Body & Mind
Incredible progress is being made in health and medicine – every day we learn more about how to maximize physical and mental health, treat and cure illness and disease, and live longer, happier and healthier lives.
Top News
-
More than 15 million Americans are putting their liver at serious risk, simply by trying to better their health. New research has revealed the extent of the damage caused by overuse of six supplements including turmeric, green tea and ashwagandha.
-
In good news for nearly half the world's men, scientists have found that a naturally occurring sugar in humans and animals can be harnessed as a an effective topical gel for baldness. It sets it up as an inexpensive and safer alternative to minoxidil.
-
In a new study from the University of Oregon, scientists turned up the temperature to see which type of passive heat therapy packs the most health punch – hot baths, traditional saunas, or those fancy far-infrared saunas.
Load More
Latest News
-
July 18, 2025 | Bronwyn ThompsonFollowing on from a breakthrough human trial that reprogrammed the immune system to overpower an aggressive brain tumor, scientists have now used the same mRNA tech to attack any cancer. It could make chemotherapy, surgery and radiation redundant.
-
July 17, 2025 | Paul McClureA massive global study has ranked the best and safest treatments for chronic hives when antihistamines fall short. The findings provide a clear treatment roadmap for both patients and clinicians alike.
-
July 16, 2025 | Paul McClureScientists have created a hydrogel “rest stop” that shields cancer-fighting T cells, delaying their exhaustion and boosting their killing power. The game-changing strategy could supercharge immunotherapy, giving T cells time to regroup and hit harder.
-
July 16, 2025 | Bronwyn ThompsonNot all physical activities are created equal when it comes to a good night's sleep. A new study has uncovered the four practices that can significantly help different aspects of sleep disorders, without medical intervention. And they're all free.
-
July 16, 2025 | Paul McClureA common anti-nausea drug used during chemotherapy may do more than ease discomfort, it could help women with aggressive breast cancers live longer, cutting the risk of death by up to 39% in some cases, according to a new study.
-
July 15, 2025 | Paul McClureA massive study of over 1.2 million children has found no link between aluminum-containing vaccines and 50 chronic childhood conditions, including autism, ADHD, asthma, and diabetes, delivering a reassuring message about vaccine safety.
-
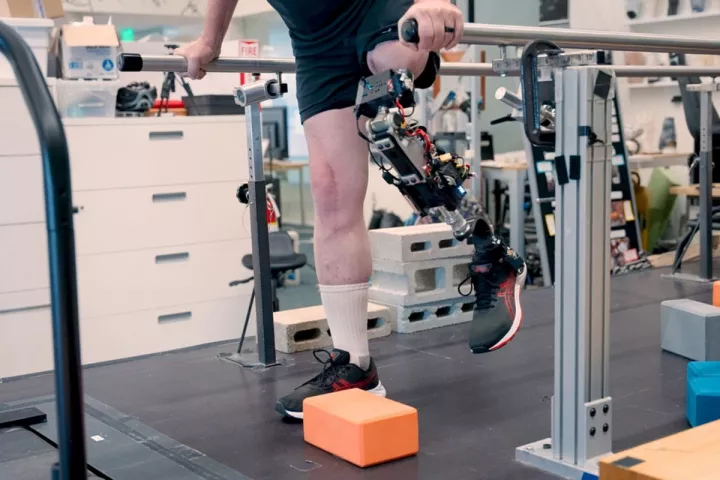
July 15, 2025 | Abhimanyu GhoshalMIT researchers have developed a method to restore natural movement in people with leg amputations above the knee. The team created a bionic knee that integrates with a patient's muscle and bone, enabling fluid motion and greater control.
-
July 14, 2025 | Bronwyn ThompsonFrom St John’s wort to vitamin D, the range of over-the-counter supplements for mental health wellbeing continues to grow. Now, scientists have looked at 64 products reviewed in hundreds of studies to shed light on how useful they are for depression.
-
July 14, 2025 | Bronwyn ThompsonFor the first time, a new study demonstrates that insomnia severity directly impacts ADHD traits and quality of life in adults. It calls for more attention to be paid to how treating sleep disorders can greatly improve wellbeing for people with ADHD.
-
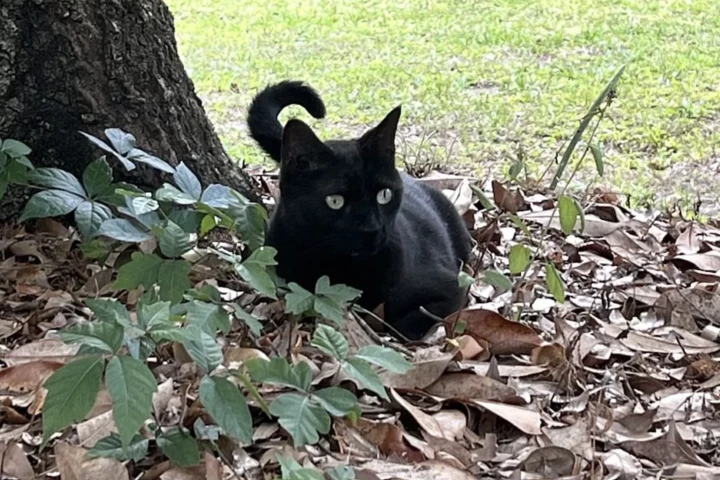
July 14, 2025 | Bronwyn ThompsonBlack cats may be a symbol of bad luck in many Western societies, but one such sooty feline has brought good fortune to scientists, playing a key role in identifying a new virus that can infect humans. It's the second novel bug Pepper has hunted down.
-
July 14, 2025 | Abhimanyu GhoshalResearchers at the University of Buffalo are hoping to make breast cancer screening easier and quicker than ever before, with a detection technique that only requires patients to press up against a window for a minute to get accurate results in 3D.
-
July 13, 2025 | Paul McClureA once-a-week Parkinson’s injection could replace multiple daily pills, thanks to a new slow-release formulation developed by researchers. It promises easier treatment, fewer missed doses, and better symptom control.
-
July 13, 2025 | Bronwyn ThompsonFor the first time, scientists have uncovered a distinct biological process triggered in those who suffer from high levels of Monday anxiety, resulting in chronic stress. And it can lead to serious health problems if it's left unmanaged.
-
July 13, 2025 | Bronwyn ThompsonSynching your daily calories with your own circadian rhythm can improve glucose metabolism, protecting against type 2 diabetes and obesity. A new study uncovers the relationship between metabolic health and our personal, inherent biological clock.
-
July 13, 2025 | Paul McClureOnce dismissed as “junk,” a group of RNA molecules has been found to help regrow damaged nerves in mice in new research. The discovery could unlock new ways to treat nerve injuries and even restore growth in the brain and spinal cord.
Load More