RNA
-
After two decades in the making, scientists have cracked the code on a drug that can repair DNA, setting the scene for a new class of therapeutics that can fix tissue damage that occurs through heart attack, inflammatory disease and other conditions.
-
Scientists have sequenced RNA from a nearly 40,000-year-old woolly mammoth leg, the oldest ancient RNA ever recovered. These fragile molecules could reveal which genes were active in the animal’s final hours.
-
The preserved lung of an 18-year-old Swiss man has been used to create the full genome of the 1918 "Spanish flu," the first complete influenza A genome with a precise date from Europe, offering insights into the pandemic that claimed up to 100 million lives.
-
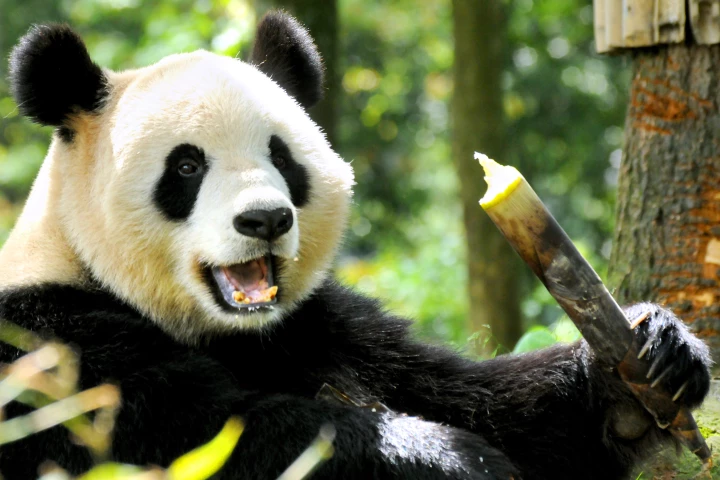
Built to be carnivorous, giant pandas spend up to 16 hours a day on their backsides eating bamboo. But contrary to all the panda jokes, it's not because they're lazy or too dumb to know better. It's far more fascinating – and it may help humans, too.
-
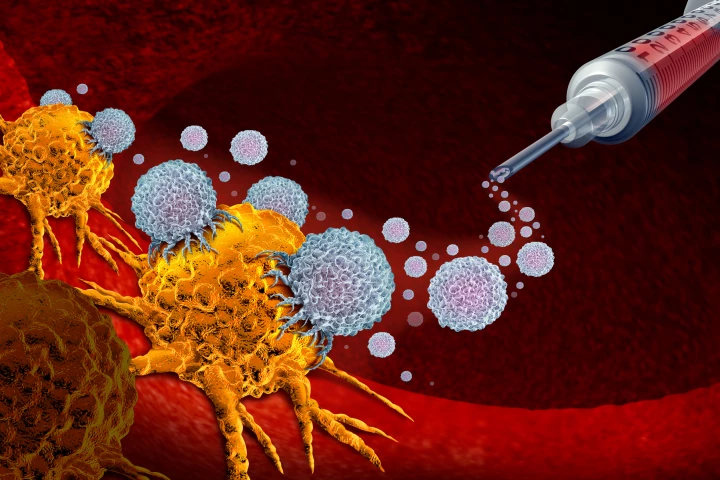
Engineered mRNA has turned cells into tiny biofactories, producing medications to successfully treat an inflammatory skin condition and two types of cancer, according to a new study. The tech paves the way for therapies in which patients’ bodies make their own drugs.
-
Glioblastoma is one of the most deadly cancers, with few treatment options available. Now, a small human clinical trial has demonstrated an mRNA vaccine that quickly rallies the immune system to fight off the tumors, with promising results.
-
Cow’s milk contains nanoparticles that can be used to deliver RNA therapy orally, say researchers. With such drugs currently only administrable by injection, the discovery opens the door to cheaper, more accessible treatments for a range of diseases.
-
A man that police caught taking 217 doses of COVID vaccine has offered himself up to researchers for a study looking into what happens to the immune system after so many doses. The results offer surprising insight into these new mRNA vaccines.
-
Our bodies are home to trillions of microbes, including bacteria, viruses, fungi, and a whole host of others. Now, Stanford scientists have discovered an entirely new class of biological entities inside us, which they’ve ominously named “Obelisks.”
-
Researchers have created a ‘two-headed’ drug that prevents the production of the toxic protein linked to Parkinson’s disease before destroying the RNA machinery that makes it. The drug may be a way of slowing or even stopping the disease’s progression.
-
Moderna has announced results of a Phase 2b trial of its mRNA treatment for skin cancer. When paired with immunotherapy, the treatment significantly reduced risks of recurrence, metastasis and death, paving the way for trials against other cancers.
-
Researchers have discovered that mice possess a natural form of gene therapy, a non-coding RNA that can sidestep genetic mutations. They were able to engineer a programmable version that might be used to treat genetic diseases in humans.
Load More