Nagoya University
-
In a breakthrough, scientists have transferred a courtship behavior from one species to another, triggering the recipient to perform this completely foreign act as if it was natural. It's a feat that has never been genetically engineered before.
-
Researchers have found a genetic link between the nighttime production of the sleep hormone melatonin and ADHD severity in children. The study enhances our understanding of the complexities associated with this prevalent neurodevelopmental condition.
-
For ages, Earth has been known as a blue planet, a vision largely shaped by the vast oceans that cover three-quarters of its surface. But what if this wasn't always the case, and our oceans used to be green?
-
Nobody likes being carsick, seasick or airsick, but what can you do to keep from getting that way? Well, according to a new study, simply listening to an audio tone for one minute might be all it takes to stop you from losing your lunch.
-
Japanese scientists have created what may be the world’s smallest video game. Using a regular controller, players can control a tiny digital ship, firing nanoscale bullets to push around a physical polystyrene ball just a few microns wide.
-
A change in shape to a particular structure of neurons was found to have a significant impact on obesity in rats. Researchers believe the finding will translate to humans and could help us fight our own middle-aged bulges one day.
-
A study has found that an electric eel’s discharge is strong enough to transfer genetic material from the environment into the cells of nearby animals. The finding suggests that electric eels could affect genetic modification in nature.
-
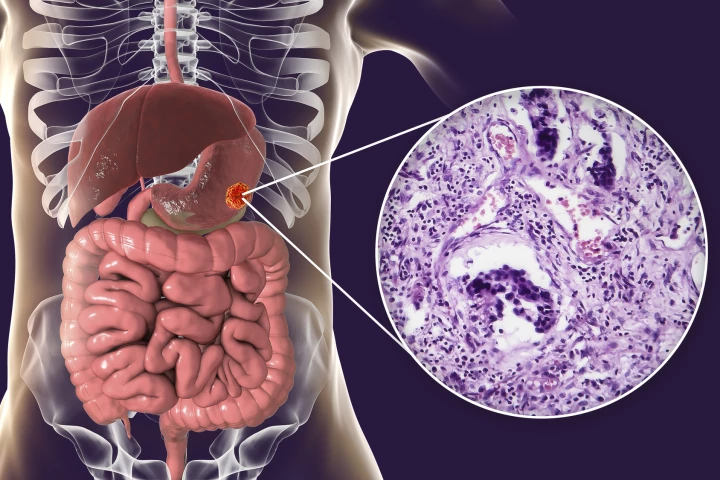
Researchers have identified a blood protein that can diagnose gastric and other cancers and is more accurate than existing biomarkers, even in the early stages of the disease. It may lead to the earlier diagnosis of these often stealthy cancers.
-
Delivering electric shocks to 1mm-long roundworms may sound rather meanspirited, but scientists have used this stimuli to uncover some curious behaviors of C. elegans that could further our understanding of human emotional mechanisms.
-
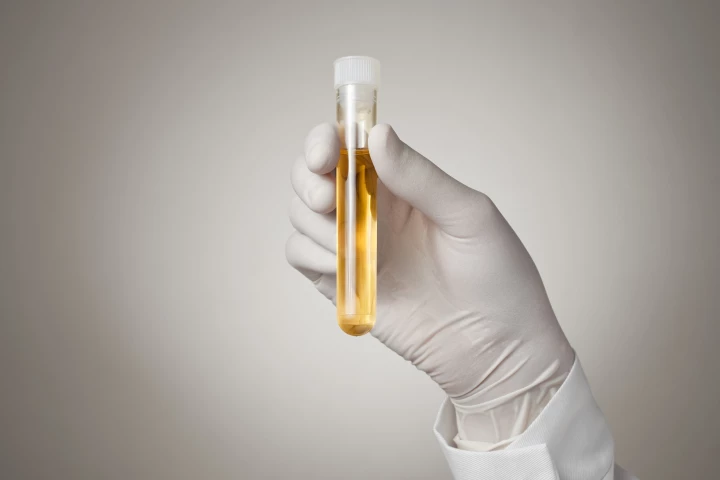
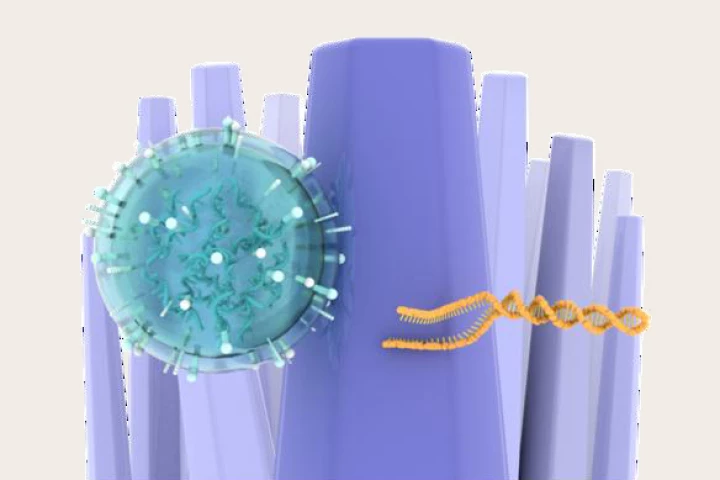
Researchers have used nanowires to ‘catch-and-release’ DNA in urine, enabling them to detect mutations that signify the presence of a brain tumor. Their method may one day mean that invasive tissue biopsies are no longer required.
-
For now, quantum computers are mostly limited to labs and big experimental setups. But Japanese researchers have now made a step towards more accessible quantum computing devices, finding a way to “twist” light at room temperature.
-
Scientists at Japan's Nagoya University have demonstrated how brain tumors might be detected far earlier, leading to better outcomes for patients, through a simple urine test that has shown high accuracy in early experiments.
Load More