Stanford University
-
More than a third of large animals that feast on dead animals are struggling to survive, and a new report from scientists warns that their downfall could present a serious risk to human life, with an uptick in zoonotic disease spread as a result.
-
When trying to remove life-threatening clots from blood vessels, current technologies are successful on only about half of the first attempts – if at all. A new surgical tool, however, is claimed to boost that figure to an astounding 90%.
-
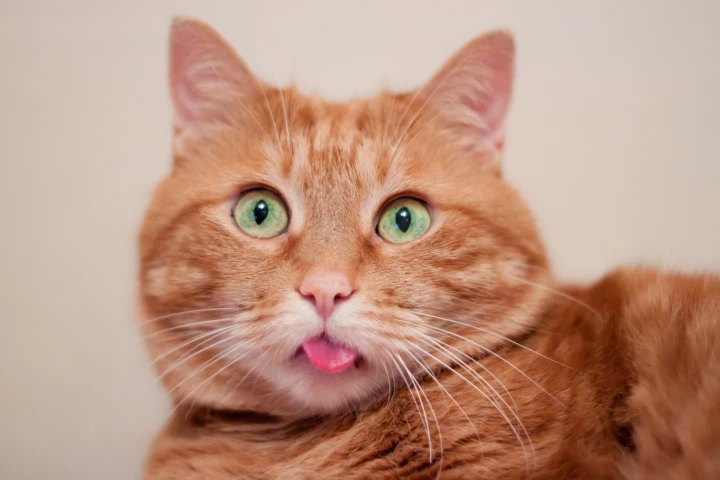
The existence of orange cats dates back to the 12th century, but the DNA driving this color has been a mystery – until now. Scientists have solved the puzzle, finding a surprise variant that triggers ginger fur, one not seen in any other orange animal.
-
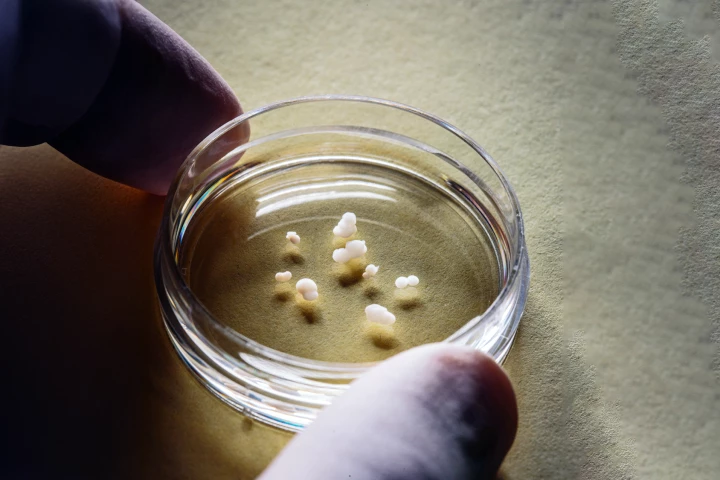
Tiny 3D organs connected themselves in a lab dish, forming a replica of the human pain pathway, in a new study. The discovery allows scientists to better understand chronic pain and offers an animal-free method of testing pain treatments.
-
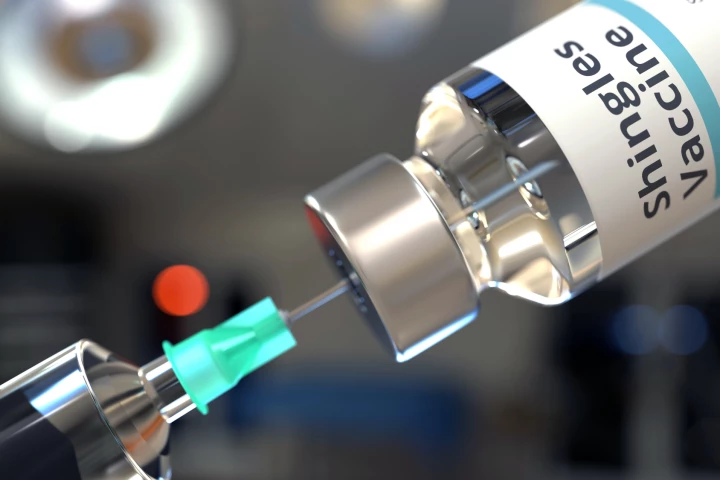
Taking advantage of a unique public health policy in the UK, a new study has found that receiving the shingles vaccine reduces dementia risk by 20%. The findings bolster growing evidence linking the vaccine to lower numbers of dementia cases.
-
Injection needles can be scary, and the larger ones for longer-term medications are far more intimidating. Researchers have created a better way to deliver drugs into patients' systems, and it involves turning those drugs into tiny crystals.
-
Dr. Frankenstein might not have needed a lightning bolt to bring his monster to life after all. A new study from Stanford suggests that life might have been kickstarted by constant zaps from “microlightning” between water droplets.
-
After screening 20,000 protein-encoding genes in the human body, Stanford researchers have identified a naturally occurring molecule that works like semaglutide, most popularly known as Ozempic, to put the brakes on appetite and weight gain.
-
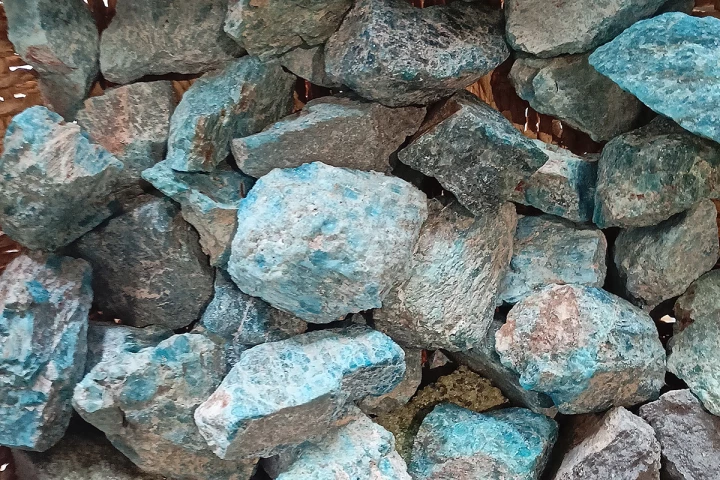
Stanford researchers have found a way to activate commonly found rocks so they capture CO2 out of the air at room temperature. The team believes it could be relatively inexpensive, and can easily scale to help sort our emissions problem worldwide.
-
HIV has become a more manageable condition in recent years, but a full cure remains elusive. Now, scientists have found promise in permanently eliminating the virus, thanks to a drug already approved by the FDA to fight cancer.
-
Brain-computer interfaces may allow paralyzed people to perform basic tasks, but there's more to life than eating and typing. That's where a new BCI comes in, as it has allowed a man to fly a virtual drone just by thinking of moving his fingers.
-
In order for a VR environment to seem real, it definitely helps if you can experience the sensation of touch within that virtual world. A special sleeve could soon allow people to better do so, using air instead of electric motors.
Load More