Blood
-
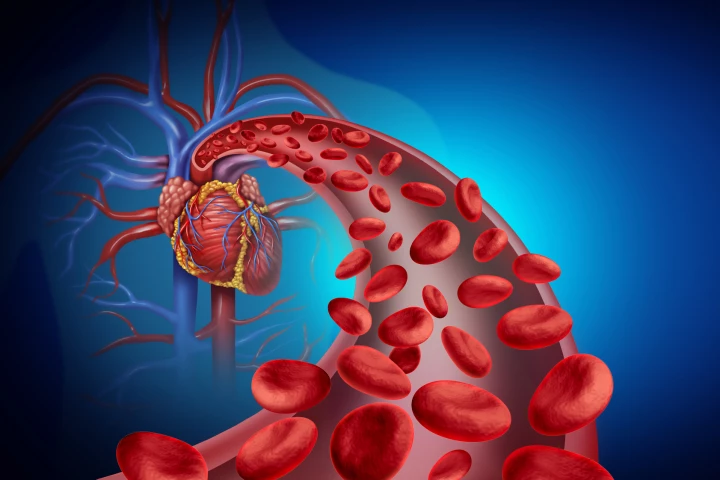
Researchers have found that red blood cells have an innate ability to trigger a pathway that protects the heart from injury during periods of low oxygen, such as during a heart attack. The discovery could lead to new drugs that activate this pathway.
-
Researchers have discovered the way that red blood cell particles interact with white blood cells called macrophages to reduce the formation of fatty deposits on arterial walls, offering a potential treatment for this common condition.
-
Researchers have found that inflammation leads to changes in the makeup of blood plasma that slow the growth of the parasites that cause malaria. They hope their discovery may one day be used to control or even prevent the disease.
-
In a glimpse of what could become a future Black Mirror episode, scientists have hooked the circulatory systems of old mice to young mice, and found that it slows the aging process in the older animals and increases their lifespan by up to 10%.
-
Researchers have identified biomarker proteins in genetically predisposed children that predict the autoimmunity that leads to type 1 diabetes months before symptoms appear. The discovery could lead to earlier detection and treatment of the disease.
-
The blood-brain barrier performs a vital function in keeping out toxins and pathogens, but it can become “leaky.” Now Stanford scientists have identified therapeutic molecules that could help patch it up, to potentially prevent neurological diseases.
-
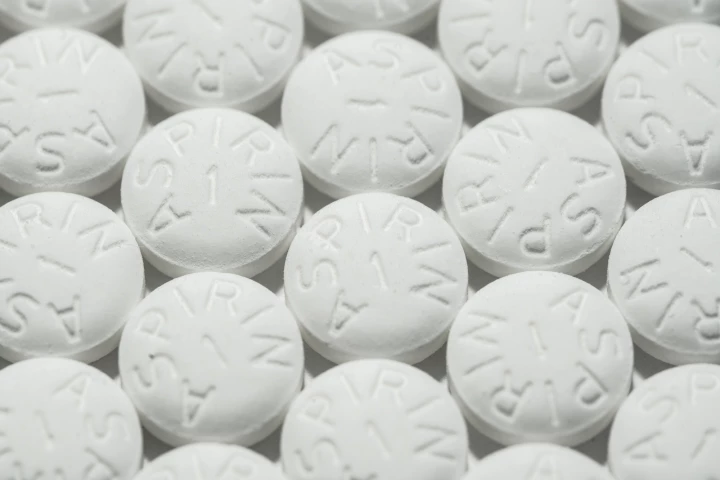
A large new study has found that healthy older adults taking a long-term low dose of aspirin may be at increased risk of developing anemia. The researchers say their findings suggest that these patients may need regular monitoring.
-
Scientists have discovered a gene variant that causes a common type of high blood pressure – and found a cure. A simple surgical procedure saw patients with previously severe hypertension needing no drugs or further treatment for years afterwards.
-
As a way of treating hemophilia, researchers have, for the first time, delivered gene therapy directly into the livers of baboons without using a viral carrier. The study shows it is safe and effective and may lead to a new treatment for the disease.
-
MIT scientists have developed a synthetic system that can stem internal bleeding, to help save lives after a traumatic injury. Two components come together at a wound to form a clot, without doing so elsewhere in the body where it might be dangerous.
-
Bears don't move much all winter long, but people are advised to get up frequently during a long flight to prevent blood clots. A new study uncovers why this discrepancy exists, and how it might lead to safer replacements for blood thinners.
-
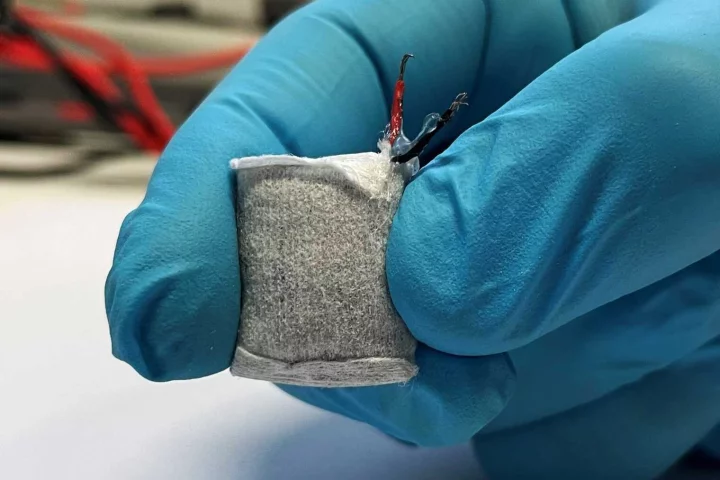
This internal fuel cell powered by excess glucose in the blood works in tandem with engineered beta cells that can produce and secrete insulin on command. It could spell a new level of autonomy in treatment for type 1 diabetes sufferers.
Load More