University of Michigan
-
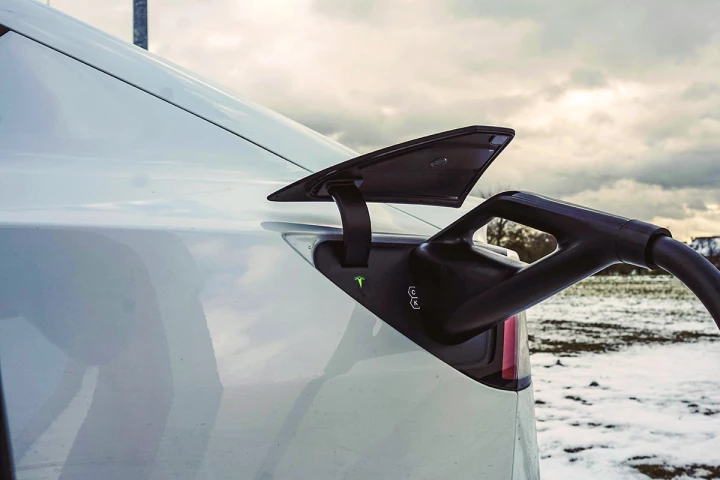
Researchers at the University of Michigan have developed a way to enable rapid EV battery charging at awfully low temperatures – up to five times as fast – without reducing the batteries' energy density.
-
A test for pee-based markers of prostate cancer has previously relied on an uncomfortable first step. A new study has revealed that the now-available test remains just as accurate without it, paving the way from an easy in-home testing option.
-
Forget LEDs, researchers from the University of Michigan have developed a new type of incandescent light bulb. The device is capable of emitting elliptically polarized light, described as "twisted" light.
-
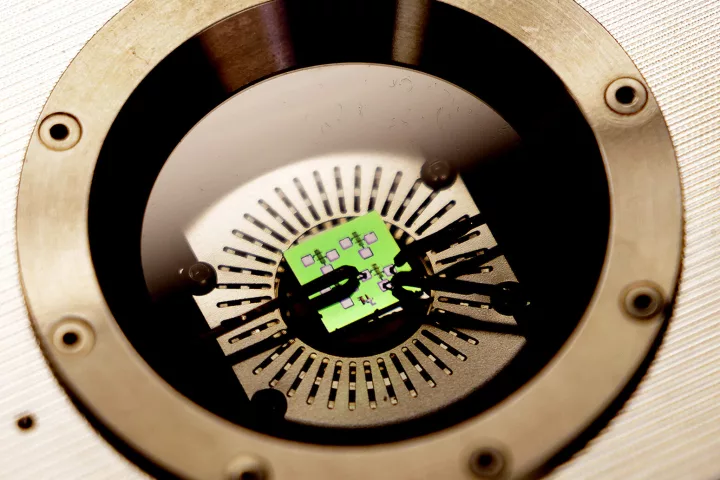
Computers generally go a bit wonky when you stick them in the oven for a bit, but engineers at the University of Michigan are looking to change that by developing a new computer memory that can run at the temperature of molten lead.
-
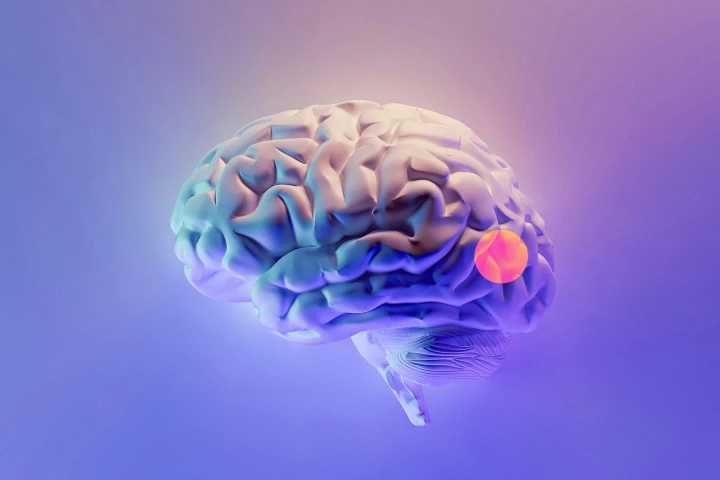
Researchers have developed an AI model that can spot bits of brain tumors that surgeons may miss while removing them from patients. It can detect these remaining tissues in as little as 10 seconds, and help prevent post-procedure complications.
-
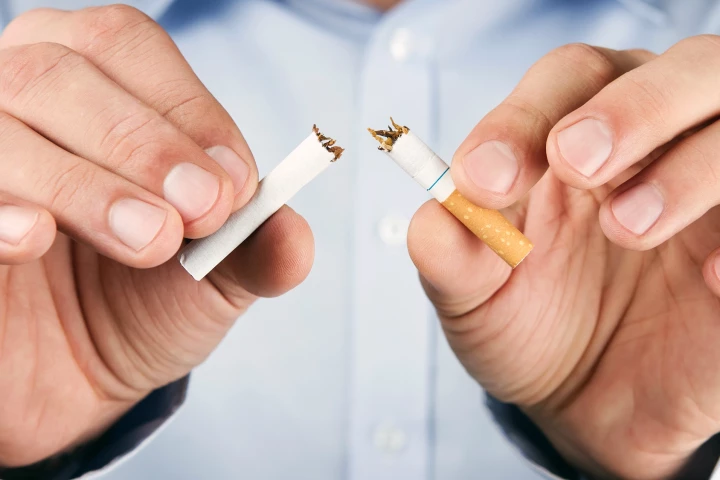
A new study has found that, whether you do it at 35 or 75, quitting cigarette smoking will add years to your life. The findings go to prove that you’re never too old to reap the benefits of stopping smoking.
-
Inspired by the color-changing skin of squids and other cephalopods, researchers have developed a flexible screen capable of storing and displaying encrypted images without using electronics – just tiny magnetic particles.
-
A poll of Americans aged 50 and over on their use of cannabis has provided some interesting insights into how often they use the drug, how and why they use it, and the behaviors they engage in while under the influence.
-
More than 15 million Americans are putting their liver at serious risk, simply by trying to better their health. New research has revealed the extent of the damage caused by overuse of six supplements including turmeric, green tea and ashwagandha.
-
Engineers at the University of Michigan (U-M) have developed a new camera that renders entire scenes normally, but uses onboard AI algorithms to turn every person into a simplistic stick figure before the images leave the camera.
-
A new device has been shown to protect wearers from airborne viruses while leaving their face mask-free. It blocks microbes via a curtain of air which has itself been pretreated to kill any viruses present within it.
-
Increasing the expression of a protein responsible for maintaining neuron health led to better-than-normal processing of auditory information, according to a new study. The findings open the door to new treatments for some forms of hearing loss.
Load More