UC Santa Barbara
-
Since the 1800s, civilization has been fascinated by the idea of capturing lightning in a bottle. Over time, the idea evolved from literal to figurative. Today, we may be seeing a reversal. Scientists may have figured out a way to "bottle the sun."
-
Could you imagine being able to "feel" the images on your screen? UCSB researchers have made this sci-fi-like idea a reality. They've developed a display where pixels physically rise off the surface when activated by laser light.
-
While 3D printing is a burgeoning technology, it's limited by the fact that items can only be printed from a single material. A new system still uses just one print resin, but that substance can form into two different solid materials as needed.
-
Genetic studies have revealed that when male mosquitoes lose their hearing, they also lose their sex lives. The surprising discovery could lead to new ways to reduce mosquito populations and the diseases they spread.
-
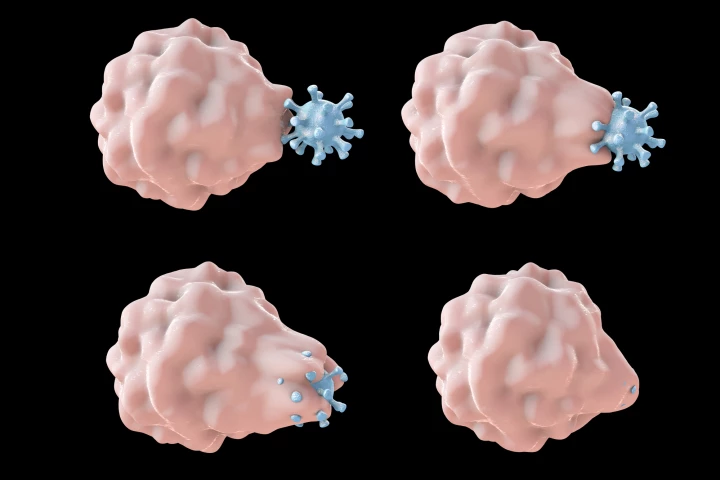
Researchers have found adding a hyperactive form of the protein Rac2 to macrophages, immune cells that eat pathogens, causes them to cannibalize T cells. The novel technique could potentially boost the effectiveness of an emerging cancer treatment.
-
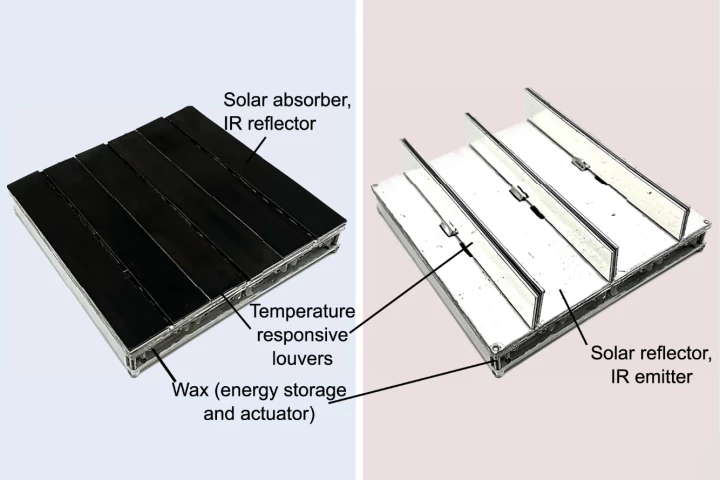
Using a temperature-driven "wax motor," researchers have created an adaptive roof tile system that helps keep a room at a comfortable 18 °C (65 °F). It delivers an extraordinary 3.1X reduction in cooling energy consumption, and 2.6X for heating.
-
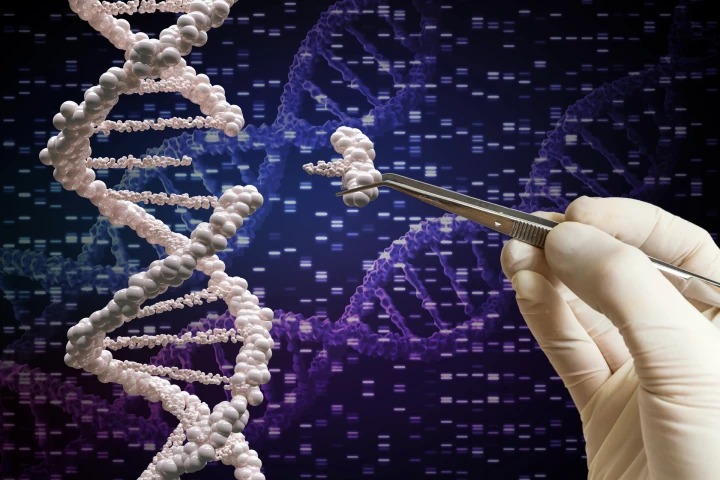
Modified viruses have proven a handy way to get CRISPR/Cas9 gene editing materials into the nucleus of cells – but they're expensive, difficult to scale and potentially toxic. Now, researchers have found a non-viral approach that does the job better.
