peptide
-
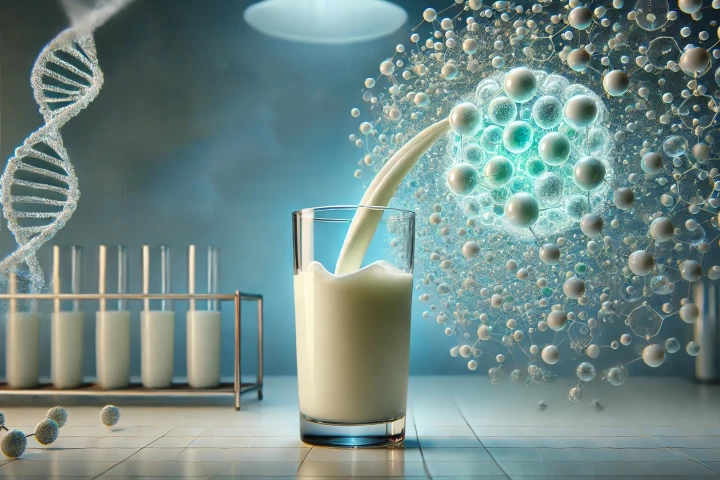
A couple of University of Nebraska professors have launched a startup company with the goal of bringing to market an innovative method for delivering drugs and other therapeutics to targeted locations in the human body. The key ingredient? Milk.
-
Using DNA and proteins, scientists have created new synthetic cells that act like living cells. These cells can be reprogrammed to perform multiple functions, opening the door to new synthetic biology tech that goes beyond nature’s abilities.
-
Researchers have developed a peptide that targets a protein implicated in 75% of human cancers and found that it slowed the proliferation of cancer cells in the lab. It’s the first step towards developing an effective treatment for a range of cancers.
-
Peptide therapeutics – like insulin – are typically restricted to administration by invasive injection. Now, researchers have reached a "major milestone", creating an oral peptide that could revolutionize how disease treatment is delivered.
-
Imagine being able to take a peptide that could stave off obesity, reverse osteoporosis and combat inflammatory and cardiovascular issues? Scientists have made the first step, discovering how a key protein communicates cell shape changes with the brain.
-
In the neverending human-vs-virus battle, scientists often focus on disrupting the protein coating on the bugs. New research shows an alternative: using certain compounds to act as molecular "pins" that pop the membranes holding viruses together.
-
Researchers have developed a highly efficient new gene-editing method that uses virus-based protein fragments. The method could be used to level up existing cell and gene therapies used to treat cancer and other diseases.
-
One of the most profound mysteries facing science is how exactly life arose from non-living matter. Now, scientists have pinpointed a particular peptide that potentially kickstarted life – and it could all be nickelback’s fault.
-
Bacteria are fast developing resistance to our antibiotics, potentially ushering in a new “dark age of medicine” where basic infections become lethal again. Now scientists have developed self-assembling “nanonets” that can trap and kill superbugs.
-
In frontotemporal dementia and motor neuron disease, nerve cells are attacked and killed off, leading to the fast progression of the degenerative conditions. Now, a novel breakthrough might be able to stop this process without invasive surgery.
-
It's always good if the use of antibiotics can be avoided, to keep harmful bacteria from developing a resistance to them. A new wound-treatment spray could help, as it kills bacteria using peptides that occur naturally in our bodies.
-
Instead of injections or pills, why not engineer bacteria to secrete therapeutic molecules from within our gut? A new study is showing how a genetically modified probiotic can produce an anti-inflammatory molecule to treat rheumatoid arthritis in rats.
Load More