Stanford University
-
Although they're constantly improving, robots aren't necessarily known for their gentle touch. A new robotic system from MIT and Stanford takes a unique stab at changing that, with a robot that uses vine-like tendrils to do its lifting.
-
A new “audio shield” uses earbuds connected to hand-mounted microphones for hearing the subtle sounds of everyday tasks. The mechanism helps users block the perpetual hurricane of distractions and achieve mindfulness, reducing the effects of ADHD.
-
Scientists have found the clearest evidence yet that Epstein-Barr virus – which nearly all of us carry for life – is directly responsible for hijacking our immune system's cells to cause lupus, a chronic disease that affects up to a million Americans.
-
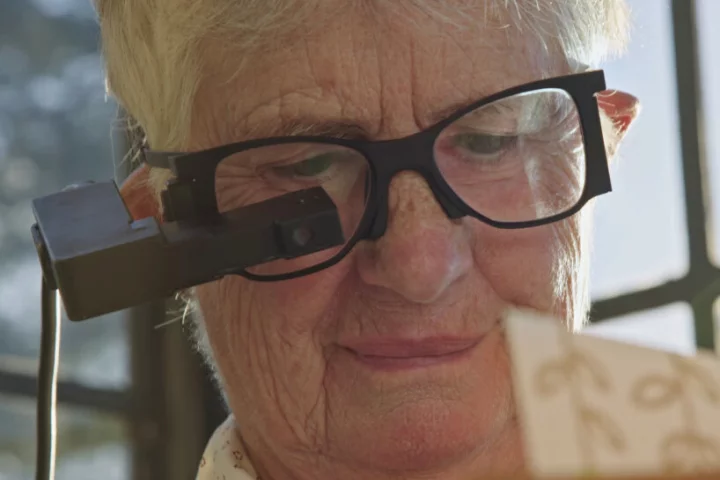
Stanford researchers and global collaborators have developed a wireless retinal implant called PRIMA that's helping people with untreatable eyesight loss see not just light, but actual shapes and patterns – what scientists call form vision.
-
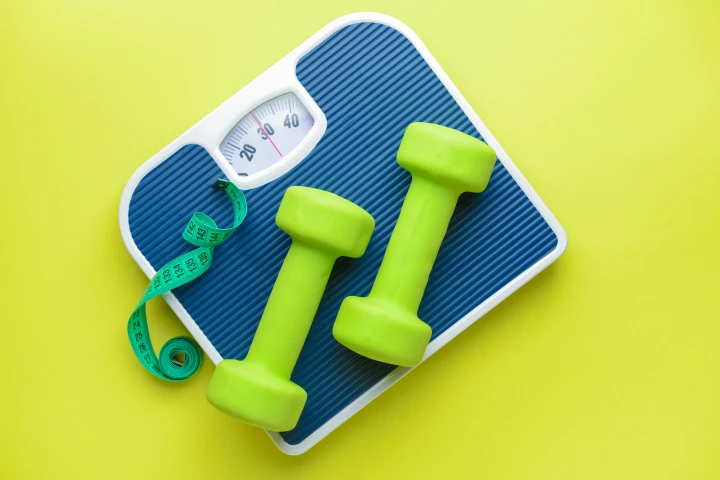
Scientists have found out exactly how an exercise-triggered molecule suppresses hunger signals in the brain, leading to weight loss. It could be harnessed as a therapeutic, providing the same benefit without the work it takes to produce it naturally.
-
It's an inconvenient fact that many drugs have to be administered in the form of a slow intravenous (IV) drip, as opposed to a single quick injection. That may be about to change, however, thanks to a new take on an existing "spray drying" technique.
-
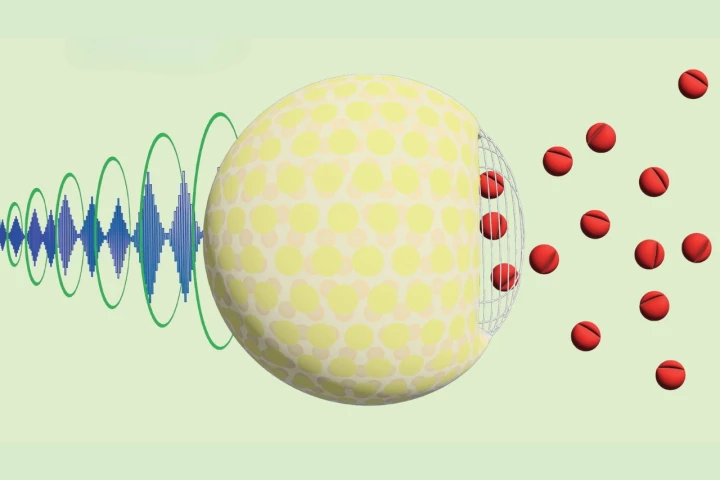
How do you send drugs to specific parts of the body so they do their job and avoid causing side effects elsewhere? According to researchers at Stanford University, the answer is a combination of nanoparticles, a pulse of ultrasound, and sugar.
