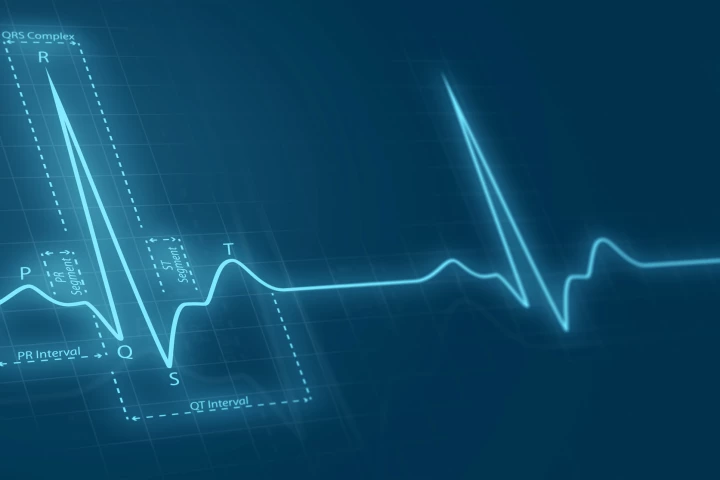
ECG
-
A new continuous glucose monitor (CGM) that is not only non-invasive but that predicts blood sugar levels from ECG data promises to shake up diabetes management. The device is being showcased at the 2024 Taiwan Innotech Expo.
-
A new injectable, temporary pacemaker could help correct a heart arrhythmia in an emergency. This nanoparticle gel can regulate the heart’s electrical signals for up to five days before dissolving harmlessly in the body.
-
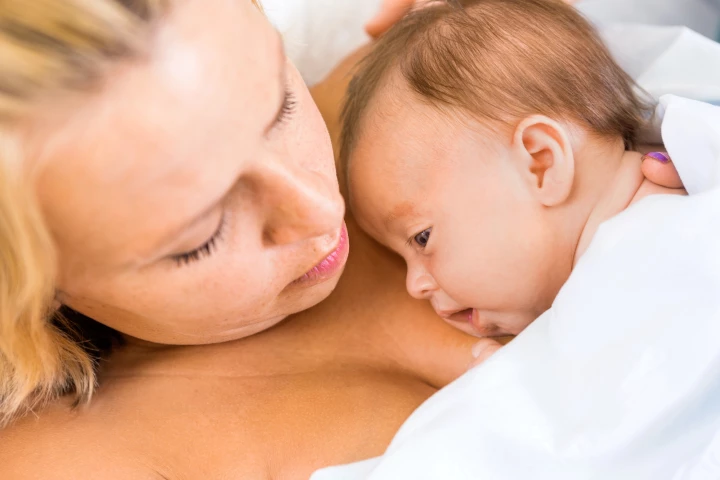
For low-birth-weight (LBW) babies, skin-to-skin contact with their mother can literally be a lifesaver. A new high-tech necklace ensures that they get enough of that snuggling, while also providing essential data on their vital signs.
-
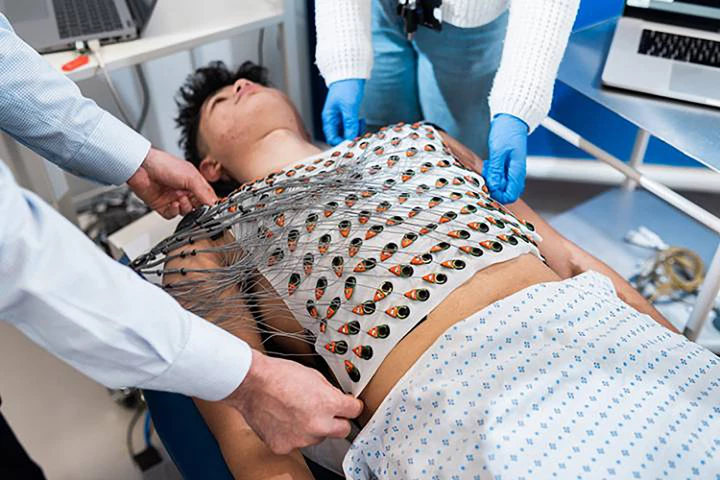
Researchers have developed a reusable ECG vest that takes high-resolution images of the heart's electrical activity that can better identify people at risk of future heart problems and could pave the way for more personalized treatment of heart disease.
-
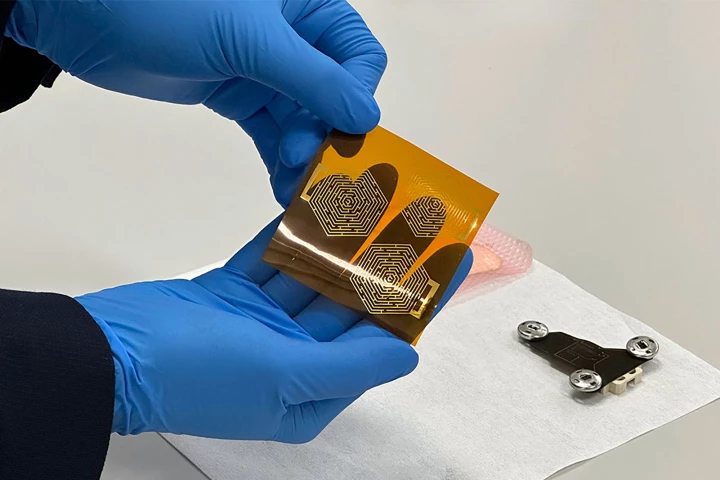
Researchers have developed an ultrathin, waterproof, gel-free ECG electrode for continuous heart monitoring that offers greater comfort than current devices on the market, while still precisely measuring the heart’s electrical activity.
