Body and Mind
Incredible progress is being made in health and medicine – every day we learn more about how to maximize physical and mental health, treat and cure illness and disease, and live longer, happier and healthier lives.
Top News
-
In a new study from the University of Oregon, scientists turned up the temperature to see which type of passive heat therapy packs the most health punch – hot baths, traditional saunas, or those fancy far-infrared saunas.
-
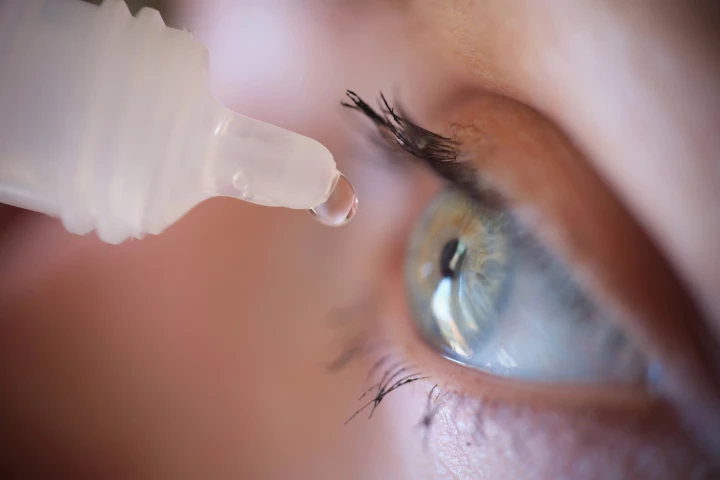
The first aceclidine-based eye drop to improve near vision in adults with age-related presbyopia, which affects more than 100 million adults in the US alone, has been approved by the Food and Drug Administration and will be on sale by November.
-
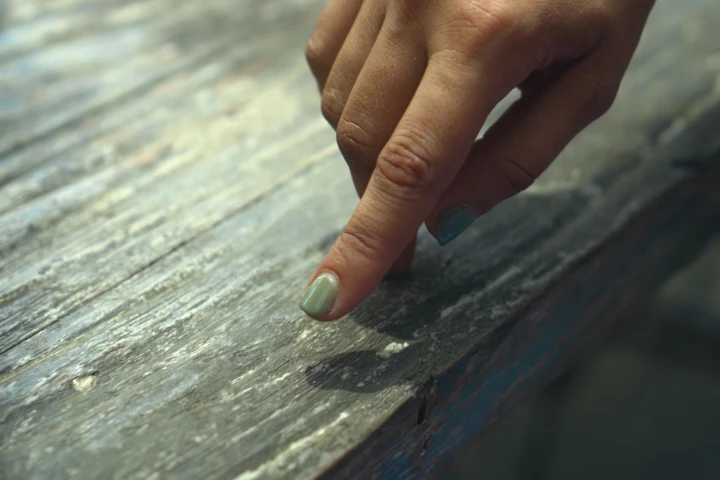
Scientists have uncovered an odd superpower triggered by tapping your finger to a beat – it may help you understand someone talking to you in a noisy place, like at a busy cafe. While it sounds a little woo-woo, there's emerging science behind it.
Load More
Latest News
-
December 30, 2025 | Malcolm AzaniaA new MIT method eliminates the need for hour-long infusions of antibodies for immunocompromised patients. With highly concentrated particles of antibodies created without a centrifuge, mass-manufacturing of better single-shot antibodies is here.
-
December 29, 2025 | Chelsea HaneyAn antiviral targeting the dengue virus was quietly abandoned by industry, but it's now suddenly back in the spotlight. A new study suggests it didn’t just slow the dengue virus, it blocked viral replication and reduced infection rates at high doses.
-
December 29, 2025 | Malcolm AzaniaScientists at Northwestern University have developed a sub-scalp device that beams light through bone into the brain, teasing a future of drug-free pain relief, cybernetic control of robotic limbs, and the simulation of sight, hearing, and touch.
-
December 28, 2025 | Pranjal MalewarTea and coffee are two of the most popular drinks in the world – daily rituals that are linked to culture, comfort, and productivity. Now scientists have new insights into how each affects bone health, especially the risk of osteoporosis.
-
December 28, 2025 | Pranjal MalewarBlinking isn’t just about keeping eyes moist. New research suggests we blink less when listening becomes hard, with each pause reflecting increased focus. The findings hint that blinking may track how hard our brains are working to listen among noise.
-
December 25, 2025 | Michael Franco2025 certainly saw some major health-related breakthroughs including a universal cancer vaccine. But the year was also filled with smaller findings that can still have a big impact on your day-to-day health. Here are 18 of them.
-
December 23, 2025 | Bronwyn ThompsonThe next transformative phase of weight-loss medication is upon us, with the US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) approving Novo Nordisk's highly anticipated oral GLP-1 drug – with a starting dose available in early January for US$149.
-
December 21, 2025 | Bronwyn ThompsonIn the first long-term and real-world reflective study of its kind, scientists have uncovered new detrimental health impacts of the artificial sweetener aspartame that echoes those found in shorter research.
-
December 20, 2025 | Jay KakadeTattoos have gained widespread popularity but according to a new study they may not be harmless decorations. Tattoo ink doesn’t just stay in the skin; it travels and accumulates in the lymph nodes, potentially causing lifelong changes to the immune system.
-
December 19, 2025 | Pranjal MalewarScientists have developed a new rapid test for hepatitis C. It is easy to use, highly sensitive, and made for point-of-care places like clinics and community centers. The speed allows clinicians to diagnose and start treatment in the same visit.
-
December 19, 2025 | Pranjal MalewarA new study shows that briefly and reversibly anesthetizing the retina of the amblyopic eye for just a few days can restore the brain's visual responses to that eye, even in adults.
-
December 18, 2025 | Bronwyn ThompsonIf you're after a free, simple boost for pushing through challenges, try swearing your way to your goals. A new study has uncovered the surprising psychological effect that cursing in the heat of the moment has – for the swearer, at least.
-
December 18, 2025 | Michael FrancoResearchers have homed in on a single gut microbe that acts to prevent fat gain, even with a high-fat diet. The discovery adds to the booming science of finding ways to enlist the microbes that already live in our bodies to help us improve our health.
-
December 17, 2025 | Bronwyn ThompsonThe use of blood-flow restriction cuffs that "hack" your physiology to speed up strength and muscle gains has been growing in popularity. However, researchers have now found that they come with a big downside during use – especially the older you get.
-
December 16, 2025 | Bronwyn ThompsonA bacterium from the gut of Japanese tree frogs has "exhibited remarkably potent" tumor-killing abilities when administered intravenously, outperforming current standard therapies and paving the way for an entirely new approach to treating cancer.
Load More