Oxford University
-
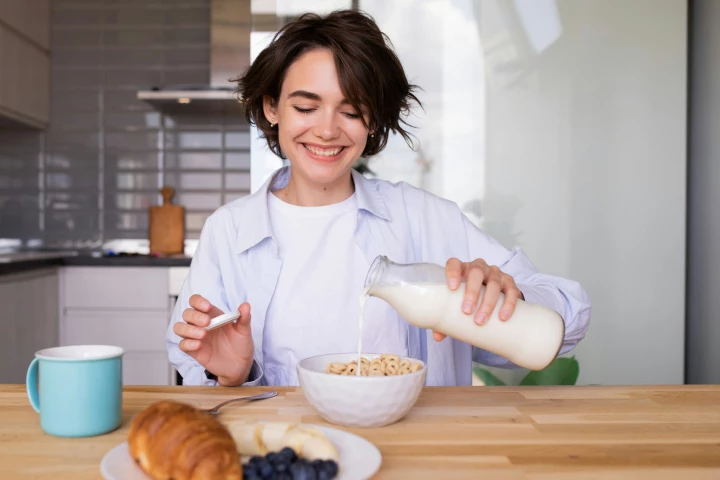
In what they've confirmed as the largest study looking at the effects of diet on rates of colon cancer, researchers in the UK say that calcium-rich foods offer significant protections against the disease. Alcohol and red meat? Not so much.
-
Individuals who suffer head trauma from sports, accidents, or other causes often go on to develop neurodegenerative diseases like Parkinson's or Alzheimer's. A new study sheds light on why that might be and offers a way to prevent it.
-
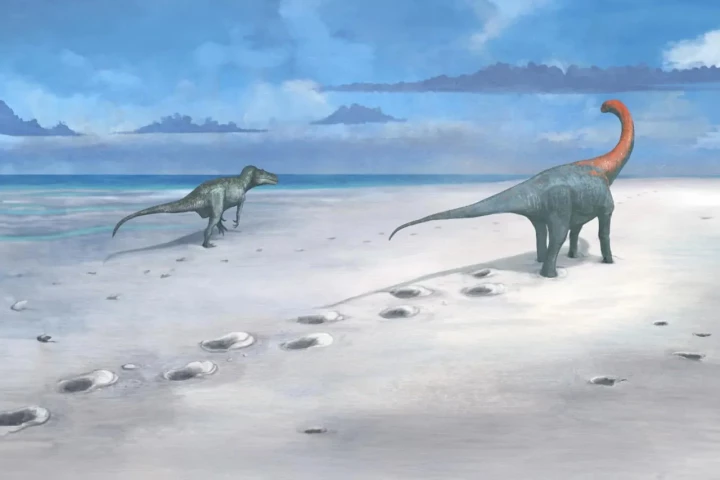
A quarry in South East England has yielded a fascinating paleontological discovery: long tracks with a total of 200 footprints left by enormous dinosaurs that roamed the earth during the Middle Jurassic Period, some 166 million years ago.
-
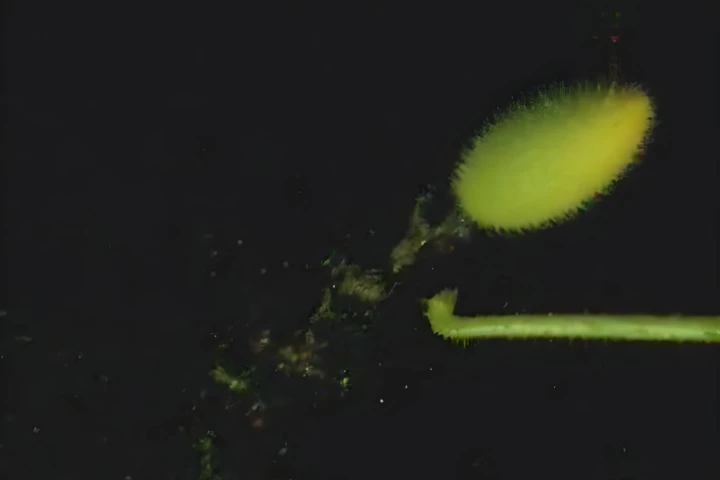
Unlike nearly all flowering plants, which rely on the likes of wind or animals to reproduce, the squirting cucumber instead uses "ballistic seed dispersal," shooting a forceful, watery jet more than 30 feet into the air. And now we know how it does it.
-
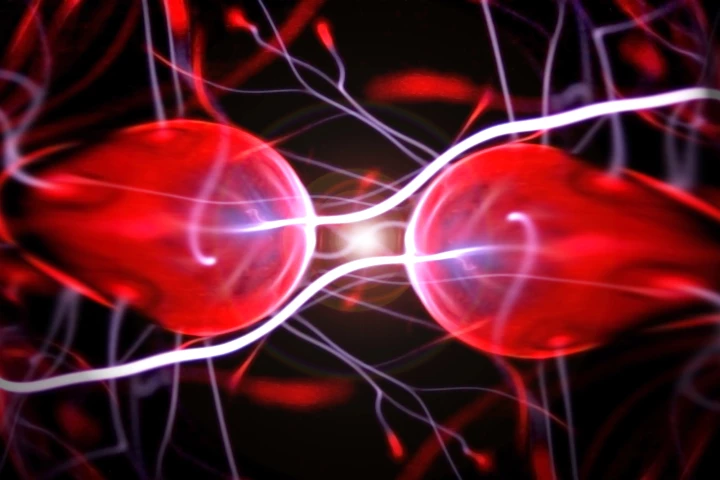
It’s a fundamental principle of physics that particles with opposite charges attract each other, while those with the same charge repel. Scientists have now discovered that under certain conditions, particles can attract those of the same charge.
