University of Manchester
-
In the first study of its kind, neuroscientists have shown the real-world benefits that sunlight gives the brain, beyond laboratory experiments, linking brighter and more regular daytime light to better alertness and faster attention in everyday life.
-
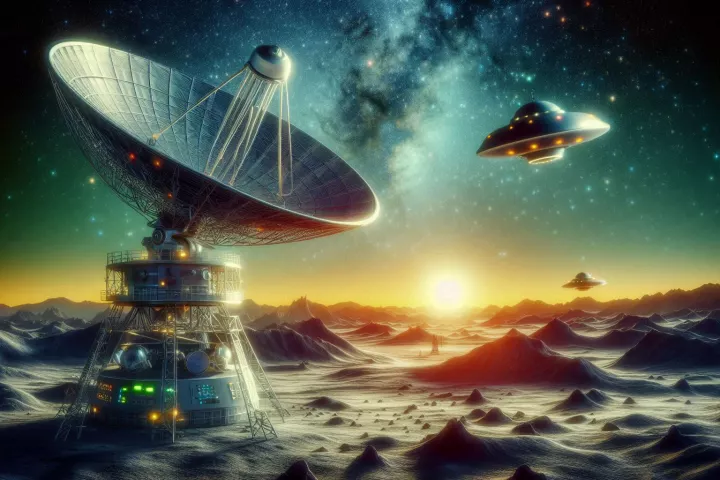
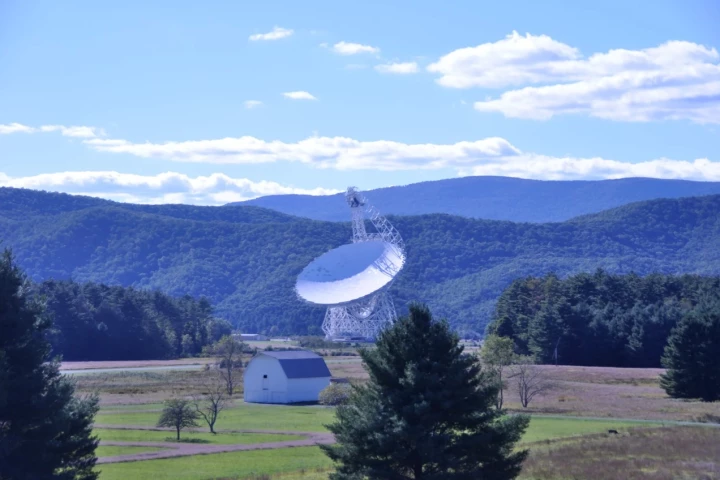
If you're hoping that we can avoid the attention of alien civilizations by lying low, it's a bit late now. A new study released by the Royal Astronomical Society indicates that our radar systems are already screaming our location to ET eavesdroppers.
-
A team of chemists has developed a new type of magnetic molecule that could be the key to storing vast amounts of data on absolutely miniscule drives. That could be huge for data centers in the future.
-
You may think that if a species died out millions of years ago, its design would be too old to have any applications in our technology. A new analysis of pterosaur bones, however, suggests that they could inspire lighter, stronger aircraft materials.
-
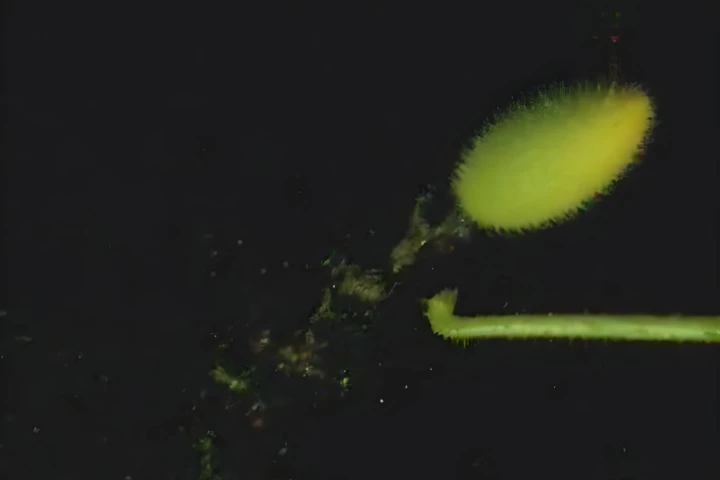
Unlike nearly all flowering plants, which rely on the likes of wind or animals to reproduce, the squirting cucumber instead uses "ballistic seed dispersal," shooting a forceful, watery jet more than 30 feet into the air. And now we know how it does it.
-
A surprise result in a lab experiment has led to the discovery of an ancient biological stress pathway that triggers cells to stop making what's needed to grow hair. Blocking this process could protect follicles from this process and prevent hair loss.
-
Silicon is so important for electronics and computing that it’s become synonymous with technology, but the stuff has its flaws. Now scientists have created a way to make super-pure silicon chips that could pave the way for stable quantum computers.
-
For the first time, scientists have found how our internal body clocks that govern the brain and skeletal system sync up, and upsetting this balance might contribute to injury and accelerate age-related bone and joint decline and disease.
-
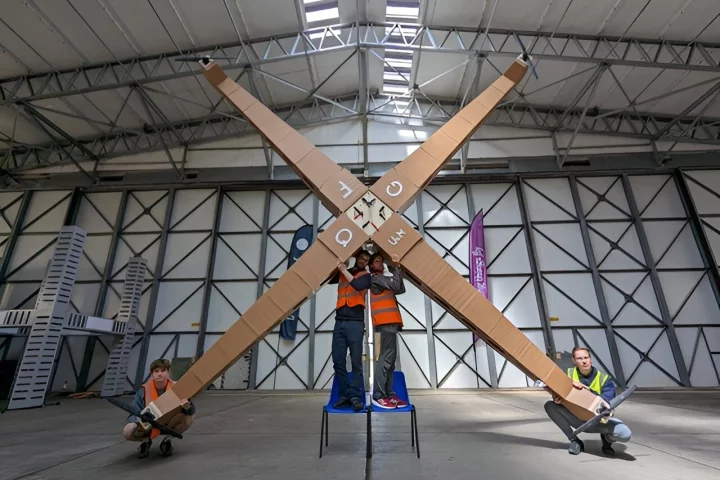
University of Manchester engineers set themselves the task of building and flying the biggest quadcopter drone in history, and to keep things legal with aviation authorities, they made some interesting materials choices.
-
When diagnosing type 2 diabetes, physicians can look for a range of typical symptoms such as frequent urination and excessive thirst. Now, researchers say the development of other illnesses in the body might need to be added in as a predictive tool.
-
A new study suggests that if any alien civilizations are turning their radio telescopes toward Earth, they may be able to not only detect our mobile phone signals, but could deduce a lot about our planet and even produce crude maps of it.
-
While many companies claim that their products contain recycled (as opposed to 100% virgin) plastic, how can we know if they're telling the truth? According to a new study, a fluorescent molecule could blow the whistle on manufacturers who are lying.
Load More