Mice
-
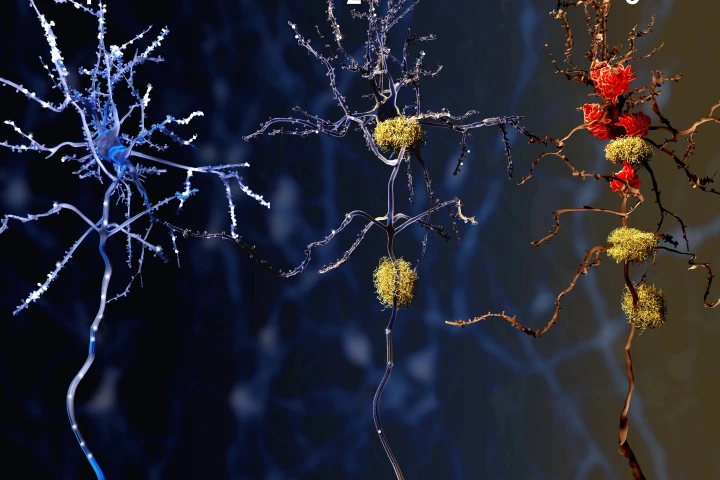
Taking inspiration from the CAR T-cell technology used to provide personalized cancer treatments, researchers have conducted a proof-of-concept study showing how similar compounds can precisely target protein tangles and plaques in the brain.
-
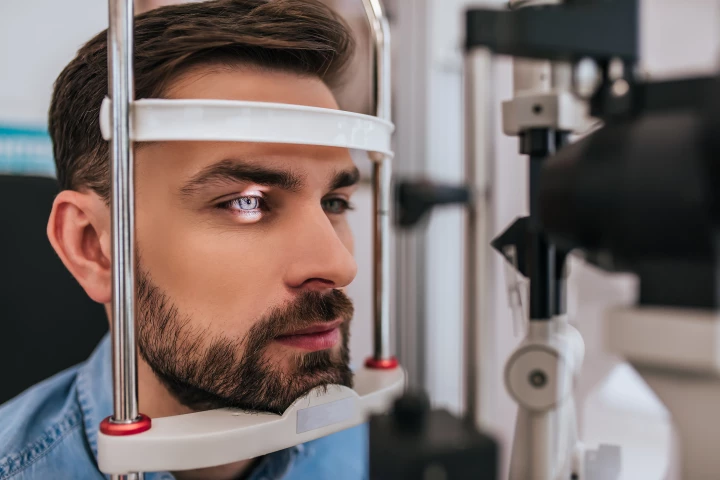
A breakthrough treatment has allowed damaged retinal cells to regenerate themselves. The current research has been conducted on mice, but the pathways are the same in humans, which opens hope for a new way to treat certain kinds of blindness.
-
A surprising finding from researchers in Japan has shown how an environmental factor can influence the development of sex organs in unborn mice. The discovery challenges the longstanding belief that sex is determined purely by genetic factors.
-
You might not hear it, but rodents are known to speak to each other in voices so high-pitched that human ears can’t pick them up. Now scientists have found that these vocalizations might have a second purpose – they help them smell better.
-
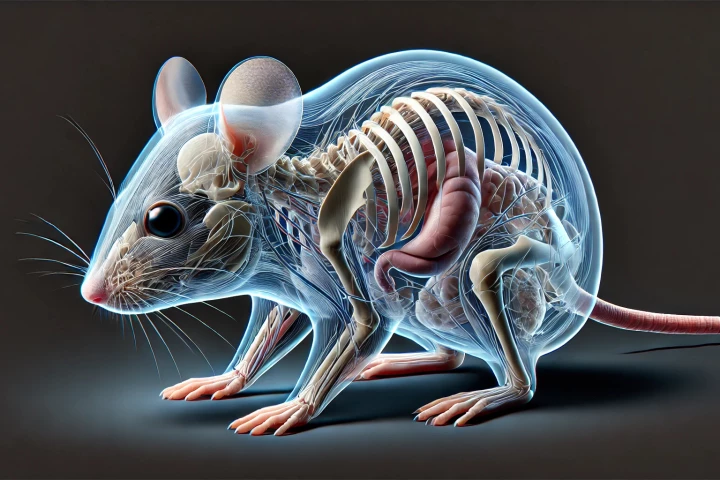
In an effort to enhance the research abilities of biologists, Stanford University researchers have discovered that applying a popular food coloring to the skin of mice allowed them to see through to the rodents' internal organs and other structures.
-
A new study from MIT has revealed the exact mechanism by which fasting causes intestinal stem cells to regenerate, which is one of the practice's benefits. However, the study also showed a downside that needs to be considered when breaking a fast.
-
For the first time, scientists have successfully created a mouse with a 100% functional human immune system and microbiome. This 'humanized' mouse takes the guesswork out of research and may revolutionize how we test new drugs and understand diseases.
-
RFID cat flaps are great for keeping animals from wandering into your house, but they don't stop your cat from bringing dead animals into said dwelling. The ZeroMouse was designed to address that shortcoming, by blocking access to cats carrying prey.
-
Normally, staying up for extended time periods leads to the need for extra sleep. But researchers have just found that activating astrocyte cells in mice caused the rodents to stay awake for six hours longer than usual, with no noticeable sleep debt.
-
In a glimpse of what could become a future Black Mirror episode, scientists have hooked the circulatory systems of old mice to young mice, and found that it slows the aging process in the older animals and increases their lifespan by up to 10%.
-
We’re getting closer to being able to induce hibernation on demand in humans for surgery or space travel. Scientists have now demonstrated a way to induce a hibernation-like state in mice and rats using non-invasive ultrasound pulses to the brain.
-
By digging up and eating sown wheat seeds, mice can have a huge impact on farmers' crops. In an eco-friendly effort to stop the rodents from doing so, scientists are now using wheat germ oil to make entire fields smell appetizing.
Load More