Indiana University
-
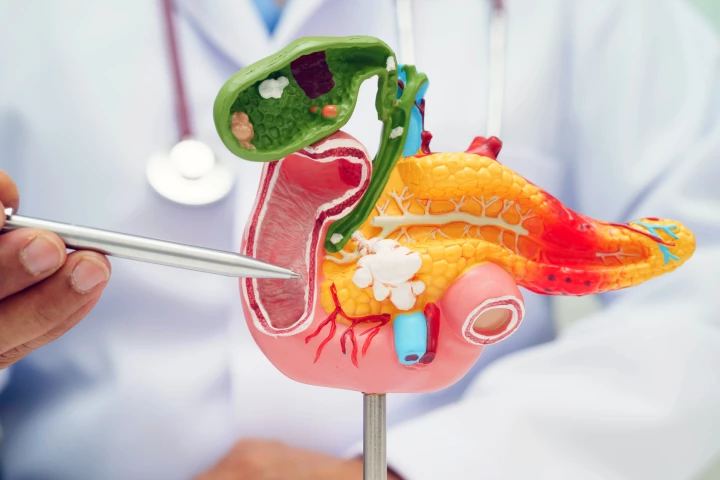
By knocking out a protein duo’s “bodyguard” role, researchers have exposed a hidden weakness in pancreatic cancer. It’s a discovery that could lead to smarter, more effective treatments for one of the deadliest cancers.
-
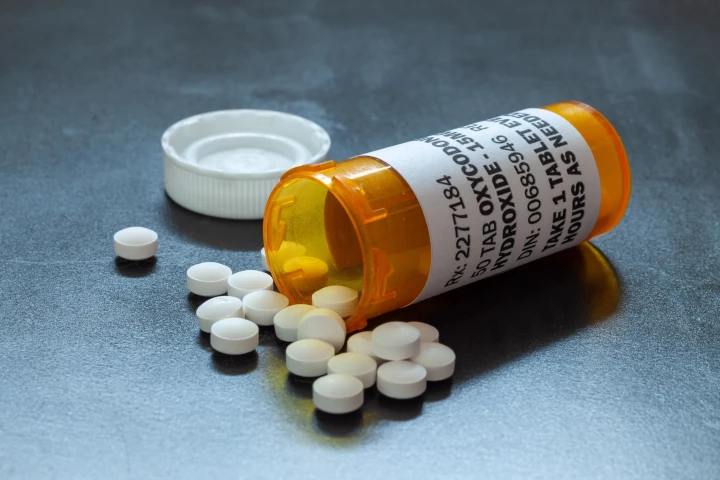
In a massive study, scientists have failed to find any meaningful link between the use of opioid painkillers and the prevalence of autism spectrum disorder and attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder, challenging earlier research suggesting otherwise.
-
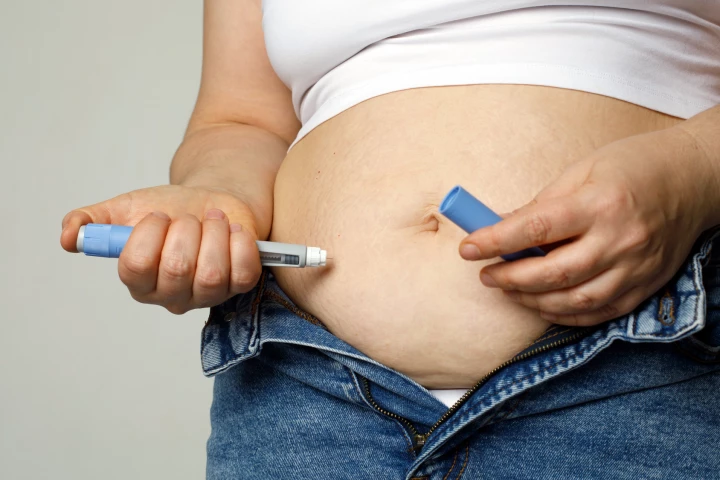
A clinical trial has shown that Ozempic improves blood glucose levels and weight loss in overweight type 1 diabetics who use an automated insulin delivery system. It’s hoped this will lead to the approval of Ozempic for this patient population.
