Regeneration
-
Heart attacks are dangerous not just because of the initial event, but the long-term damage afterwards. Now scientists have discovered a dormant gene that could be reactivated to regenerate heart tissue, preventing the progression to heart failure.
-
The body has a remarkable ability to heal injuries, but it has its limits. Now scientists have developed a way to improve on the natural process, making implants created from a patient’s own blood to regenerate injuries, even repairing bone.
-
A surprise result in a lab experiment has led to the discovery of an ancient biological stress pathway that triggers cells to stop making what's needed to grow hair. Blocking this process could protect follicles from this process and prevent hair loss.
-
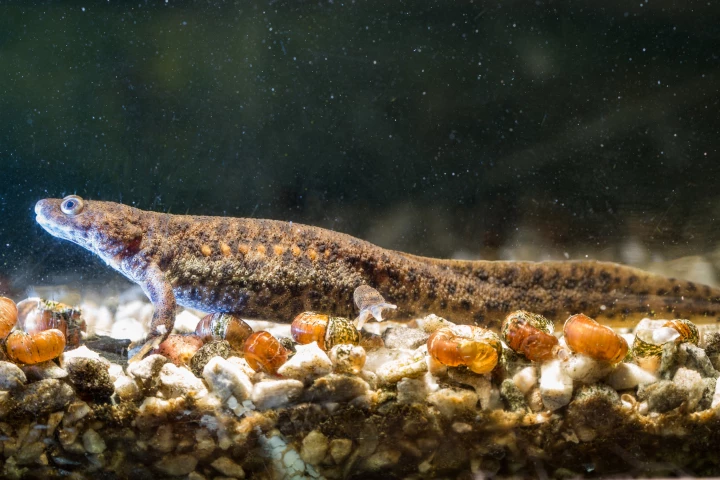
It might sound like something out of the X-men but it came from a lab in California: mutant newts that grew perfect limbs after defective appendages were cut off. The findings help science get one step closer to understanding how regeneration works.
-
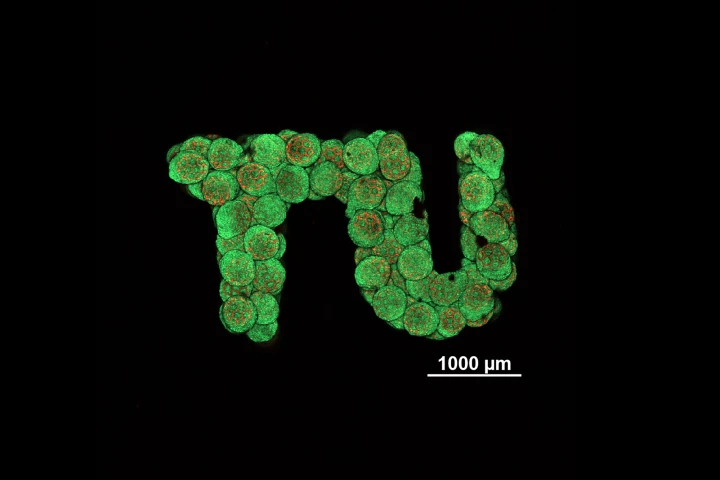
Researchers at TU Wien have developed a new way to grow cartilage from stem cells and guide it into basically any shape required. The breakthrough could lead to better ways to patch up injuries.
-
Heart tissue normally can't regenerate after an injury. But now, scientists at Max Planck have shown in mice that reprogramming the energy metabolism of the heart allows it to regenerate after a heart attack, which could open new therapies.
-
A complete spinal cord injury results, tragically, in total paralysis of all limbs and muscles below the injury site. But now, scientists at EPFL have demonstrated in mice a new gene therapy that can regenerate nerves and restore the ability to walk.
-
Scientists at Daegu Gyeongbuk Institute of Science & Technology (DGIST) in South Korea have developed a novel bioelectric therapy that restored muscle cells in aging mice, and they’re confident of its promise to have a similar effect in human models.
-
A new technique may one day help restore sight to patients with inherited vision impairment. The regenerative therapy works by expressing genes that convert dormant cells into new light-sensing cells in the retina to replace those lost to disease.
-
An international team of scientists has found a way to regenerate kidneys damaged by disease, restoring function and preventing kidney failure. The discovery could help improve treatments for complications stemming from diabetes and other diseases.
-
A torn meniscus, the cartilage in the knee, is a common sports injury, and unfortunately it doesn’t heal well. But researchers in Japan have now identified a hormone that helps repair the cartilage after a surgical treatment.
-
Researchers have demonstrated a new technique for helping heart cells regenerate after a heart attack, using mRNA to return the cells to a stem-cell-like state. Tests in mice showed drastic improvements to heart function a month after a heart attack.
Load More