University of Wisconsin
-
You might be familiar with dry mouth from partaking in a certain kind of recreational substance (or you might not be, we're not judging), but the condition can actually have verifiable medical causes. A new gel-based blob could be a great cure.
-
A study has found that the regret reported by transgender individuals following gender-affirming surgery is less than 1%, which is significantly lower than the regret associated with having children, getting a tattoo, or undergoing plastic surgery.
-
The popular pain-killing drug paracetamol, also known as acetaminophen, has always been made from chemicals derived from environmentally damaging coal tar or crude oil. Now researchers have devised a greener way of producing the drug using wood.
-
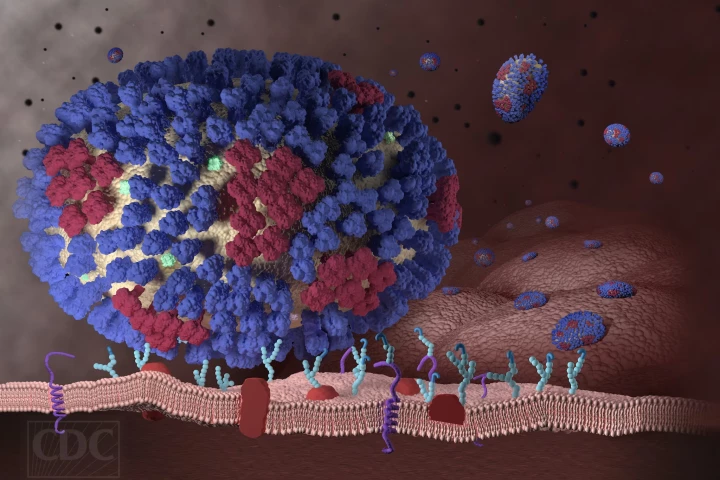
A single-shot vaccine that protects against multiple coronaviruses, including the one that causes COVID-19, has been developed. It erased all viral traces from the lungs of animal subjects, opening a pathway for a similar human vaccine.
-
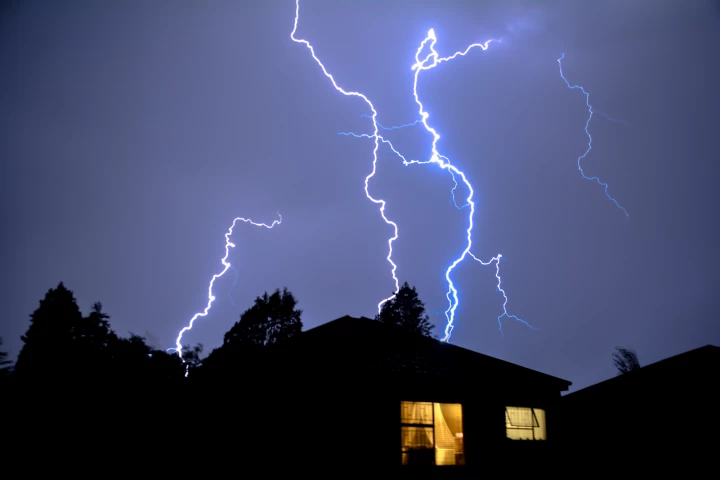
Do you live in a lightning hotspot? A new set of maps shows just where all that discharged electricity makes contact with the ground across the United States each year. Tip: If you're worried about getting hit, you might want to skip Florida.
-
Researchers have used a novel technique to 3D print brain tissue whose cells developed into functional neurons that communicated with each other in a matter of weeks. The approach could be used to study the healthy and unhealthy brain or test drugs.
-
Researchers have developed a new, lightweight foam made from carbon nanotubes that, when used as a helmet liner, absorbed the kinetic energy caused by an impact almost 30 times better than liners currently used in US military helmets.
-
The insides of nuclear fusion reactors are violent and chaotic places. A new cold-spray coating can take the heat and also trap some rogue hydrogen particles at the same time, potentially making for smaller, better plasma chambers.
