Brigham and Women’s Hospital
-
Phones can help with navigation on road trips, but they can also be dangerous distractions. A new study shows just how big that distraction is among teen drivers, and the number one reason the phones are used has nothing to do with directions.
-
Researchers have used Fitbit data to train a machine learning algorithm to accurately predict mood swings associated with bipolar disorder. It opens the door to using a personalized algorithm to drive treatment of the life-impacting condition.
-
Nobody wants to get a respiratory infection, but vaccines aren't 100% effective, and constantly taking drugs can be problematic. That's where a new nasal spray may come in, as it's been shown to prevent such illnesses without the use of drugs.
-
T cells are our first line of defense against cancer, but the battle tends to exhaust them. Now, scientists have found a way to give them extra “batteries” to keep them fighting longer, with promising early results in mice.
-
When someone overdoses on opioids, it's critically important that they receive a dose of the opioid-reversing drug naloxone as soon as possible – otherwise, death is a distinct possibility. That's where a new implant comes in, as it automatically dispenses naloxone from within the body.
-
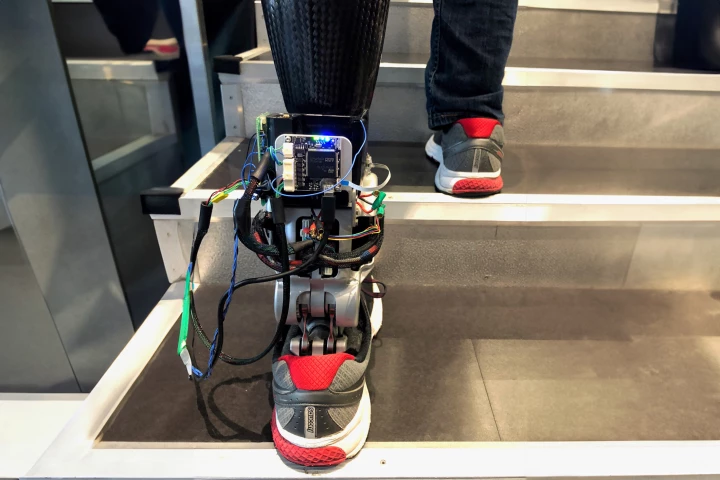
A new surgical technique for below-the-knee amputations retains a person’s ability to receive sensory feedback from remaining muscles. Having a prosthetic leg driven by an amputee’s own nervous system enables them to walk much more naturally, new research has shown.
-
In the hunt for cancer cures, researchers work with structures known as tumor spheroids. A new method of producing these structures has emerged using simple parts, which could lead to the cheap, reliable generation of these valuable research tools.
-
Research has revealed how genetic changes in a specialized population of brain cells called microglia contribute to neuroinflammation and, in turn, to Alzheimer’s disease. The findings could lead to more effective, targeted therapeutics.
-
Researchers have gained new insights into largely overlooked circular RNAs in brain cells and the crucial role they play in diseases like Alzheimer’s and Parkinson’s, opening the door to developing diagnostic tests and treatments for them.
-
Researchers have found that an intranasal drug, currently being tested as an MS treatment, reduced brain inflammation and improved cognition in mice with Alzheimer’s disease, independent of the amount of beta-amyloid plaques present.
-
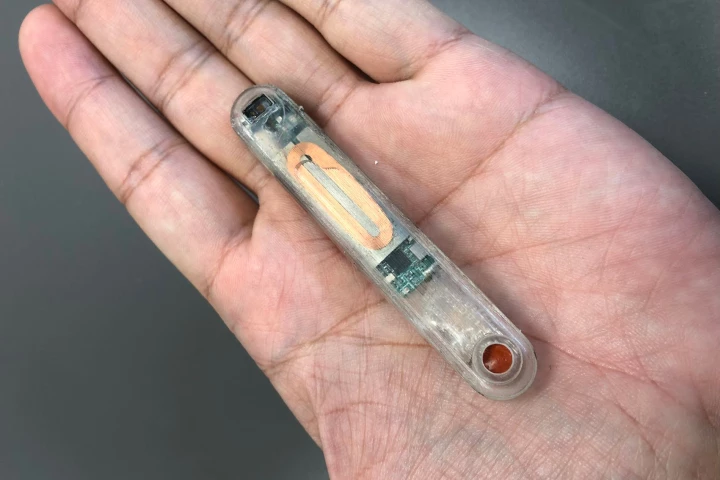
Not only are colonoscopies invasive and uncomfortable, they may also miss gut-problem-related biomarkers that are only present in the body for a short time. A new "smart pill" is designed to address such shortcomings, using live light-up bacteria.
-
Scientists have demonstrated in mice that specially designed probiotics can reduce brain inflammation from diseases like multiple sclerosis. The study points to new potential therapies for chronic conditions that may be as simple as popping a pill.
Load More