Johns Hopkins University
-
In new hope for aggressive brain cancers, injecting a drug-laden hydrogel into the brain after tumors were surgically removed was found to launch a combined chemo- and immunotherapy attack, preventing cancer from returning in 100% of treated mice.
-
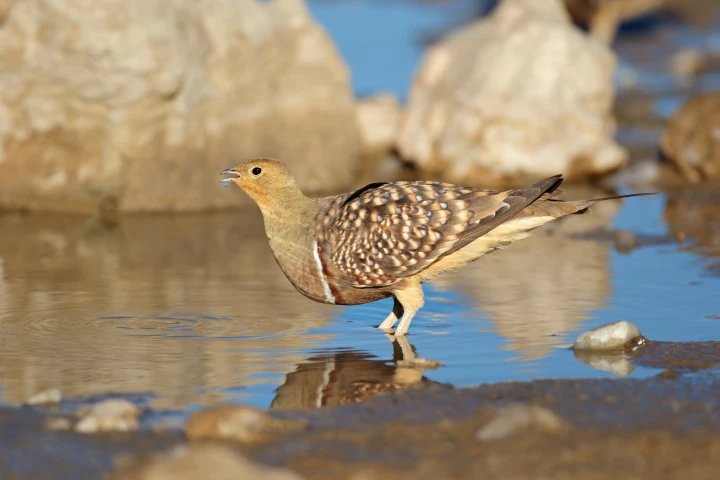
The belly feathers of the male desert sandgrouse can absorb and carry water. Researchers have, for the first time, closely examined the unique structure of these feathers to see how they do it and whether the process might be adapted for human use.
-
A new study suggests natural selection was at work before life itself existed on Earth. By recreating the primordial soup, scientists identified how a cocktail of specific amino acids informed the genetic code of every single lifeform on the planet.
-
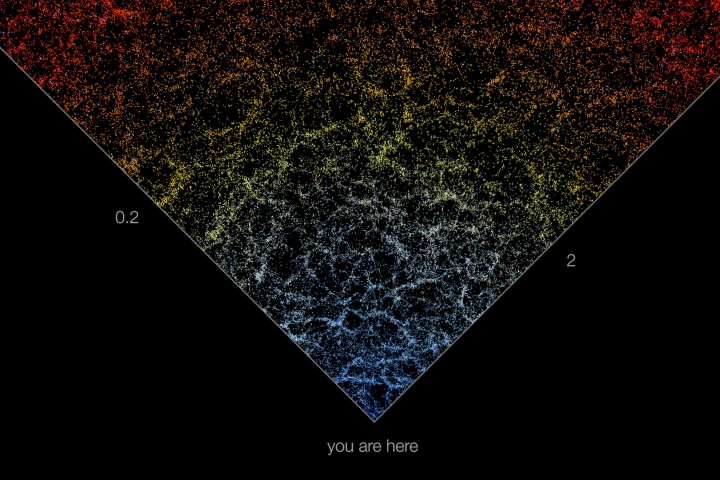
Astronomers at Johns Hopkins University have created an interactive map of the universe, charting the positions and colors of 200,000 galaxies stretching from here to the very edge of the observable universe.
-
Our immune system can unfortunately go rogue and attack healthy tissues. Scientists at Johns Hopkins University have now engineered a protein that may help prevent these autoimmune diseases by boosting the number of regulatory T cells (Tregs).
-
Today, NASA will explore a planetary defense technique through a world-first mission to crash into the asteroid Dimorphos and alter its orbit. We checked in with the team behind this landmark mission to understand some of the mechanics at play.
-
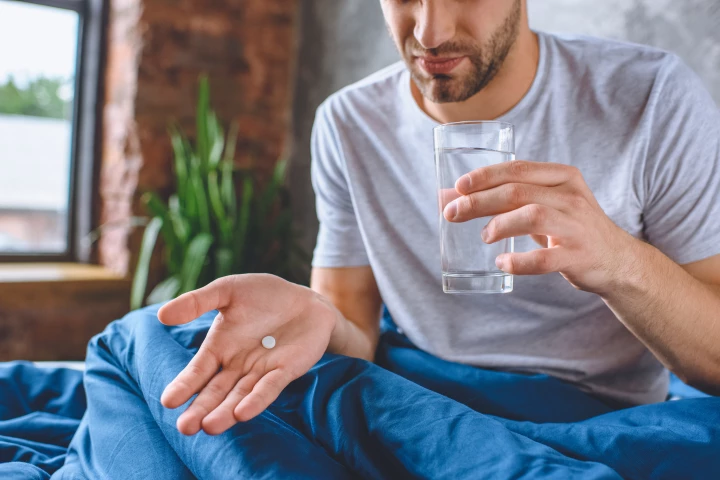
When taking a pill such as a pain reliever, it goes without saying that you want it to work as fast as possible. According to a new study, taking that pill while lying on your right side will help it to do so.
-
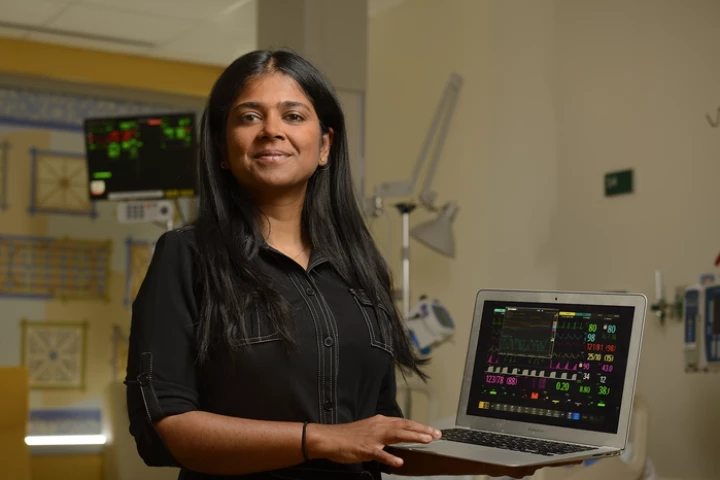
Sepsis is a life-threatening complication causes more than 250,000 deaths in the US each year, but a new AI system developed at Johns Hopkins University promises to make a real difference in this area, by catching key symptoms early on.
-
Scientists at Johns Hopkins have identified a previously unknown mechanism of cocaine’s activity in the brain, which could open new types of treatment for addiction to the drug. Intriguingly, it seems to work differently in male and female mice.
-
How exactly kidney cells transport blood through the organ's tubes has remained a mystery. Now researchers at Johns Hopkins University have investigated the mechanical forces at work and found a previously unobserved pumping action by kidney cells.
-
There's a belief that when someone loses one ability, another improves correspondingly. New research bears this out – in one scenario, at least – as it indicates that blind people remember spoken information better than their sighted counterparts.
-
Researchers at Johns Hopkins University have developed a new shock-absorbing material that is super lightweight, yet offers the protection of metal. The stuff could make for helmets, armor and vehicle parts that are lighter, stronger and reusable.
Load More