University of Minnesota
-
A new two-step process that safely rewarms frozen tissues using nanoscale magnetic rods could preserve donor organs long-term. The procedure provides an alternative to current time-limited methods and paves the way for more life-saving transplantations.
-
Using the neuroimaging data of nearly 12,000 participants, researchers have confirmed there is a critical need for taking a ‘whole brain approach’ when diagnosing, researching and treating attention-deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD).
-
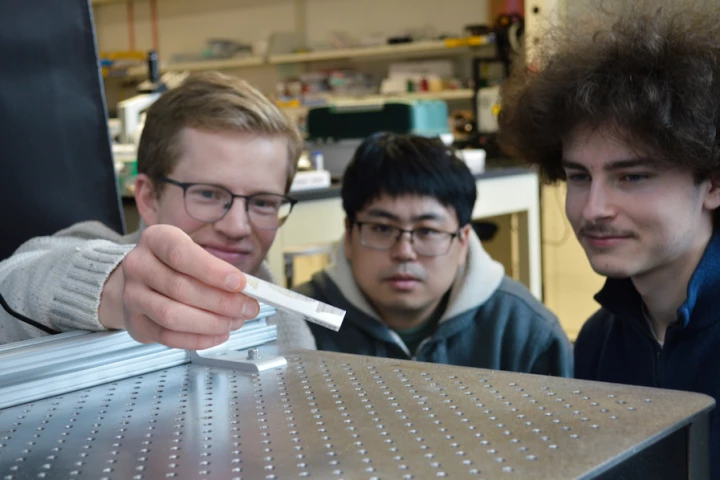
Scientists have performed the first successful transplant of an organ that had been cryogenically frozen and rewarmed. Rats that were given transplants of kidneys preserved through a new technique regained regular organ function within weeks.
-
Engineers have developed a new system that can move objects without physical contact. The technique involves ultrasound waves acting on specialized surfaces to push or pull objects in set directions, which could help in manufacturing and robotics.
-
A team of engineers has developed a new type of camera that can detect radiation in terahertz wavelengths. This new imaging system can see through certain materials in high detail, which could make it useful for security scanners and other sensors.
-
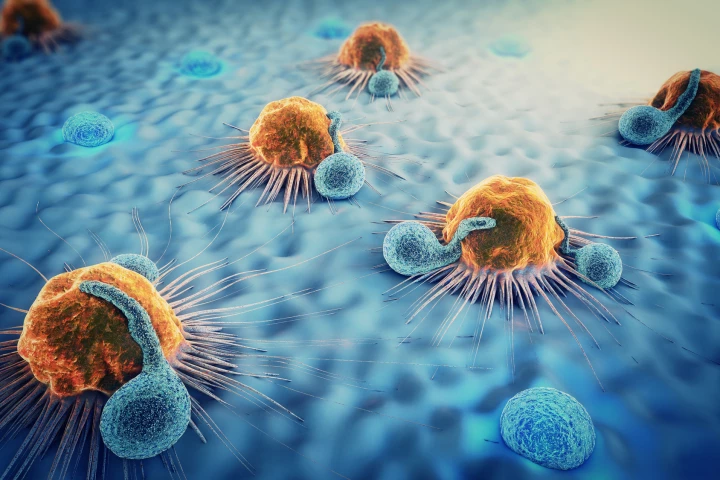
A research team working to better understand the movements of cancerous cells has made an important breakthrough, describing a "sweet spot" where these cells like to congregate, which could reveal new ways to stop them in their tracks.
-
It’s an unfortunate truth that many important chemical reactions require rare and expensive metals as catalysts. But now, scientists have developed a device that actively tweaks plain old aluminum to make it behave like other metals on the fly.
-
Researchers have developed a non-hormonal male contraceptive pill that disrupts a protein involved in sperm formation. Tests in mice have so far been promising, showing effective prevention of pregnancy, reversibility within weeks, and no side effects.
-
Presently, OLED screens are manufactured by trained technicians in large high-tech factories. Now, however, scientists have managed to 3D print a flexible OLED display, paving the way for small businesses to one day be able to do the same thing.
-
Patients don't like getting needles, nor do clinicians like having to keep protein-based vaccines cold at all times. A new polymer wafer – which dissolves when placed under the tongue – could address both issues.
-
When a child receives a replacement heart valve, the device doesn't grow along with them. This means it will have to be surgically replaced, multiple times. Such may not be the case, however, with a new valve that's currently in development.
-
A number of hearing aids are now able to amplify one person's voice while filtering out distracting background voices. Well, it turns out that female tree frogs are able to perform a similar task, in order to hear the mating calls of males.
Load More