-
A cannabinoid our bodies produce naturally has been found to play a role in the fear responses characteristic of conditions like anxiety and PTSD. The discovery opens the door to developing a treatment that targets this specific chemical.
-
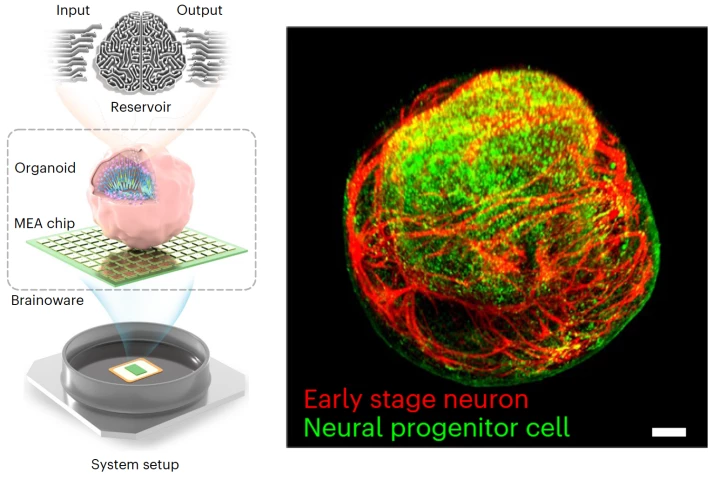
Scientists have grown a tiny brain-like organoid out of human stem cells, hooked it up to a computer, and demonstrated its potential as a kind of organic machine learning chip, showing it can quickly pick up speech recognition and math predictions.
-
How small a canvas can evolution work on? Scientists have experimented with a synthetic lifeform designed to have the simplest possible genome, and found that given the chance it can evolve lost fitness back, showing that indeed, “life finds a way.”
-
Compelling research has homed in on a degenerative mechanism that could explain why symptoms such as apathy are the first signs of Alzheimer’s disease. It is possible disrupting this process could slow the progression of Alzheimer’s-related dementia.
-
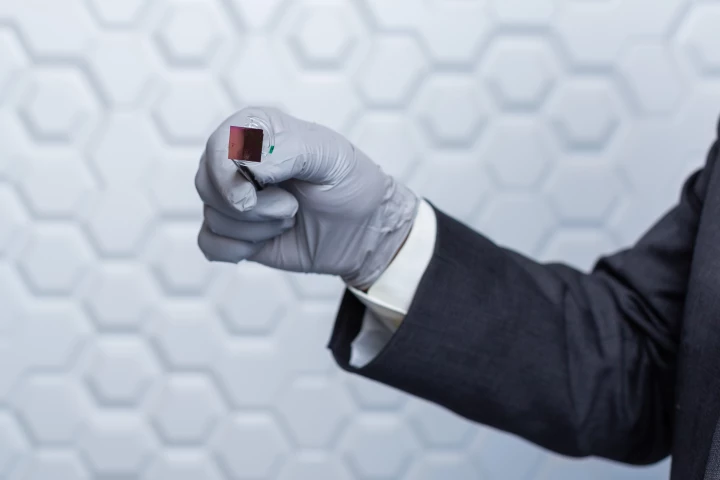
A team of researchershas advanced development of a nanochip device that can reprogram cells in the body to become new blood vessels and nerve cells. It could be used to repair brain damage resulting from a stroke or nerve damage caused by diabetes.
-
For people with particularly cavity-prone teeth, daily brushing and flossing aren't always enough. A new treatment could help, as it uses tiny particles known as nanozymes to break down plaque and kill cavity-causing bacteria.
-
A team at Indiana University School of Medicine has taken a promising step towards a future of self-adjusting insulin, demonstrating a type of "synthetic hinge" that swings into action when blood glucose levels call for corrective action.
-
Researchers at Indiana University have linked a protein secreted by the stomach to obesity. In tests in mice, the team switched off the protein and found that it reduced the animals’ body fat levels, even when fed a high-fat diet.
-
While we've seen fossilized dinosaur eggs and embryos before, paleontologists have now discovered an unprecedented three-for-one – a fossilized dinosaur parent sitting on a nest of eggs, in which embryos are present.
Load More