Karolinska Institutet
-
If you have a high level of interaction with patients, students, clients or the general public in your work, you might be at much higher risk of developing type 2 diabetes. And, if you also have poor support at work, it could worsen your odds further.
-
Eating a Western diet permanently affects insulin production and blood sugar control even after the diet is changed and weight is lost. The new research suggests that early intervention is needed to prevent permanent damage from diet-related obesity.
-
Swedish scientists have demonstrated a new potential way to manage diabetes, one of the most pressing health problems of our time. It turns out the eye might be a useful place to implant insulin-producing cells to control blood sugar levels.
-
Does early childhood exposure to a broad variety of bacteria make one less likely to develop allergies? A new animal study challenges this popular idea, finding diverse microbial exposure when young may have little effect on allergic immune responses.
-
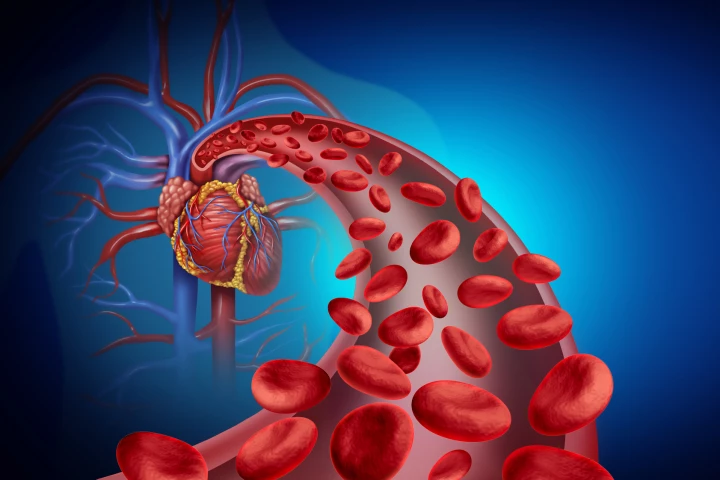
Researchers have found that red blood cells have an innate ability to trigger a pathway that protects the heart from injury during periods of low oxygen, such as during a heart attack. The discovery could lead to new drugs that activate this pathway.
-
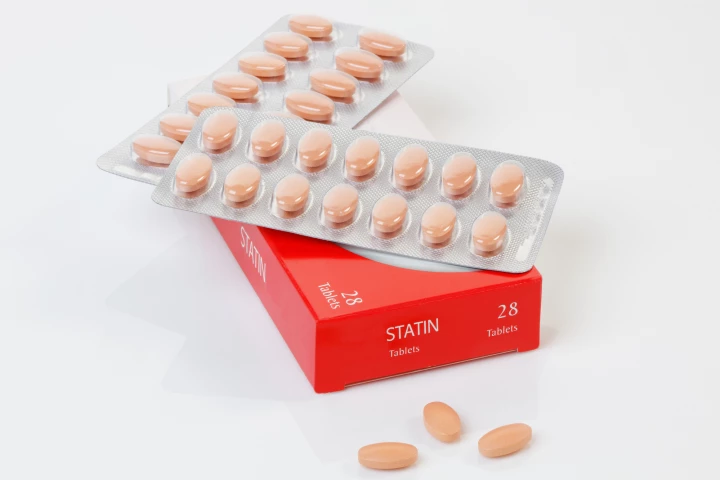
A new study has found that people with ulcerative colitis who take cholesterol-lowering statins have less chance of developing colorectal cancer. The commonly drug could be used as a preventive for cancer in cases of inflammatory bowel disease.
-
Researchers have found that antioxidants like vitamins C and E trigger a mechanism that stimulates the growth of new blood vessels in cancer tumors, helping them to grow and spread. They say it highlights the risk of taking unnecessary supplements.
-
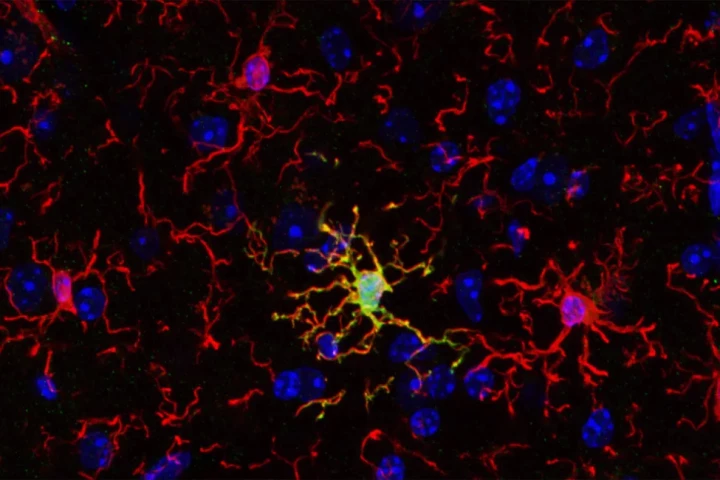
A new study has identified a subset of microglia, the brain's immune cells, and their important role in brain development and cognition that could pave the way for new treatments for neurodegenerative conditions like Alzheimer’s disease.
-
In new research, the presence of a blood-based sugar molecule helped predict the onset of Alzheimer's up to a decade before symptoms appeared. The protocol could join others in spotting the condition early and slowing its progression.
-
The health benefits of caffeine have been studied for years. Researchers have examined the genes associated with caffeine metabolism to see whether blood caffeine levels affect body fat levels and risk of type 2 diabetes and cardiovascular disease.
-
Scientists investigating the way a certain type of fat behaves in response to cold have made a discovery that could have ramifications for cancer treatment, showing how tumor cells can be starved of a vital fuel source they need to thrive.
-
Diabetes can result from a loss of cells that produce insulin. Swedish researchers have now identified a molecule that helps stimulate the growth of new insulin-producing cells, and uncovered how it works, opening up new potential diabetes treatments.
Load More