University of Nottingham
-
A mineral-recruiting gel that rebuilds tooth enamel from saliva could change the future of dental treatment. To date, we don't have any way to effectively regenerate this all-important outer layer of our teeth that erodes as we age.
-
Even without infection, the COVID-19 pandemic aged our brains. A new study found that accompanying stressors like isolation and uncertainty accelerated brain aging, especially in men, older adults, and those from disadvantaged backgrounds.
-
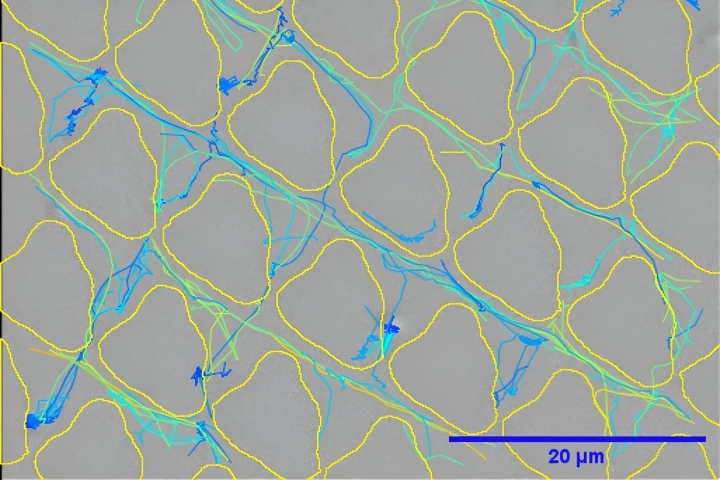
We've seen surfaces that kill microbes on contact, but scientists in the UK have recently gone a potentially more effective route. They've created maze-like surface patterns that keep bacteria from sticking around to establish biofilm colonies.
-
It's never a good thing when harmful bacteria are present on surfaces in hospitals, as they can cause life-threatening infections in patients. A new paint could help keep that from happening, by quickly killing any microbes that land on it.
-
Taking one of the most widely-used painkillers for a prolonged period increases the risk of serious complications in older folks, according to a new study. It may mean rethinking the drug’s use as a first-line treatment for chronic conditions.
-
The body has a remarkable ability to heal injuries, but it has its limits. Now scientists have developed a way to improve on the natural process, making implants created from a patient’s own blood to regenerate injuries, even repairing bone.
-
Treatment for irritable bowel syndrome, IBS, often includes restricting certain foods, such as carbohydrates, but that doesn’t work for everyone. A new study found that genetics might be the reason for this, opening the door to genetically tailored diets to treat IBS.
-
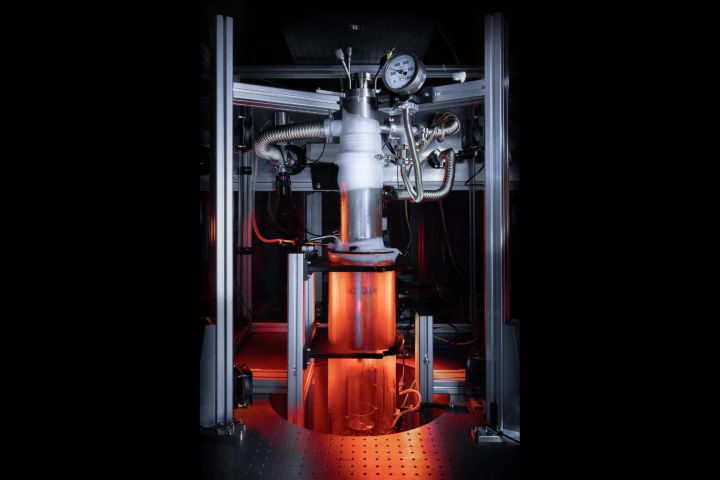
A giant quantum vortex has been created in superfluid helium in a lab at the University of Nottingham. Its behavior was found to mimic that of black holes and may help astrophysicists gain deeper insight into these galactic gravity gobblers.
-
A study has found that the frequency by which children and young people attend healthcare services – for a wide range of complaints – may be a sign of undiagnosed ADHD, highlighting the need to look for signs other than the condition's core symptoms.
-
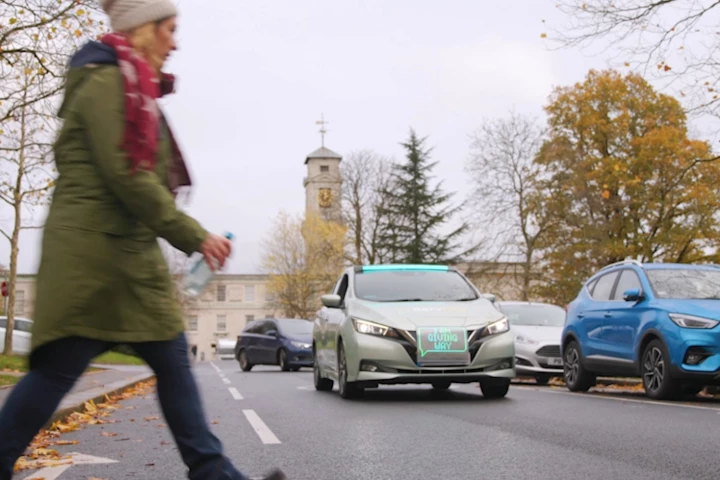
With autonomous vehicles already rolling on public roads, researchers from the University of Nottingham in the UK have used a camouflaged driver to look at how pedestrians react to visual cues from oncoming cars without a human at the wheel.
-
While weight-loss surgery is effective, it can also be expensive and come with a host of unpleasant side effects. Scientists hope that by regulating a certain bile acid, the benefits of surgery can be replicated without a single invasive procedure.
-
There may be new hope for people afflicted with Tourette's syndrome, in the form of a wrist-worn device. In a test of the technology, the majority of participants experienced a reduction in tic severity of at least 25%.
Load More