University of Glasgow
-
In a large study, the drug leading the charge in anti-aging science has shown to be just as effective in protecting cells and cognitive function as cutting calories or intermittent fasting. It's the most comprehensive study of rapamycin yet.
-
People with photosensitive epilepsy could soon be able to watch TV without worry. Scientists in the UK have created glasses that can block out specific wavelengths of light known to cause seizures.
-
Brain parasites are something that most people would naturally want to avoid, but maybe they can be used for good. A new study has found that a common brain parasite could be engineered to deliver drugs past the blood-brain barrier.
-
An important iteration of the robotic seeing eye dog has been shown off, the RoboGuide AI-powered quadruped. The future for robotic canine assistants looks not just commercially huge, but also massively empowering for the world's visually impaired people.
-
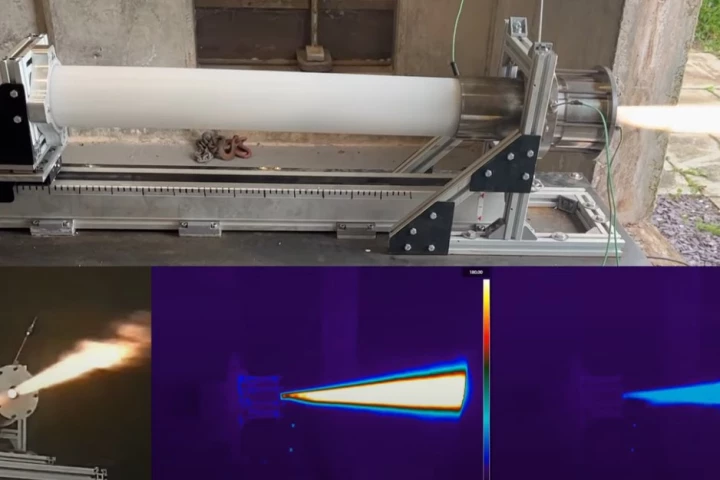
If a new rocket developed by University of Glasgow engineers seems to get smaller as it burns, your eyes aren't playing tricks. It is. The new Ouroborous-3 (sic) rocket engine conserves fuel by eating itself as it burns.
-
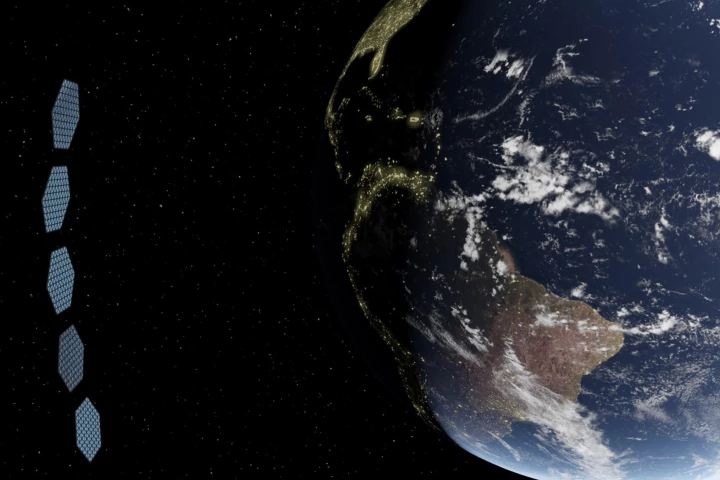
Power demand spikes in the early morning and later evening, when solar arrays can't help. But researchers in Scotland say orbital launch costs are getting so cheap that giant space-based reflectors could soon be a viable way to power these timeslots.
-
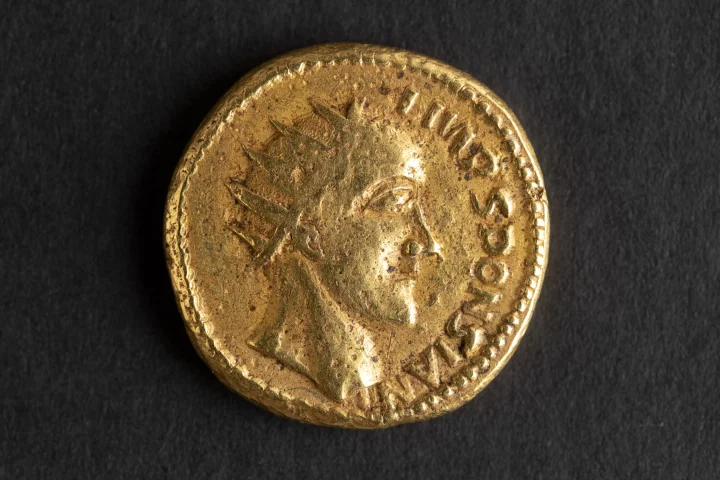
History is full of artifacts that later turn out to be fakes, but occasionally the opposite can happen. New analysis of ancient Roman coins long dismissed as forgeries has found they seem to be authentic, revealing a previously unknown Roman emperor.
-
X-ray vision has long been a superpower, but soon mere mortals could see hidden objects with help from AI. A new “ghost imaging” system reads the brainwaves of a person looking at light scattered off a wall to identify an object around a corner.
-
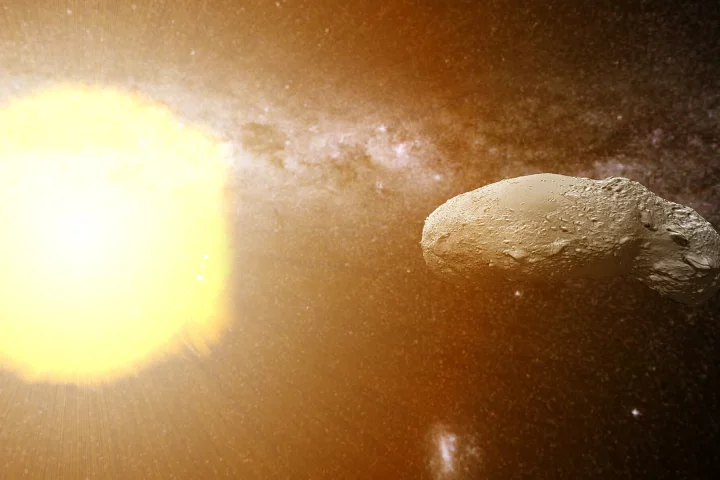
Accounting for where all of the Earth's water came from is a longstanding puzzle, but an international team of scientists led by the University of Glasgow has proposed that the Sun may be a major source of our planet's H₂O.
-
New research is shedding light on how specifically targeted pulses of magnetic stimulation to the brain can improve episodic memory. The work found inhibiting activity in the left dorsolateral prefrontal cortex enhances memory formation.
-
Scientists pushing the frontiers of soft robotics continue to find inspiration in the animal kingdom, with the latest examples that move move like inchworms and earthworms deploying some novel sensor technology to give them proprioception.
-
In order to stay warm on frigid winter days, small birds may do more than just fluff up their feathers. According to new research, they're actually able to make their blood run hotter, creating a sort of central heating system.
Load More