University of Virginia
-
New research has found that the loss of social memory – recognizing friends and family – in Alzheimer's disease (AD) could come down to specific structures around brain cells. And targeting this delicate scaffolding may potentially prevent this heartbreaking stage in cognitive decline.
-
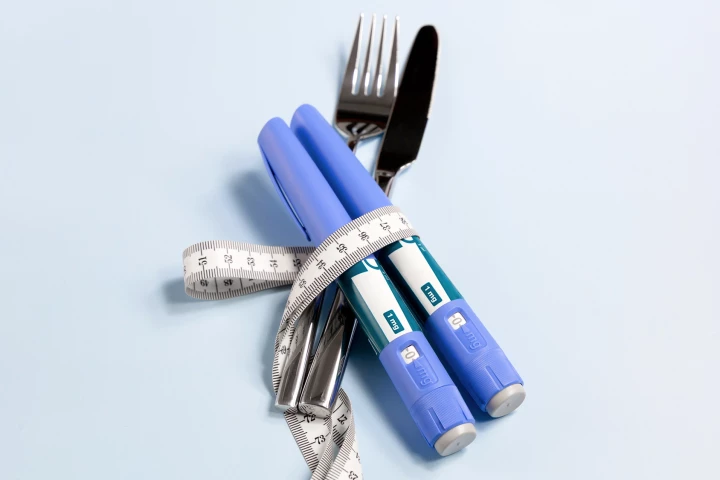
Weight-loss drugs like semaglutide and tirzepatide may help shrink waistlines, but new research shows they fail to boost fitness and can cause serious muscle loss, potentially undermining the long-term health benefits of slimming down.
-
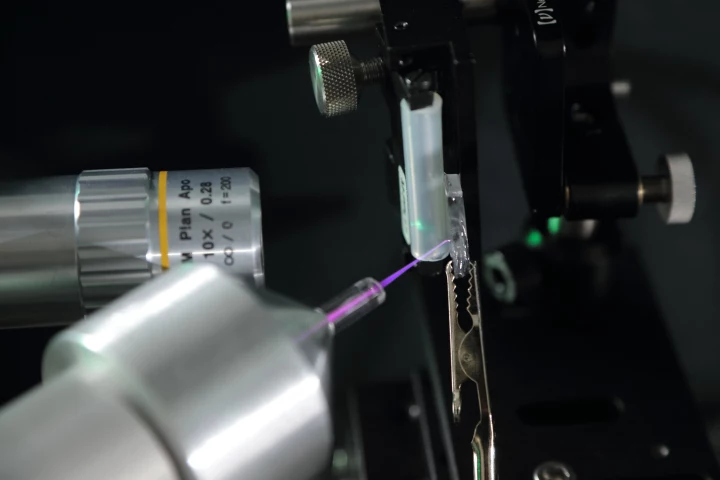
A new organelle has been found by scientists at the University of Virginia. The super-small specialized structure has a role recycling material inside our cells, and its discovery could lead to improved treatments for a wide range of diseases.
-
The heat from within your laptop disperses slowly, like ripples in a pond. What if we could turn that heat into channeled waves that travel away from the source up to a hundred times faster? Researchers are giving it a go – with crystals.
-
Touch is a vital sense in human survival and experience, yet not all touch is equal. Men have less touch sensitivity than women, which comes down to biology. Using biomechanics, scientists have found that you can hack nature with hyaluronic acid.
-
Calls to US poison centers reporting intentional exposure resulting in deaths and serious harm to adults and children have risen significantly over a 15-year period, a new study found. Researchers say the alarming statistics warrant an examination of their root cause.
-
Researchers have identified how Lactobacillus, a member of our guts’ microbiome community, affects a critical immune system protein, influencing stress levels and mental health. The findings could lead to new treatments for depression and anxiety.
-
A team of scientists led by University of Virginia professor Patrick Hopkins is developing a plasma "freeze ray" that will be less interesting to super villains than to engineers looking for ways to cool electronics in the vacuum of space.
-
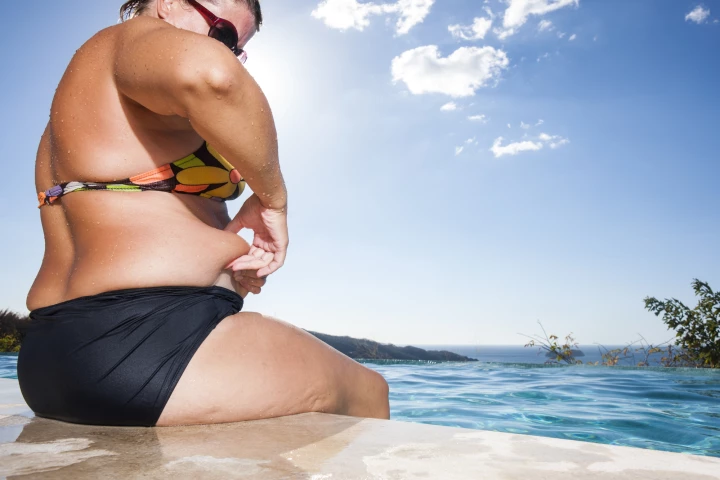
Traditionally, doctors have linked waist fat to a higher risk of type 2 diabetes. New research says that our waist size is only part of the equation, and that some of the same genes that make us store belly fat may also protect us from the disease.
-
Many of us accept that we’ll naturally lose some hearing as we age, but there may be a way to slow that down. Scientists have identified a mechanism that lets hair cells repair themselves, which could be hacked for therapies that restore lost hearing.
-
Investigating ways to head off the chain of events that leads to multiple sclerosis, researchers have found a chemical regulator in mice that causes the inflammatory cascade associated with the disease. They also figured out how to switch it off.
-
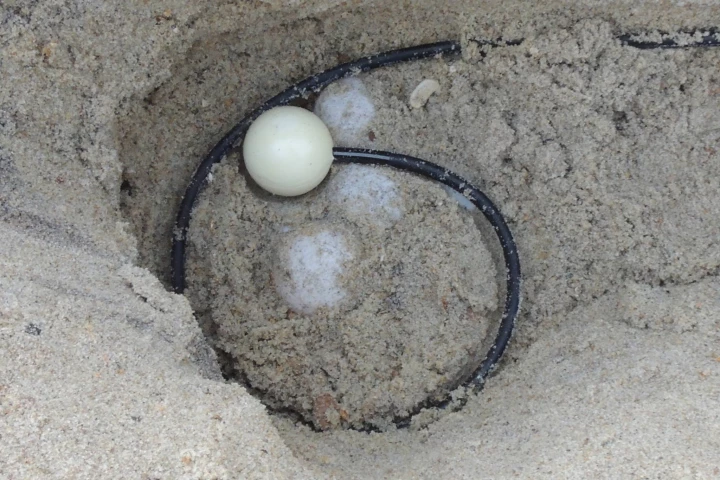
When sea turtles lay and bury eggs in a nest on a beach, that beach is often closed to the public until those eggs hatch. A nest-monitoring sensor – which looks like an egg – has been created to help predict when such beaches can be reopened.
Load More