Cooling
-
As our personal devices get smaller and are expected to do more – your phone, smartwatch, or wearable AI assistant – they can get hotter on the inside. xMEMS' tech can deliver airflow in these products with a chip smaller than a microSD card.
-
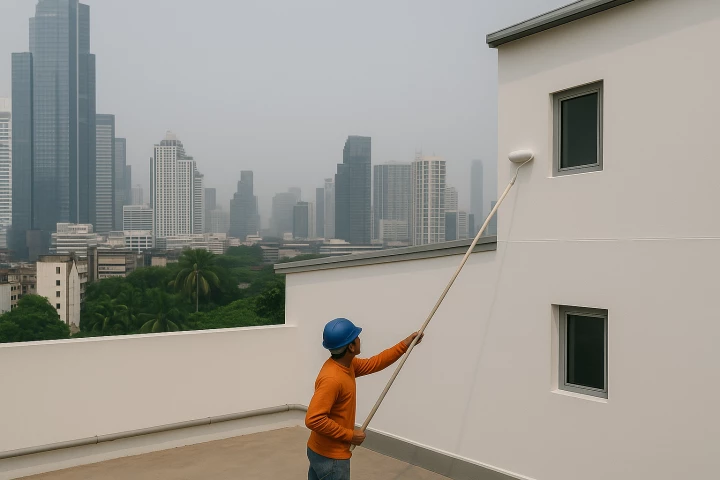
A new kind of paint might be the key to cooling homes in humid climes like Singapore. Researchers based in the island country found their custom white paint, specially developed to 'sweat,' significantly reduced the need for air conditioning.
-
Nobody likes buildings that are too hot in the summer or too cold in the winter. That's where the FlectoLine facade comes in, as it uses two bio-inspired mechanisms to regulate how much solar thermal energy gets through a building's windows.
-
Solo Stove has long built its brand around fire, but now it's expanding into other product categories. A cooler seemed almost inevitable, but this one goes a step further as a fire pit-like gathering point with A/C and misting to keep everyone cool.
-
The heat from within your laptop disperses slowly, like ripples in a pond. What if we could turn that heat into channeled waves that travel away from the source up to a hundred times faster? Researchers are giving it a go – with crystals.
-
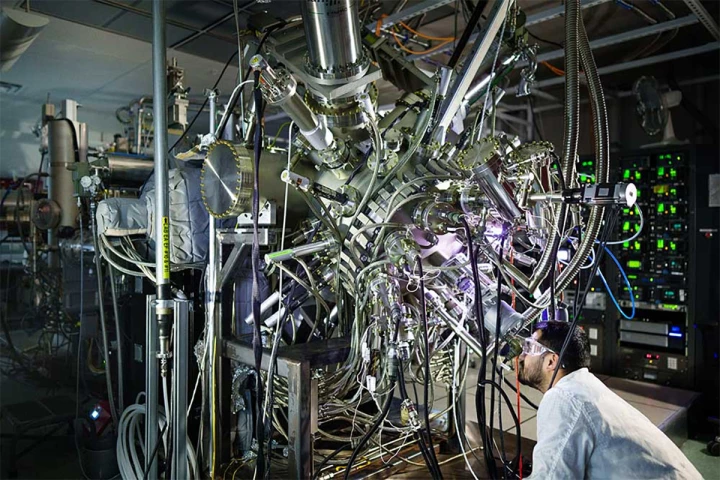
Under specific conditions, lasers can cool things down – and that might just be what we need to tackle way-too-toasty data centers. A new technology called laser-based photonic cooling can target tiny hotspots on chips to zap heat away.
-
Oyster mushrooms and bits of bamboo sound more at home on a Chinese menu than stuck to the wall, but scientists have used this mix to make aesthetically pleasing tiles with bumps and textures that help regulate temperature much like elephant skin does.
-
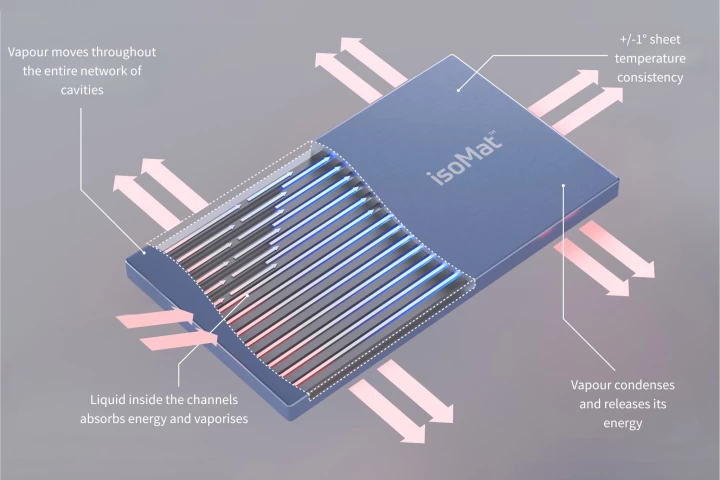
How's this for a set of promises? Flint Engineering claims its new, flat, thermal-transfer "IsoMat" can power entire homes, cut refrigerator energy consumption by 30%, and radically speed up EV charging while also extending battery life.
-
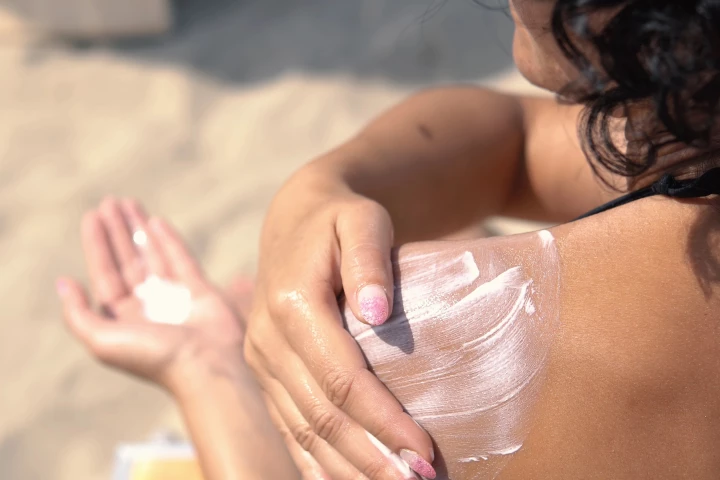
Although sunscreen does help protect our skin from the sun's harmful UV rays, it isn't designed to keep that skin cool. An experimental new sunscreen does that very thing, however, while maintaining an SPF rating of about 50.
-
Cranking up the air conditioner keeps buildings cool, but it guzzles energy. Passive materials can regulate temperatures more efficiently, and now scientists have developed a new coating that keeps glass much cooler, while still being transparent.
-
Although hot tubs may get all the glory, cold-plunge tubs are the ones that really help reduce muscle inflammation and soreness. The Snowcap tub makes that process more doable than ever, by chilling water without using any ice or refrigerants.
-
We're caught in a vicious circle of facing increasing temperatures across the planet, and combating that with air conditioning – which in turn causes global warming. A problem worth throwing a whole lot of science at, if there ever was one.
Load More