Biotechnology
-
Scientists have hacked the meaning of a "light meal," creating microlasers that use natural products to emit beams through food. They're also completely safe to eat. It's the first demonstration of laser emission from an entirely edible system.
-
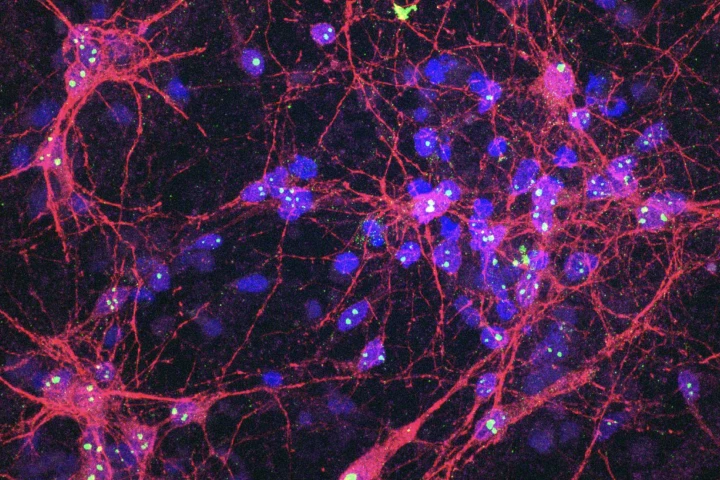
For the first time, Cortical Labs' mini-brain system has shown how its breakthrough biological computer system can, in response to drug intervention, alter activity and improve performance. It's a huge milestone for synthetic biological intelligence.
-
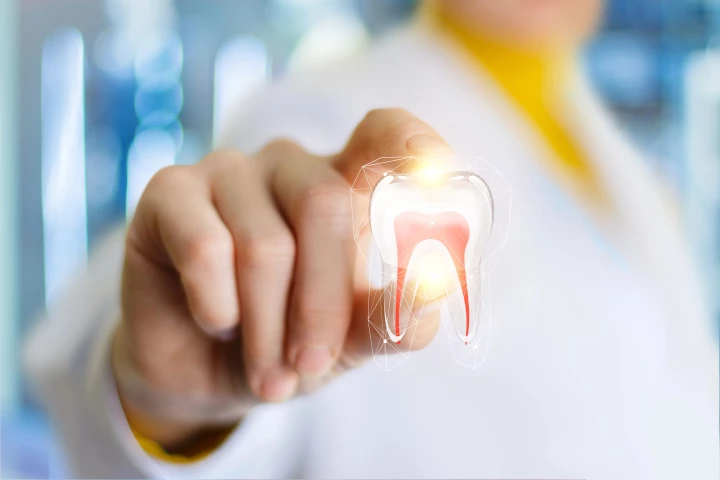
Scientists have developed an innovative new stem cell-infused implant that "grows" into the gum and fuses with existing nerves to function much like a real tooth. It's also gentler on the patient, expanding like memory foam to sit securely in place.
-
The first-ever "biological computer" powered by human cells, which form an ever-learning neural network, has been launched. It's an entirely new kind of AI – Synthethic Biological Intelligence – and not even its creators can predict its full potential.
-
Americans will soon have access to an infusion treatment that provides round-the-clock relief of Parkinson's symptoms. The US FDA has green-lit this innovative drug delivery system, which is expected to be available in the fourth quarter of 2025.
-
A pair of $139 brainwave-synching earbuds uses your body's data to shape your sleep. Whether it's a peaceful night or quality power naps, they stand to be a game-changer for anyone who has trouble getting enough shut-eye naturally.
-
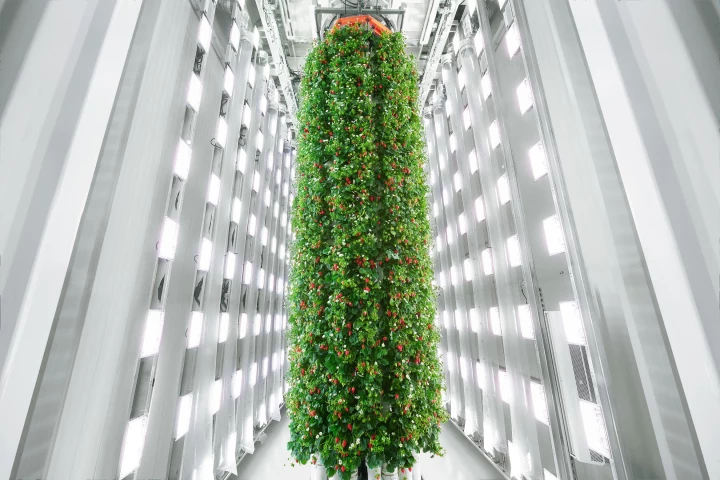
Major steps towards better, sustainable and affordable food production free of environmental challenges have been taken, with the with the opening of the "world's first farm to grow indoor, vertically farmed berries at scale".
-
Treating life-threatening bloodstream infections in combat situations is challenging, especially when the pathogen responsible is unknown. So, DARPA has called on Harvard’s Wyss Institute to use its groundbreaking biotech to fight this deadly threat.
-
A pigment molecule in cephalopod skin has had its antioxidant and sun-protection properties harnessed, inspiring the first ultra-protective, skin-restorative and environmentally safe sunscreen of its kind. And it could revolutionize the skincare world.
-
Your boots may soon have a tropical touch, with a breakthrough in using pineapple leaves to make a strong, 100% natural, sustainable leather. It comprehensively outperformed mushroom leather, and has serious potential for scalable, commercial use.
-
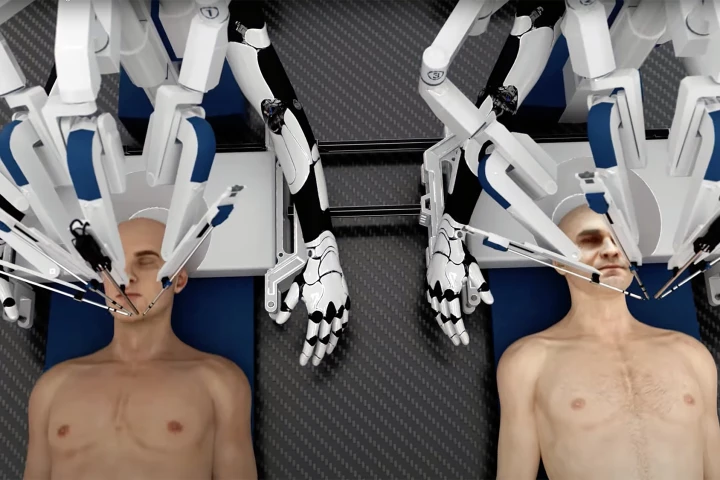
In what sounds more like the opening scene from a B-grade sci-fi/horror flick, head transplant operations performed entirely by AI-robot surgeons could be coming to a hospital near you within a decade, if startup BrainBridge is to have its way.
-
It's super-sustainable, easily made and nutrient-dense. And it puts all other food production to shame. Now, the first air-protein factory is open. It's the food of the future, and soon a $100 million industry – but will you be putting it on your plate?
Load More