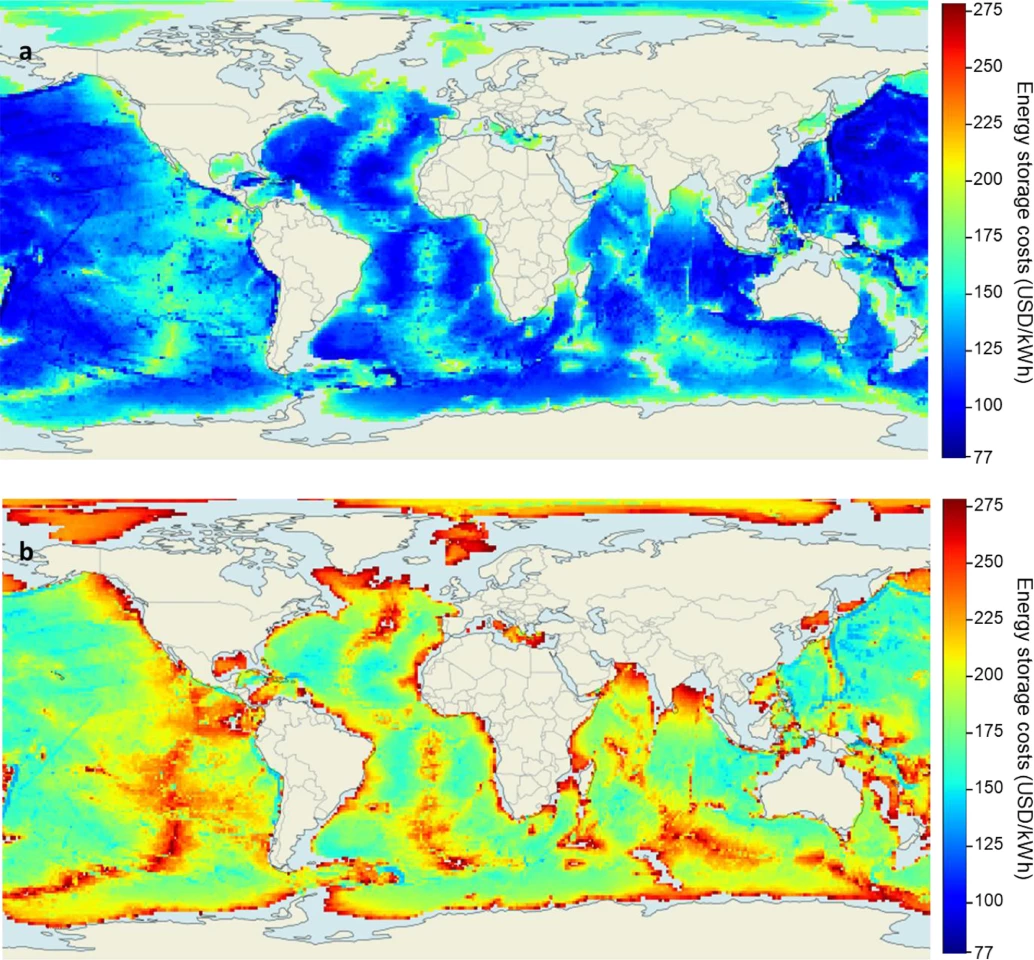
But there's another interesting wrinkle with hydrogen: the BEST system could easily be adapted to become a super-cheap hydrogen compression system as well as an energy storage system. By the time the tubes full of gas are pulled to the sea floor, they're already compressed thanks to the high ambient pressure levels in the deep ocean. At this point the hydrogen could be captured in a pressure tank whose design gives it just enough buoyancy to float back up to the surface. Alternatively, it could be pumped around through undersea pipelines.
Compressing hydrogen in this way, say the researchers, can be done with efficiencies as high as 90 percent, compared to land-based compressor efficiencies closer to half that. Investment costs are also estimated to be around 30 times lower than conventional compressors, thus cutting down one of the key costs in the hydrogen supply chain.
Editor's note: Julian Hunt contacted us with some fresh figures that contradict those published above. We asked some further questions and reproduce the exchange below.
Julian Hunt: Hi Loz, I am sorry for the confusion. After answering your questions, it became more clear to me how the economics of the technology work. If I had submitted the paper today, it would have been a much better paper. Thanks for your contributions.
1) So the levelized cost per MWh is actually $496 – several times higher than the levelized cost of using a battery? And that's in an ideal setup?
I estimated the levelized cost per MWh to be $496. After using the NREL Calculator https://www.nrel.gov/analysis/tech-lcoe.html.
The investment cost of storage is low 100 USD/KWh, however, the investment cost for the installed capacity is high 8,000 USD/kW. Just for comparison a wind turbine has a cost of 1,600 USD/kW. Today, if you charge and discharge a battery in a daily cycle, it would cost around 100 USD/MWh. But if you charge and discharge the same battery in a weekly cycle, it would cost 700 USD/MWh. If the only option that you have to use wind power is to have weekly energy storage, then a BEST system is already a better option than batteries.
Note that the levelized cost is $496 if someone would build the system today with the equipment and materials that I found on the web and being conservative due to the high operational depths. However, this cost would significantly reduce if an Elon Musk wannabe put 1 billion dollars into the technology, and the FED and society put more 50 billion dollars. This money would be used to develop new materials and technology for the cables, anchor and generators, and used to build the factories for these equipments. This would reduce the costs of the equipment substantially and the levelized costs could reduce to 50 $/MWh, storing energy in a weekly cycle.
2) This means both the upfront costs AND the usage costs are much higher than a battery installation?
The cost of storage of BEST is a bit lower, but the installed capacity is much higher. However, if you change and discharge both systems in a weekly cycle the BEST system is a better alternative than batteries.
3) If so, are there any advantages?
It stores energy in weekly cycles.
4) Please explain this quote: “While the cost of batteries today is around $150/MWh, the cost of BEST is just $50 to $100 per MWh,"
I would rephrase the sentence to "While the energy storage investment cost of batteries today is around $150/kWh, the cost of BEST is just $50 to $100 per kWh". Note, however, that the system also has an installed capacity, and the installed capacity for BEST is high.
Just for comparison, if the energy storage investment cost for batteries is $150/kWh and for BEST $50/kWh, and both systems are applied to store energy for 100 years to then generate electricity for 100 years (assuming that the batteries do not lose its charge), then the installed capacity costs will be tiny compared to the storage costs, and the levelized costs of BEST would be 3 times smaller than the levelized cost of batteries.
The research is open access in the Journal of Energy Storage.
Source: IIASA