-
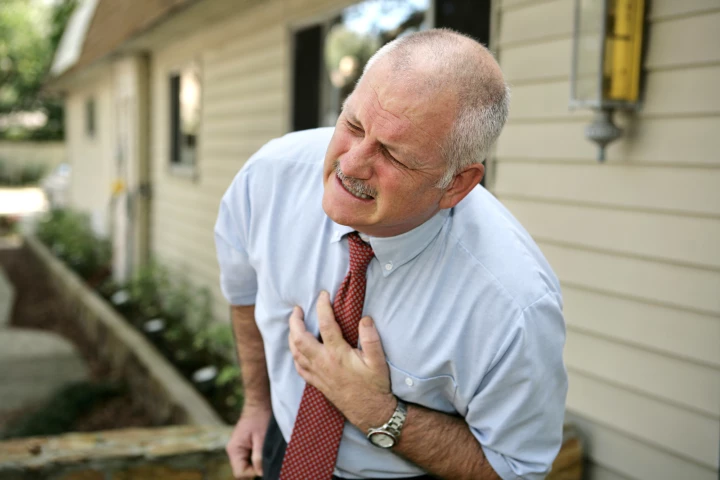
For many, Monday means the weekend's over and it's back to work. Now, there's something else to worry about. Research has found that the most life-threatening type of heart attack is more likely to occur on a Monday than any other day of the week.
-
Researchers have developed a mobile, noninvasive, ultrathin, stretchable, battery-operated electronic tattoo that simultaneously measures the heart’s electrical and mechanical activity, offering a new way of diagnosing and monitoring heart disease.
-
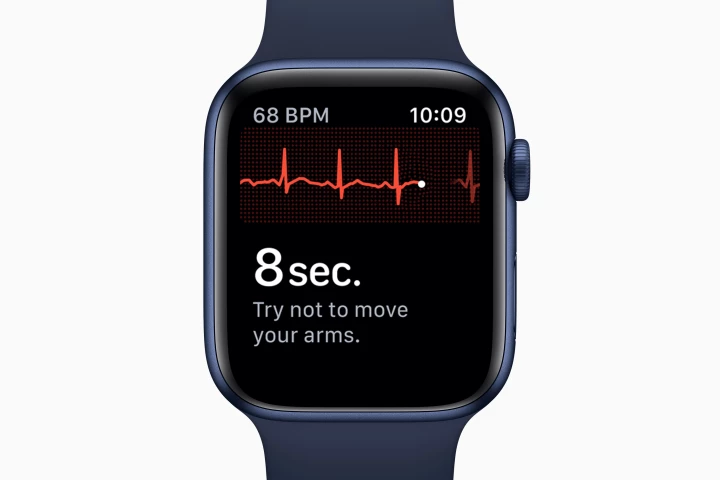
A new algorithm can effectively detect patients with a dangerous heart dysfunction using ECG data gathered by an Apple Watch. A large trial is now currently underway looking to test the clinical utility of the algorithm in one million people.
-
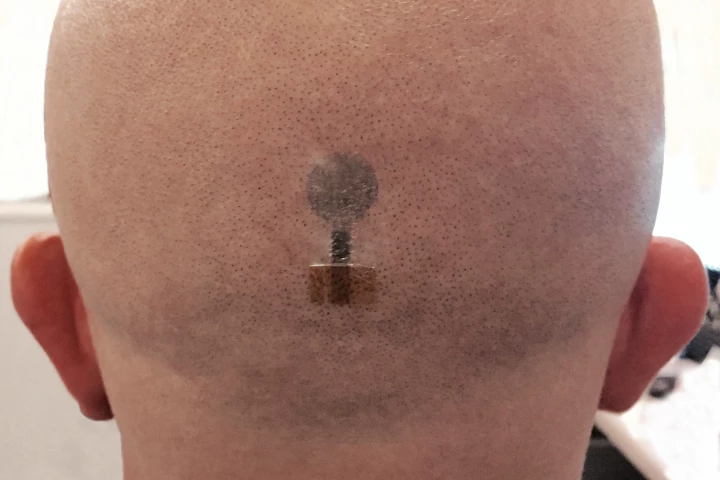
Engineers have optimized a novel technology that uses temporary tattoo electrodes to record EEG brain activity. The technology is cheap, can be produced using an inkjet printer, and delivers EEG measurements as accurately as traditional electrodes.
-
An abnormal heart rhythm called atrial fibrillation is one of the leading causes of strokes, yet it's often symptomless, so it frequently goes undetected. An experimental new necklace, however, could make checking for it a quick and simple process.
-
The dream of a non-invasive device to continually monitor blood glucose levels has never become reality. The latest prospective technique, from the University of Warwick, uses artificial intelligence to detect low blood glucose from simple ECG data.
-
A new AI diagnostic method, using a neural network, can accurately identify congestive heart failure instantly by checking ECG data from just one heartbeat.
Load More