-
Scientists have identified two molecules that could help treat leukemia, in a way that’s far less damaging to healthy cells than existing chemotherapy. The compounds work using a different mechanism that’s more selective for cancerous cells.
-
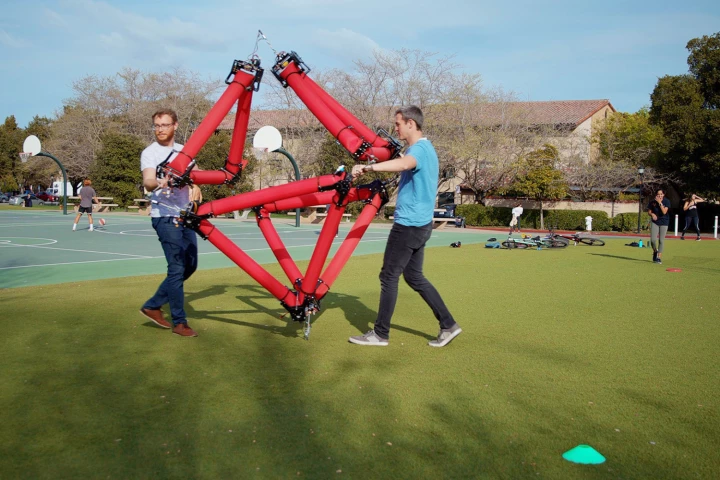
If you say “jump” I say “how high?” – and a new robot from UC Santa Barbara says “over 100 ft.” The researchers say that’s higher than anything else has ever jumped, be it robot or animal, thanks to a unique design that multiplies its stored energy.
-
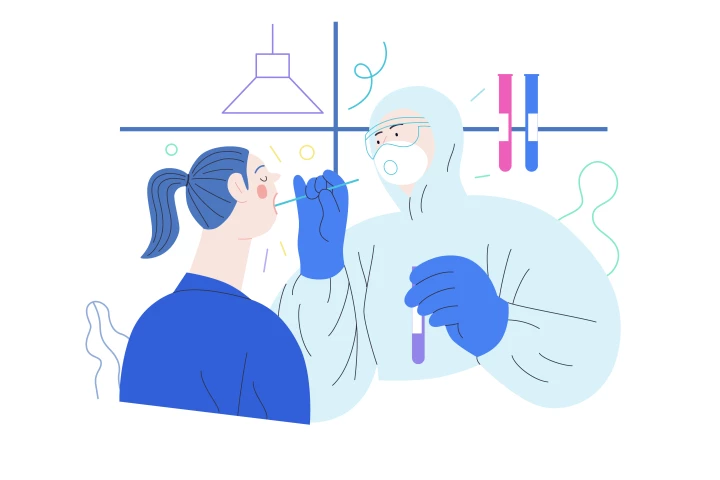
US researchers have developed an innovative smartphone-based kit that can test saliva samples for the presence of SARS-CoV-2 and influenza viruses. Early studies have found the cheap system is as accurate as current lab-based testing and much faster.
-
Scientists at Stanford University and University of California, Santa Barbara have put forward a particularly interesting soft robot design, showing off an inflatable machine that can change shape and roll in controllable directions while untethered.
-
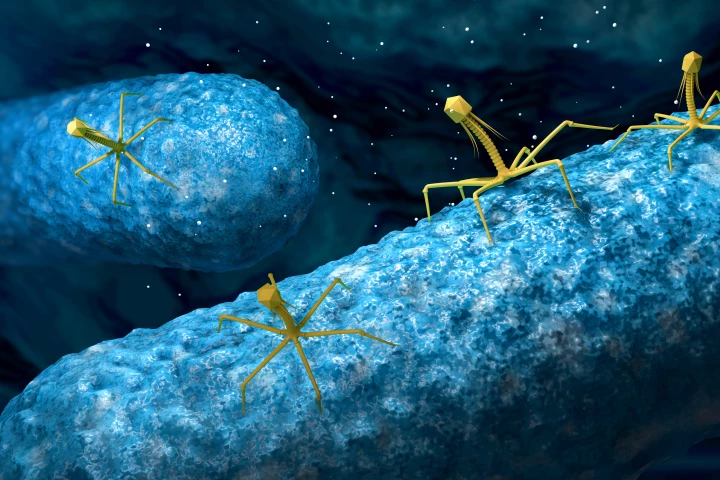
Phages, viruses that thrive by infecting bacteria, have long been mooted as a potential replacement for antibiotics, but they pose risks due to their own rapid evolution. New research suggests it may be possible to mitigate their risks.
Load More