Testing
-
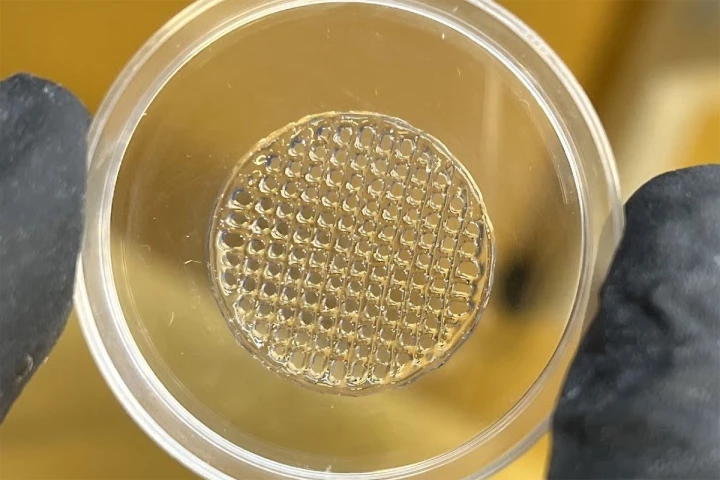
While we're making progress in phasing out animal testing in the cosmetics industry around the world, there's still a ways to go in developing reliable alternatives. 3D-printed 'imitation skin' could be the ticket.
-
China is now home to the world's most powerful centrifuge capable of creating artificial gravity. This facility will enable a range of experiments to help make sense of scientific phenomena, simulate geological events, and test new materials.
-
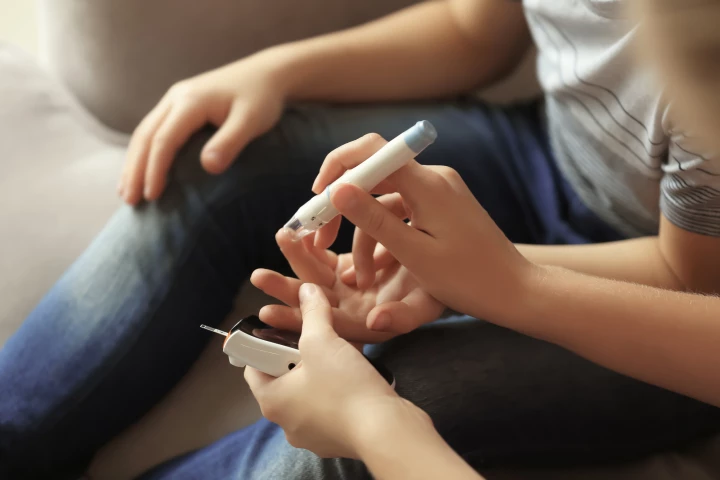
Daily finger-prick blood tests are an uncomfortable fact of life for diabetics, but they may not always have to be. Scientists from Canada and the US have developed a prototype home-use device that measures blood glucose levels via saliva samples.
-
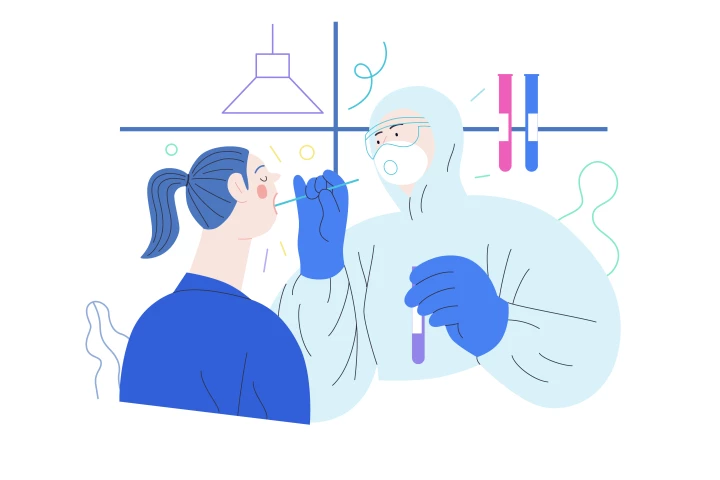
Sexually transmitted infections (STIs) are on the rise globally. A series of studies have found that testing for STIs in the privacy of your own home is accurate and could remove the stigma associated with maintaining sexual health.
