U.S. National Institutes of Health (NIH)
-
Children with high-threshold peanut allergies showed incredible improvements after undergoing an 18-month program using store-bought peanut butter to desensitize them. The approach could help nearly a million kids with this type of allergy.
-
CRISPR systems are powerful tools for genetic engineering, but they have their limitations. Now, scientists have discovered almost 200 new CRISPR systems in bacteria, and found that some can edit human cells even more precisely than existing ones.
-
A new study has found that specific regions of the brain are activated after a drug is taken intravenously but not when the same drug is taken orally. The findings could lead to new treatments for addiction.
-
A new study has investigated the biological mechanisms brought about by calorie restriction and found that a moderate reduction in calorie intake can improve muscle health and activate biological pathways important for good health.
-
It may seem like snail's pace compared to our COVID-19 vaccines, but the wheels are certainly turning in the development of a universal mRNA influenza vaccine. The latest has just entered trial, with many others at the same stage or even further along.
-
Autism spectrum disorder (ASD) symptoms generally appear in the first two years of a child’s life. A new study has found that toddlers’ visual attention to geometric images is a reliable biomarker for the early identification of autism.
-
According to a recent large, multi-country clinical trial, the risk of postpartum sepsis and death in women who plan to deliver vaginally can be reduced by one-third by administering a single dose of the antibiotic azithromycin.
-
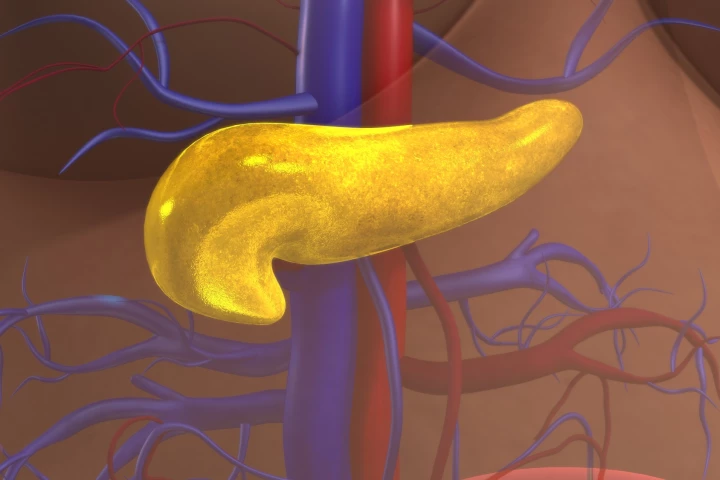
A large-scale genetic analysis has revealed microRNAs in human pancreatic cells strongly associated with type 2 diabetes (T2D). The results can be used in future research into how the condition develops and how it can best be detected and treated.
-
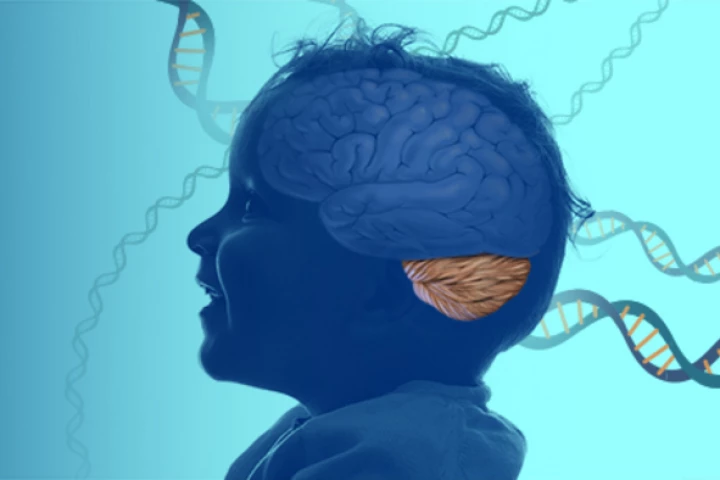
A neurological disorder affecting speech and coordination has been identified in three children. It is believed the condition is caused by a genetic mutation that affects the ability of neurons to carry out autophagy, a cellular recycling function.
-
In a blow to researchers across the world, the only HIV vaccine currently in Phase 3 human trials has been deemed a failure. The experimental vaccine's failure turns the current research focus onto several other candidates only in early-stage human trials.
-
In the most comprehensive autopsy tissue study conducted to date, researchers have found traces of SARS-CoV-2 throughout the entire body, from the brain to the heart. The findings support research into antiviral drugs as possible treatment for long COVID.
-
In the first big real-world test for monoclonal antibodies against malaria a new study has reported extraordinarily promising results, with a novel therapy found to be 88.2% effective at preventing infections across a six-month period.
Load More