-
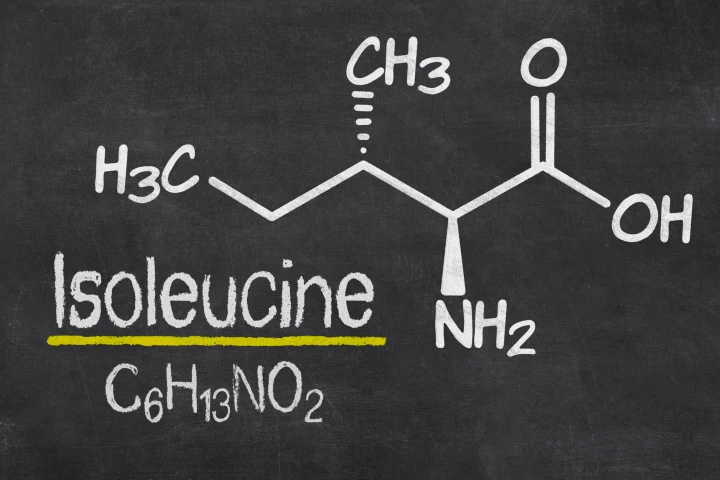
Research found that reducing the intake of a single amino acid by two-thirds improved the lifespan, weight, and health of middle-aged mice without requiring a drop in calorie intake. Limiting isoleucine intake may be a key to healthy aging.
-
Researchers have found that remnants left over after a cell divides contain RNA that, when taken up by other cells, can spread cancer’s genetic blueprint. The finding opens the door to harnessing this mechanism as a way of treating cancer.
-
Researchers have just uncovered how the influenza A virus is able to thrive by slicing and dicing genetic material inside our cells while keeping itself intact. The finding might arm researchers with a new way to fight the virus.
-
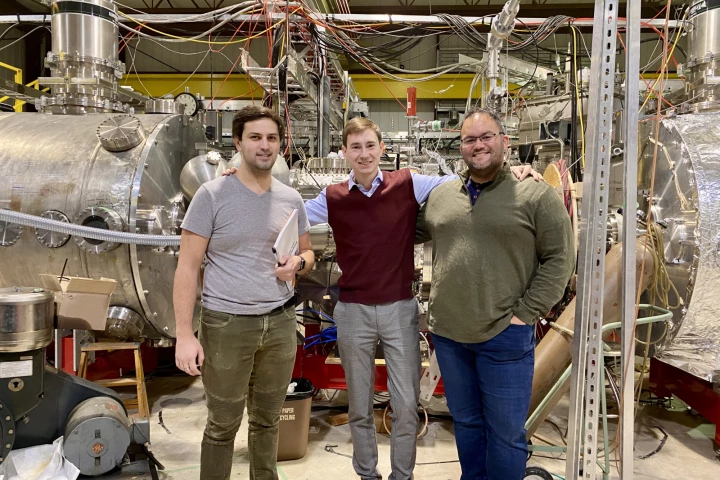
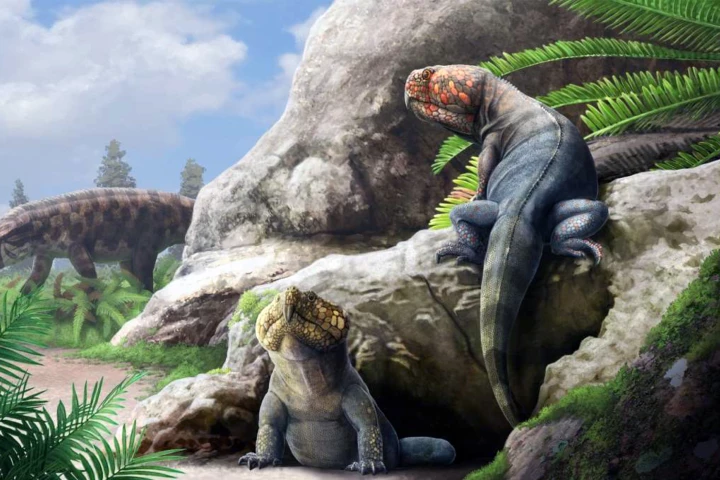
Researchers from the University of Wisconsin-Madison have discovered a new species of rhynchosaur, an ancient reptile, in central Wyoming and named it in the language of the First Nations people indigenous to the area where it was found.
Load More