Aston University
-
Scientists have demonstrated a new potential treatment for bone cancer. A bioactive glass laced with a toxic metal was able to kill up to 99% of the cancer without harming healthy cells, and could even help regrow healthy bone after.
-
An international research team has sent an astounding amount of data at a nearly incomprehensible speed. It's the fastest data transmission ever using a single optical fiber and shows just how speedy the process can get using current materials.
-
Although they have a number of potential uses, spent coffee grounds typically just end up in landfills – or at best, in compost heaps. According to a new study, however, they could soon be utilized to both support and feed biodiesel-producing algae.
-
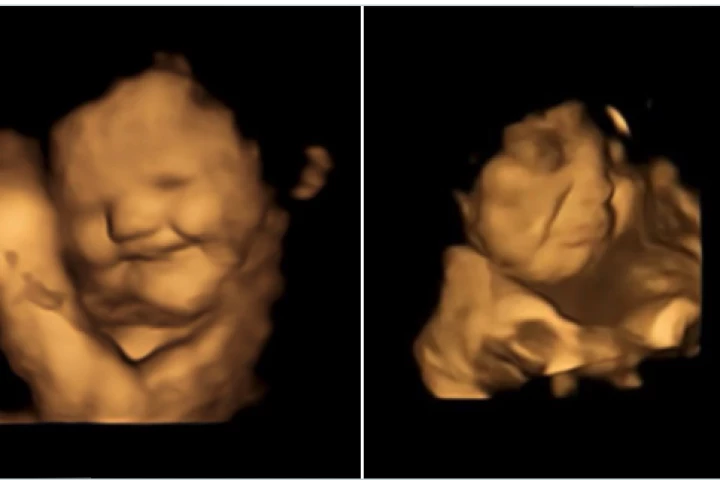
An extraordinary study has recorded the first evidence of babies in the womb reacting to flavors of foods, showing fetuses crumpling up their faces in disgust after a mother consumes kale or smiling with glee in the presence of carrot flavors.
-
People with cystic fibrosis are vulnerable to potentially fatal Mycobacterium abscessus lung infections, which are notoriously difficult to treat. A new treatment may succeed where others have failed, however – and it utilizes antibacterial honey.
-
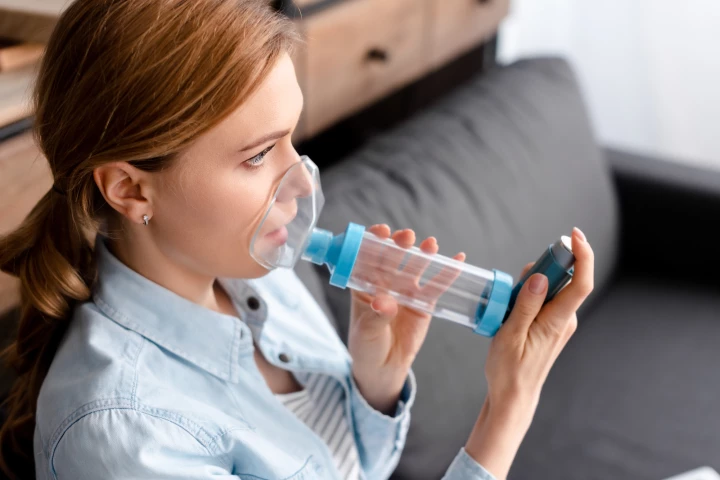
Asthma is usually managed by treating symptoms, but new research shows a potential way to target a root cause of the disease. A molecule prevented structural changes in the airways of asthmatic mice and eliminated their symptoms in weeks.
-
For some time now, antimicrobial bioactive glass has been put forward for use in applications such as medical implants, hospital surfaces and wound dressings. Now, scientists report they have boosted its bacteria-killing effect by over 100 times.
-
The number of healthcare-associated urinary tract infections could soon drop dramatically, thanks to the use of special antimicrobial glass.
-
A team from Aston University examined almost 20,000 insects collected from hospitals across the UK, and studied the kinds of bacteria they were carrying. The vast majority were found to host potentially harmful bacteria, more than half of which were resistant to some kinds of antibiotics.
-
Bacteria are a huge problem in hospitals, where colonies can build up on instruments and cause potentially fatal infections in vulnerable patients. Now, researchers at Aston University have developed a new type of antimicrobial material that’s made using a centuries-old stained glass technique.
-
In order to determine treatment for a patient's Parkinson's disease, doctors need to know the severity of their symptoms. Unfortunately, gauging that severity isn't an exact science. A new machine learning-based app, however, is intended to make it one.
-
Aston University's entry into this year's Shell Eco-Marathon may look low-tech, but that didn't stop the hydrogen-fueled cardboard and plywood flat-pack car from scooping the Eco-Design award.