-
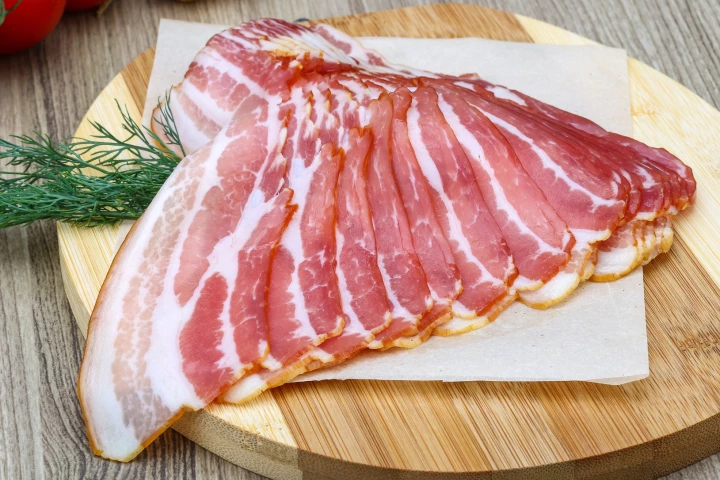
Sodium nitrite is often added to cured meats, in order to prevent spoilage and provide flavor. It can also cause health problems in large amounts, however, which is why a color-changing film has been created to indicate nitrite levels.
-
After developing a system that could detect 17 different contaminants in a drop of water, researchers have now added "molecular brains" to that setup so the hand-held device not only confirms contamination but also indicates concentration levels.
-
US researchers have developed an innovative smartphone-based kit that can test saliva samples for the presence of SARS-CoV-2 and influenza viruses. Early studies have found the cheap system is as accurate as current lab-based testing and much faster.
-
How do rapid antigen COVID-19 tests work? Why did the US government just pledge to buy 280 million of them? And is that even enough to help curb the spread of the virus?
-
In people with liver disease or other metabolic disorders, blood ammonia levels can quickly climb to dangerous levels. And unfortunately, checking those levels is not a fast and easy process. A newly developed device, however, could change that.
-
In the age of a global pandemic, some researchers are suggesting the current vaccine trial process is too slow, and to test potential COVID-19 vaccines we will have to deliberately infect healthy people.
-
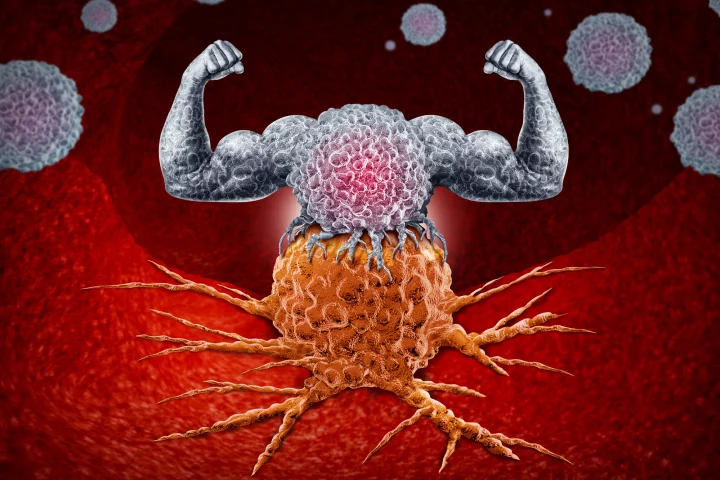
A novel form of cancer immunotherapy has shown exceptional promise in a new clinical trial, with 93 percent responding positively. The treatment involves supercharging a patient’s immune cells to fight cancer then reintroducing them to the body.
-
The James Webb Space Telescope has crossed another milestone on the path to its long-awaited launch. NASA engineers have now completed a deployment test, unfurling the telescope’s gigantic mirror into the configuration it will take in space.
Load More