-
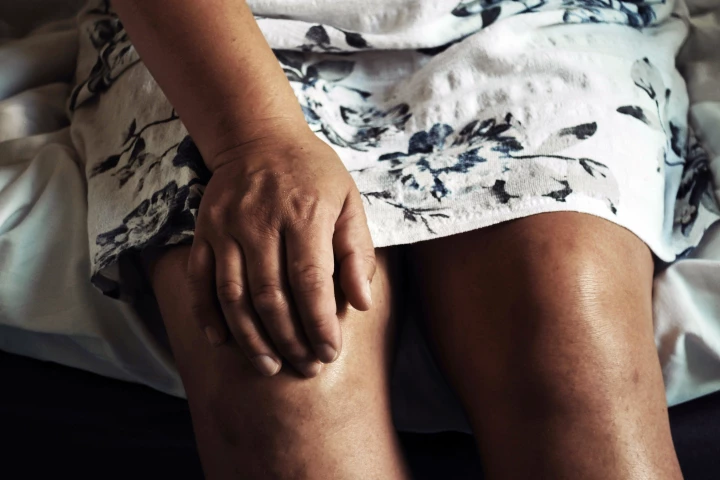
A subtle tweak in the way you walk – putting your toes in or out by a few degrees – could ease knee osteoarthritis pain and slow joint damage, according to new research that found personalized gait retraining can reduce strain on vulnerable cartilage.
-
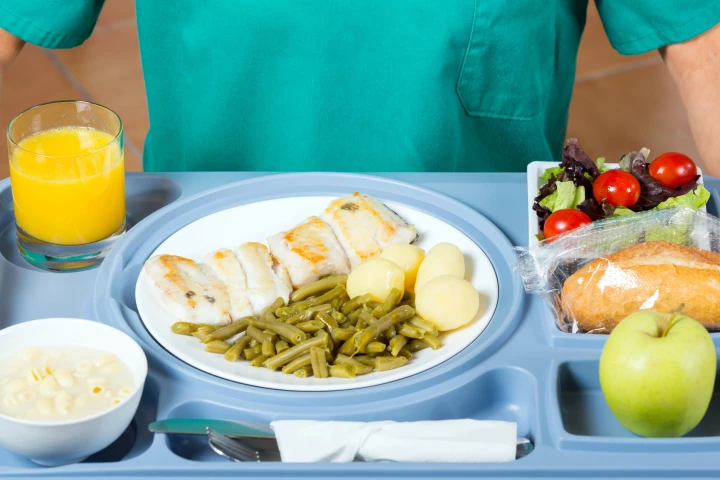
Hospital meals have long been the butt of jokes, but new research shows they might actually pose a health risk, with low-quality diets failing to meet basic nutrition standards in hospitals and nursing homes.
-
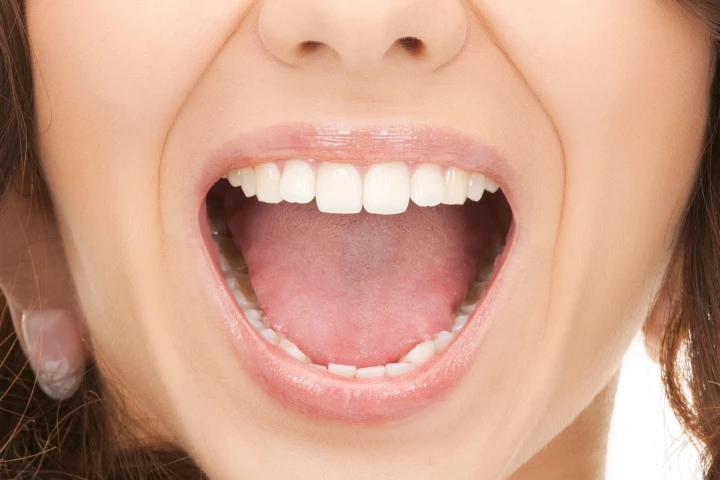
We all know that injuries inside the mouth heal quicker than those on the outside of the body. Scientists have a new understanding of why, and believe that their findings could be used in wound treatments that reduce or even eliminate scarring.
-
More than a third of large animals that feast on dead animals are struggling to survive, and a new report from scientists warns that their downfall could present a serious risk to human life, with an uptick in zoonotic disease spread as a result.
-
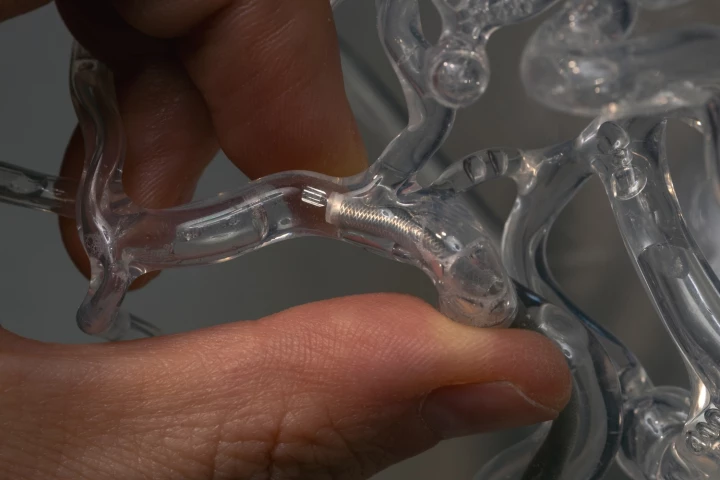
When trying to remove life-threatening clots from blood vessels, current technologies are successful on only about half of the first attempts – if at all. A new surgical tool, however, is claimed to boost that figure to an astounding 90%.
Load More