Empa
-
Conventional tests for Alzheimer’s disease don't provide information about what stage it's at. Now, viewing pathological protein clumps with atomic-force microscopy may help doctors not just detect the disease but determine how far it has progressed.
-
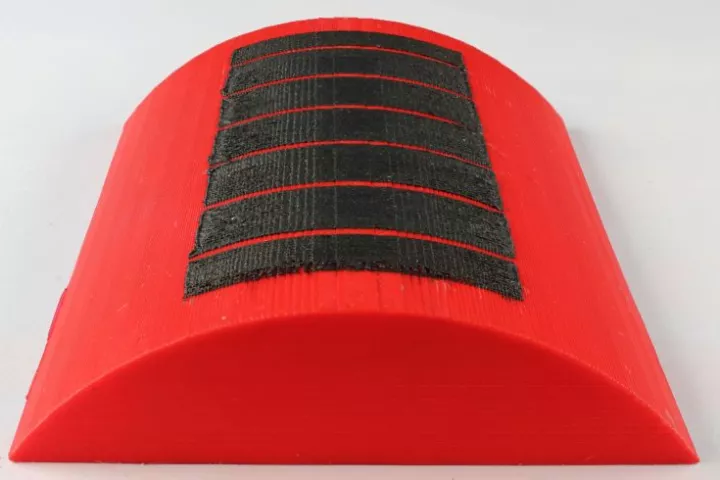
While glass bricks are effective for allowing daylight into buildings, they're not good insulators and they can't be used for entire load-bearing walls. Such is reportedly not the case, however, with experimental new aerogel-filled translucent bricks.
-
Whether you're an athlete or someone experiencing foot pain, it's important to eliminate high-pressure areas in the soles of your shoes. An experimental insole could help, by showing where such areas are located during a variety of activities.
-
The installation of a cochlear implant is a tricky procedure, in which certain nerves may be damaged if the surgeon isn't careful. A new "smart" surgical drill is designed to help, by automatically shutting off if it gets too close to those nerves.
-
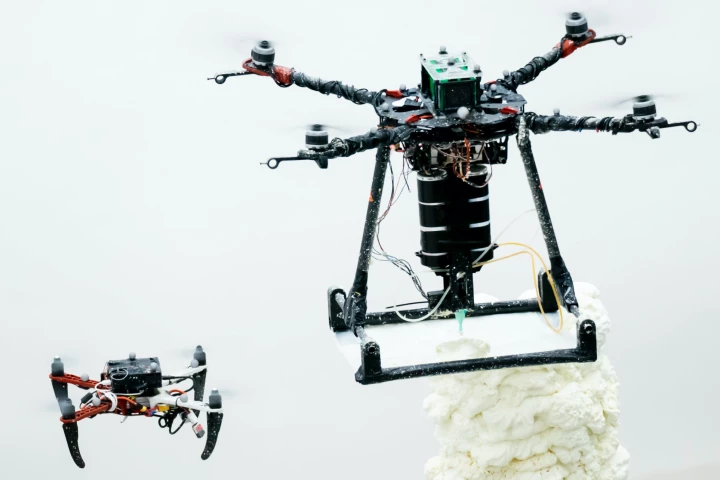
Building structures in difficult-to-reach locations is a daunting task, as bringing in the cranes, scaffolding and whatnot can be difficult. That's why scientists are creating a bee-inspired system, which uses flying 3D-printing drones to do the job.
-
Although it's always best to reuse and recycle, many small, simple, low-power electronic devices tend to be single-use. A new paper battery could make them more eco-friendly, as it's activated by water, and it biodegrades once discarded.
-
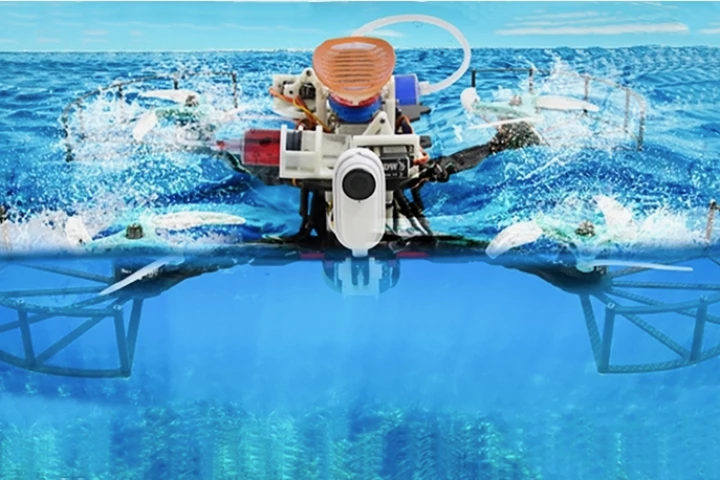
Although aerial drones can travel much faster than their underwater counterparts, they certainly aren't as good at gathering water-related data. The MEDUSA multi-rotor drone addresses this conundrum, by landing on the water and deploying an underwater pod.
-
While we have heard of a few aerial drones that are also able to operate underwater, a new one takes that concept considerably further. Using a fish-inspired suction disc, it can hitch rides underwater – possibly even on submarines – to save power.
-
While antibiotics are very effective at treating infected wounds, they should definitely be used sparingly. An experimental new bandage was designed with this fact in mind, as it only dispenses medication when it detects the heat of an infection.
-
As 3D-printed electrical circuits become more widely produced, the problem of electronic waste could correspondingly get worse. That's why Swiss scientists have developed a new natural-source "e-ink" that biodegrades once discarded.
-
The construction industry is a big producer of CO2, and ETH Zurich has been working on new techniques that help clean up the industry's act. The result is the HiLo, which was built using minimal concrete and has impressive sustainability features.
-
Scientists in Switzerland have been working to bring the efficiency of CIGS flexible solar cells up to the levels offered by rigid solar cells, and have taken another step toward this goal by setting a new record of 21.4 percent.
Load More