University of Nottingham
-
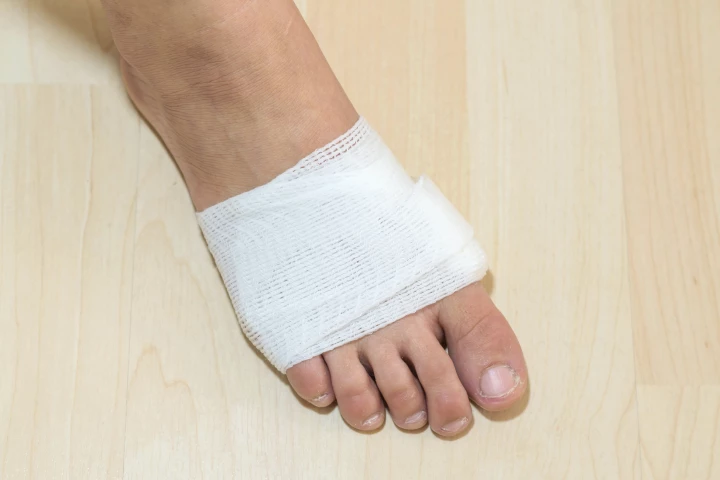
Chronic diabetic skin wounds are notoriously slow to heal, sometimes becoming so infected that amputations are required. A newly identified polymer could help keep that from happening, by radically boosting the healing process.
-
Scientists experimenting with a cutting-edge ultrasound technique have come up with a groundbreaking way to measure the elasticity of materials at a microscopic scale, by tracking sound waves as they bounce across individual crystals.
-
A new study has explored the impacts of exercise on sufferers of arthritis, and shown how the gut microbiome and cannabis-like substances produced by the body play an important mediatory role in driving anti-inflammatory effects.
-
It would be great if forensics teams could easily lift fingerprints off of bullet casings left at crime scenes, but unfortunately doing so is often very difficult. A new technique developed at the University of Nottingham could change that.
-
Scientists have developed a tiny first-of-its-kind imaging sensor designed to build detailed 3D maps of cellular structures inside the body, potentially revealing stiffness and abnormalities that may be indicative of cancer.
-
When someone has experienced a stroke or brain injury, it's not uncommon for them to lose their ability to swallow. A new study, however, suggests that a throat-zapping system could help correct the problem faster than traditional treatments.
-
When it comes to monitoring electrical activity in the brain, patients typically have to lie inside a large magnetoencephalography (MEG) machine. That could soon change, as scientists have developed a new version of a helmet that does the same job.
-
Atoms are known for forming bonds and breaking apart, but because this happens on such a tiny scale, it’s difficult to study and record. Now, researchers have managed to capture atoms forming and breaking bonds on video for the first time.
-
The universe is believed to be expanding at an accelerating rate, thanks to a mysterious force dubbed dark energy. But how exactly does this force work?
-
Although coffee consumption does potentially pose some health risks, studies have also suggested that it may lower incidences of maladies such as prostate cancer, Parkinson's, Alzheimer's and heart disease. Now, scientists believe that it could also help fight obesity.
-
Some seafood aficionados swear that you just HAVE to try pufferfish sushi – unfortunately, though, if it isn't prepared correctly, it'll kill you. Scientists from China and the UK have developed a safer alternative, by replicating the flavor of the fish without any of the poison.
-
A Stanford team has developed a “brain stethoscope” that translates brain waves into sound, allowing medical professionals to spot silent seizures. Another team has developed a wearable MEG helmet that means patients no longer need to lie down perfectly still inside a huge machine.
Load More