-
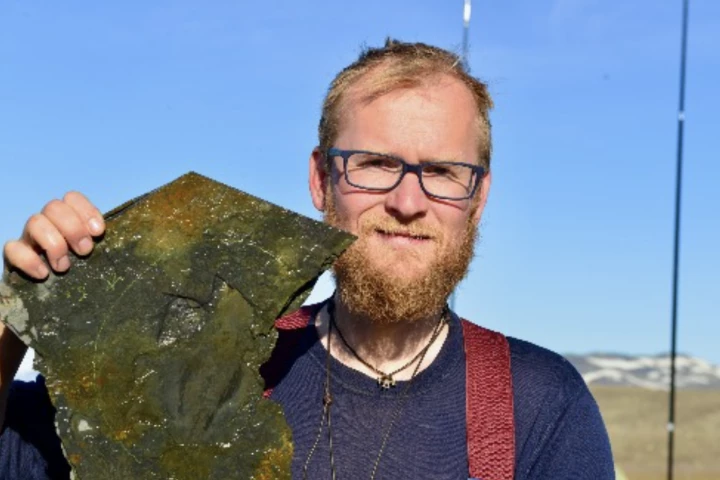
Scientists have uncovered a new huge predatory worm species thought to have hunted in the Earth’s water column around 518 million years ago. They also believe this worm, whose name means terror beast, was one the earliest carnivorous swimming animals.
-
Time capsules are a fun way to get a glimpse into life in the past, and now scientists have opened one from almost 3,000 years ago. The team successfully extracted DNA from inside an ancient clay brick, revealing the area's ecosystem at the time.
-
Scottish woman Jo Cameron is a medical marvel who feels little pain, fear or anxiety, and had faster wound healing, thanks to a specific gene mutation. Now, scientists have studied why in more detail, in the hopes of unlocking future drug targets.
-
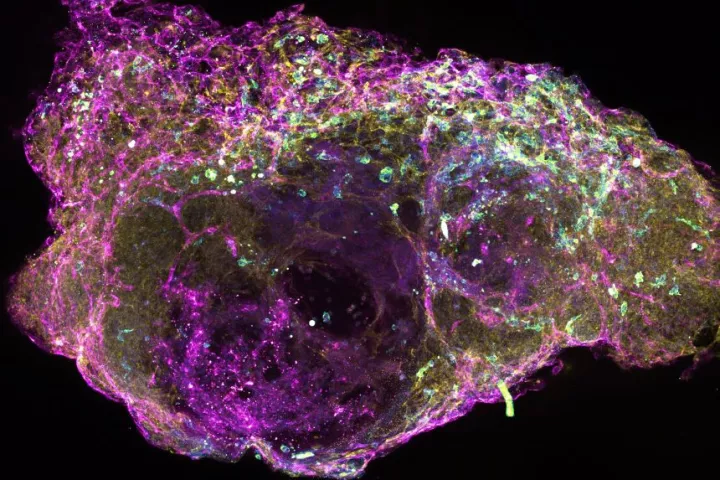
Researchers in the UK have developed first-of-a-kind bone marrow “organoids” in the lab that bear the key features of the real thing and which the team hopes can lead to a new breed of bespoke treatments for cancer.
-
University of Oxford physicists have linked two atomic clocks through quantum entanglement for the first time. The feat can help make these clocks so precise that they begin to approach the fundamental limit of precision set by quantum mechanics.
-
A comprehensive new Oxford study has added to the growing body of research highlighting the health effects of alcohol. The large-scale genetic analysis suggests that alcohol consumption directly accelerates aging, by shortening telomeres.
-
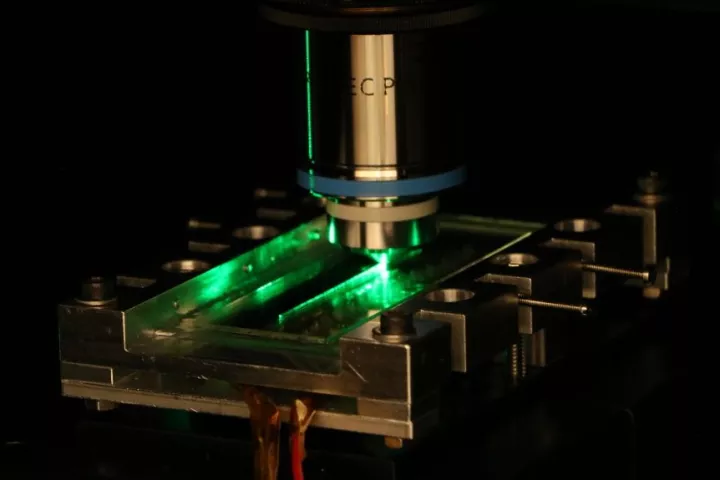
Scientists have developed a sensor made of incredibly thin strands of sapphire that can withstand extreme heat and radiation, and possibly be put to work in the harsh environment of nuclear fusion reactors and enable more streamlined air travel.
Load More