kidney
-
Harnessing the power of a metabolite produced in the kidneys and absorbed from certain foods can mimic the health benefits delivered by exercise, regulating inflammation and promoting an array of anti-aging processes without any physical activity.
-
If you have an aversion to the bitterness of foods like cabbage or broccoli, you might be a "super-taster," carrying a specific genetic code that dials up taste sensitivity. It may also put you at higher risk of kidney disease and bipolar disorder.
-
The treatment of kidney stones could soon be getting much faster, easier, and safer. Scientists have devised a method of non-invasively tearing the objects apart, using what are known as "acoustic vortex beams."
-
Be it for weight loss, cell repair, inflammation or heart health, superfoods and supplements were in the scientific spotlight. Emerging evidence suggests some are more than just wellness hype, while others came with some serious health warnings.
-
If you've never heard of fox nuts, you'd be forgiven for assuming that they don't seem particularly palatable. But they're actually starchy seeds harvested from an aquatic lily that boast vast health benefits. And no foxes are harmed in the process.
-
Not getting the optimal amount of sleep increases the risk of damage to small blood vessels in the eyes and kidneys of type 2 diabetics, new research has found. The findings suggest addressing this risk factor could prevent long-term complications.
-
A lengthy trip to Mars, which exposes astronauts to a combination of cosmic radiation and weightlessness, could result in permanent kidney damage, according to a new study. It's the largest analysis to date on how spaceflight affects kidney health.
-
Semaglutide, better known as Ozempic and Wegovy, has added another string to its therapeutic bow. A recent international clinical trial found that it significantly reduced the risk of kidney failure and death in type 2 diabetics with chronic kidney disease.
-
The first successful transplant of a genetically modified pig kidney into a human recipient is still being regarded as a medical milestone and success – even though the recipient, Rick Slayman, suddenly passed away over the weekend.
-
14% of American adults are affected by chronic kidney disease – and anyone in that category should be very careful about how much watermelon they eat. A new series of case studies examines how a favorite fruit can cause life-threatening issues.
-
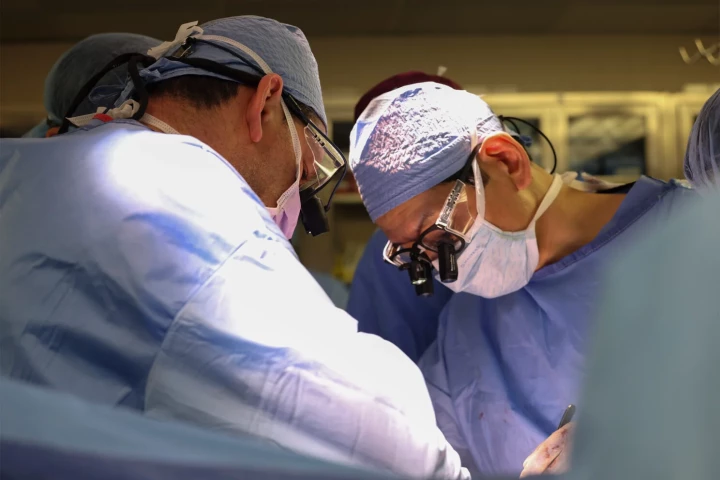
A genetically edited pig kidney has been successfully transplanted into a living patient for the first time. Reports indicate the man is doing well a few weeks on, raising hopes for a wider pool of donated organs in future.
-
Researchers have identified a novel inhibitor drug that, when given to mice, prevented both eye and kidney complications commonly seen in diabetics. Further research is being done to advance the drug to clinical trials.
Load More